Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Write the expression for the force,`vecF` acting on a charged particle of charge ‘q’, moving with a velocity `vecV` in the presence of both electric field `vecF`and magnetic field `vecB` . Obtain the condition under which the particle moves undeflected through the fields.
उत्तर
Force `vecF` acting on a charge ‘q’ moving with velocity `vecV` in the presence of both electric field `vecE` and magnetic field `vecB` ,
`vecF =qvecE +q(vecVxxvecB)`
Consider a region in which magnetic field, electric field and velocity of charge particle are perpendicular to each other.
To move charge particle undeflected the net force acting on the particle must be zero i.e. The electric force must be equal and opposite to the magnetic force.
qE = qvB
`V=E/B`
The direction of electric and magnetic forces are in opposite direction. Their magnitudes are in such a way they cancel out each other to give net force zero so that the charge particle does not deflect.
संबंधित प्रश्न
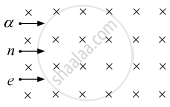
A neutron, an electron and an alpha particle, moving with equal velocities, enter a uniform magnetic field going into the plane of the paper, as shown. Trace their paths in the field and justify your answer.
A moving charged particle q travelling along the positive x-axis enters a uniform magnetic field B.
When will the force acting on q be maximum?
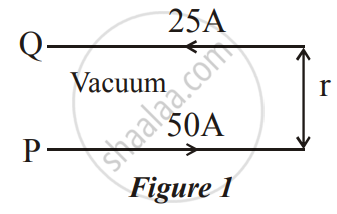
A long horizontal wire P carries a current of 50A. It is rigidly fixed. Another wire Q is placed directly above and parallel to P, as shown in Figure 1 below. The weight per unit length of the wire Q is 0.025 Nm-1 and it carries a current of 25A. Find the distance 'r' of the wire Q from the wire P so that the wire Q remains at rest
A proton and an α-particle move perpendicular to a magnetic field. Find the ratio of radii of circular paths described by them when both have (i) equal velocities, and (ii) equal kinetic energy.
An electron moving horizontally with a velocity of 4 ✕ 104 m/s enters a region of uniform magnetic field of 10−5 T acting vertically upward as shown in the figure. Draw its trajectory and find out the time it takes to come out of the region of magnetic
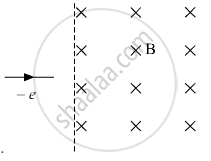
field.
A charged particle moves in a uniform magnetic field. The velocity of the particle at some instant makes an acute angle with the magnetic field. The path of the particle will be
A charged particle is accelerated through a potential difference of 12 kV and acquires a speed of 1.0 × 106 m s−1. It is then injected perpendicularly into a magnetic field of strength 0.2 T. Find the radius of the circle described by it.
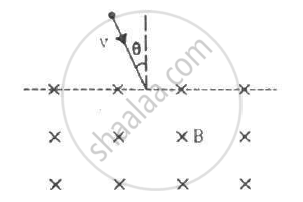
A particle of mass m and positive charge q, moving with a uniform velocity v, enters a magnetic field B, as shown in the figure. (a) Find the radius of the circular arc it describes in the magnetic field. (b) Find the angle subtended by the arc at the centre. (c) How long does the particle stay inside the magnetic field? (d) Solve the three parts of the above problem if the charge q on the particle is negative.
Doubly-ionised helium ions are projected with a speed of 10 km s−1 in a direction perpendicular to a uniform magnetic field of magnitude 1.0 T. Find (a) the force acting on an ion (b) the radius of the circle in which it circulates and (c) the time taken by an ion to complete the circle.
A long, straight wire carrying a current of 30 A is placed in an external, uniform magnetic field of 4.0 × 10−4 T parallel to the current. Find the magnitude of the resultant magnetic field at a point 2.0 cm away from the wire.
