Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A proton and an α-particle move perpendicular to a magnetic field. Find the ratio of radii of circular paths described by them when both have (i) equal velocities, and (ii) equal kinetic energy.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
If a charged particle moves unaccelerated in a region containing electric and magnetic fields
(a) `vecE "must be perpendicular" to vecB`
(b) `vecv "must be perpendicular" to vecE`
(c) must be perpendicular to v_B
When a proton is released from rest in a room, it starts with an initial acceleration a0towards west. When it is projected towards north with a speed v0, it moves with an initial acceleration 3a0 towards west. Find the electric field and the maximum possible magnetic field in the room.
Using the formula \[\vec{F} = q \vec{v} \times \vec{B} \text{ and } B = \frac{\mu_0 i}{2\pi r}\]show that the SI units of the magnetic field B and the permeability constant µ0 may be written as N mA−1 and NA−2 respectively.
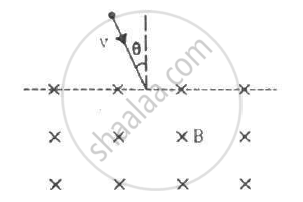
A particle of mass m and positive charge q, moving with a uniform velocity v, enters a magnetic field B, as shown in the figure. (a) Find the radius of the circular arc it describes in the magnetic field. (b) Find the angle subtended by the arc at the centre. (c) How long does the particle stay inside the magnetic field? (d) Solve the three parts of the above problem if the charge q on the particle is negative.
A particle of mass m and charge q is projected into a region that has a perpendicular magnetic field B. Find the angle of deviation (figure) of the particle as it comes out of the magnetic field if the width d of the region is very slightly smaller than
(a) `(mv)/(qB)` (b)`(mv)/(2qB)` (c)`(2mv)/(qB)`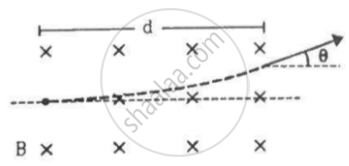
A narrow beam of singly charged potassium ions of kinetic energy 32 keV is injected into a region of width 1.00 cm with a magnetic field of strength 0.500 T, as shown in the figure. The ions are collected at a screen 95.5 cm away from the field region. If the beam contains isotopes of atomic weights 39 and 41, find the separation between the points where these isotopes strike the screen. Take the mass of a potassium ion = A (1.6 × 10−27) kg, where A is the mass number.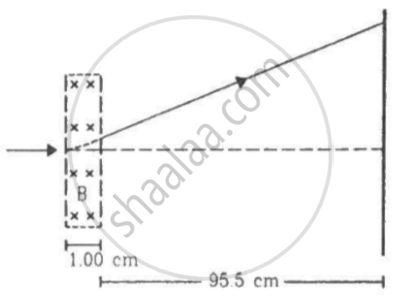
A uniform magnetic field of magnitude 0.20 T exists in space from east to west. With what speed should a particle of mass 0.010 g and with charge 1.0 × 10−5 C be projected from south to north so that it moves with uniform velocity?
When does a moving charged particle nor experience any force while moving through a uniform magnetic field?
Current flows through uniform, square frames as shown in the figure. In which case is the magnetic field at the centre of the frame not zero?
