Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Electrons emitted with negligible speed from an electron gun are accelerated through a potential difference V along the x-axis. These electrons emerge from a narrow hole into a uniform magnetic field B directed along this axis. However, some of the electrons emerging from the hole make slightly divergent angles, as shown in the figure. Show that these paraxial electrons are refocussed on the x-axis at a distance `sqrt(8pi^2mV)/(eB^2).`
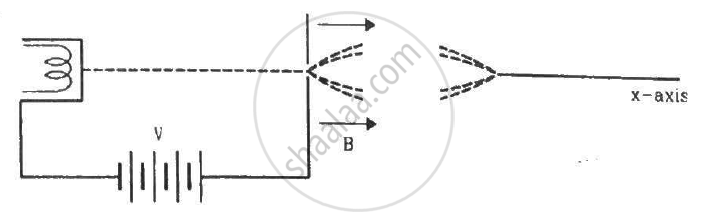
उत्तर
Given:-
Electrons are accelerated through a potential difference = V
Let the mass of an electron be m and the charge of an electron be e.
We know:-
Electric field, E = `V/r`
Force experienced by the electron, F = eE
Acceleration of the electron, a = `(eV)/(rm)`
Using the equation of motion
v2 − u2= 2 × a × s,
v2 = 2 × a × s (As u = 0)
Here, s = r
v =`sqrt(2eVr)/(rm)`
= `sqrt(2eV)/m`
Time taken by electron to cover the curved path,
As the acceleration of the electron is along the y axis only, it travels along the x axis with uniform velocity.
Velocity of the electron moving along the field remains v.
Therefore, the distance at which the beam is refocused, d = v × T
`d = sqrt(2eV)/m`
`d = sqrt(8pi^2mV)/(eB^2)`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
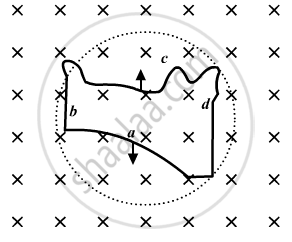
A flexible wire of irregular shape, abcd, as shown in the figure, turns into a circular shape when placed in a region of magnetic field which is directed normal to the plane of the loop away from the reader. Predict the direction of the induced current in the wire.
A proton and a deuteron having equal momenta enter in a region of a uniform magnetic field at right angle to the direction of a the field. Depict their trajectories in the field.
Write the expression for the force,`vecF` acting on a charged particle of charge ‘q’, moving with a velocity `vecV` in the presence of both electric field `vecF`and magnetic field `vecB` . Obtain the condition under which the particle moves undeflected through the fields.
Write the expression for Lorentz magnetic force on a particle of charge ‘q’ moving with velocity `vecv` in a magnetic field`vecB`. Show that no work is done by this force on the charged particle.
A positively-charged particle projected towards east is deflected towards north by a magnetic field. The field may be
If a charged particle at rest experiences no electromagnetic force,
(a) the electric field must be zero
(b) the magnetic field must be zero
(c) the electric field may or may not be zero
(d) the magnetic field may or may not be zero
If a charged particle moves unaccelerated in a region containing electric and magnetic fields
(a) `vecE "must be perpendicular" to vecB`
(b) `vecv "must be perpendicular" to vecE`
(c) must be perpendicular to v_B
A particle is projected in a plane perpendicular to a uniform magnetic field. The area bounded by the path described by the particle is proportional to
A wire, carrying a current i, is kept in the x−y plane along the curve y = A sin `((2x)/lamda x)`. magnetic field B exists in the z direction. Find the magnitude of the magnetic force on the portion of the wire between x = 0 and x = λ.
A particle of charge 2.0 × 10−8 C and mass 2.0 × 10−10 g is projected with a speed of 2.0 × 103 m s−1 in a region with a uniform magnetic field of 0.10 T. The velocity is perpendicular to the field. Find the radius of the circle formed by the particle and also the time period.
An electron of kinetic energy 100 eV circulates in a path of radius 10 cm in a magnetic field. Find the magnetic field and the number of revolutions per second made by the electron.
A square coil of edge l and with n turns carries a current i. It is kept on a smooth horizontal plate. A uniform magnetic field B exists parallel to an edge. The total mass of the coil is M. What should be the minimum value of B for which the coil will start tipping over?
Doubly-ionised helium ions are projected with a speed of 10 km s−1 in a direction perpendicular to a uniform magnetic field of magnitude 1.0 T. Find (a) the force acting on an ion (b) the radius of the circle in which it circulates and (c) the time taken by an ion to complete the circle.
A proton is projected with a velocity of 3 × 106 m s−1 perpendicular to a uniform magnetic field of 0.6 T. Find the acceleration of the proton.
A long, straight wire carrying a current of 30 A is placed in an external, uniform magnetic field of 4.0 × 10−4 T parallel to the current. Find the magnitude of the resultant magnetic field at a point 2.0 cm away from the wire.
When does a moving charged particle nor experience any force while moving through a uniform magnetic field?
