Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Write the expression for the force,`vecF` acting on a charged particle of charge ‘q’, moving with a velocity `vecV` in the presence of both electric field `vecF`and magnetic field `vecB` . Obtain the condition under which the particle moves undeflected through the fields.
उत्तर
Force `vecF` acting on a charge ‘q’ moving with velocity `vecV` in the presence of both electric field `vecE` and magnetic field `vecB` ,
`vecF =qvecE +q(vecVxxvecB)`
Consider a region in which magnetic field, electric field and velocity of charge particle are perpendicular to each other.
To move charge particle undeflected the net force acting on the particle must be zero i.e. The electric force must be equal and opposite to the magnetic force.
qE = qvB
`V=E/B`
The direction of electric and magnetic forces are in opposite direction. Their magnitudes are in such a way they cancel out each other to give net force zero so that the charge particle does not deflect.
संबंधित प्रश्न
A neutron, an electron and an alpha particle, moving with equal velocities, enter a uniform magnetic field going into the plane of the paper, as shown. Trace their paths in the field and justify your answer.
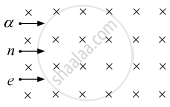
A moving charged particle q travelling along the positive x-axis enters a uniform magnetic field B.
When will the force acting on q be maximum?
A charged particle moves in a uniform magnetic field. The velocity of the particle at some instant makes an acute angle with the magnetic field. The path of the particle will be
A charged particle moves along a circle under the action of possible constant electric and magnetic fields. Which of the following is possible?
(a) E = 0, B = 0
(b) E = 0, B ≠ 0
(c) E ≠ 0, B = 0
(d) E ≠ 0, B ≠ 0
Two ions have equal masses but one is singly-ionised and the other is doubly-ionised. They are projected from the same place in a uniform magnetic field with the same velocity perpendicular to the field.
(a) Both ions will move along circles of equal radii.
(b) The circle described by the singly-ionised charge will have a radius that is double that of the other circle.
(c) The two circles do not touch each other.
(d) The two circles touch each other.
An experimenter's diary reads as follows: "A charged particle is projected in a magnetic field of `(7.0 vec i - 3.0 vecj)xx 10^-3 `T. The acceleration of the particle is found to be `(x veci + 7.0 vecj )` The number to the left of i in the last expression was not readable. What can this number be?
Consider a non-conducting ring of radius r and mass m that has a total charge qdistributed uniformly on it. The ring is rotated about its axis with an angular speed ω. (a) Find the equivalent electric current in the ring. (b) Find the magnetic moment µ of the ring. (c) Show that `pi = (q)/(2m)` l, where l is the angular momentum of the ring about its axis of rotation.
A narrow beam of singly charged potassium ions of kinetic energy 32 keV is injected into a region of width 1.00 cm with a magnetic field of strength 0.500 T, as shown in the figure. The ions are collected at a screen 95.5 cm away from the field region. If the beam contains isotopes of atomic weights 39 and 41, find the separation between the points where these isotopes strike the screen. Take the mass of a potassium ion = A (1.6 × 10−27) kg, where A is the mass number.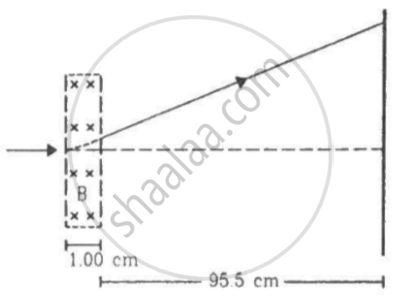
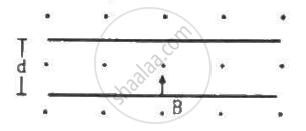
An electron is emitted with negligible speed from the negative plate of a parallel-plate capacitor charged to a potential difference V. The separation between the plates is dand a magnetic field B exists in the space, as shown in the figure. Show that the electron will fail to strike the upper plates if `d > ((2m_eV)/(eB_0^2))^(1/2)`
A particle of mass 10 mg and having a charge of 50 mC is projected with a speed of 15 m/s into a uniform magnetic field of 125 mT. Assuming that the particle is projected with its velocity perpendicular to the magnetic field, the time after which the particle reaches its original position for the first time is ______.
