Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
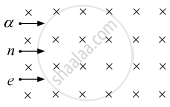
A neutron, an electron and an alpha particle, moving with equal velocities, enter a uniform magnetic field going into the plane of the paper, as shown. Trace their paths in the field and justify your answer.
उत्तर
We know that a charged particle will experience a force when it enters a magnetic field. The magnetic field will move the charged particle in a circular path, as the force is perpendicular to the velocity of particle. The radius of the circular path will be given by
`(mv^2)/r=Bqv`
`r=(mv)/(Bq)`
As B and v are constant, we can write
`rpropm/q`
The neutron will move along the straight line as it has no charge.
The electron will inscribe a circle of radius smaller than that of the alpha particle as the mass to charge ratio of the alpha particle is more than that of the electron.
So, the alpha particle will move in the clockwise direction and the electron will move in anticlockwise direction according to the right-hand rule.

संबंधित प्रश्न
A proton and an α-particle move perpendicular to a magnetic field. Find the ratio of radii of circular paths described by them when both have (i) equal velocities, and (ii) equal kinetic energy.
A straight wire of mass 200 g and length 1.5 m carries a current of 2 A. It is suspended in mid air by a uniform magnetic field B. What is the magnitude of the magnetic field?
A charged particle moves in a uniform magnetic field. The velocity of the particle at some instant makes an acute angle with the magnetic field. The path of the particle will be
If a charged particle at rest experiences no electromagnetic force,
(a) the electric field must be zero
(b) the magnetic field must be zero
(c) the electric field may or may not be zero
(d) the magnetic field may or may not be zero
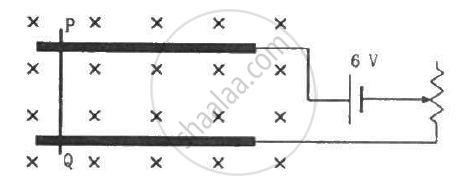
A metal wire PQ of mass 10 g lies at rest on two horizontal metal rails separated by 4.90 cm (figure). A vertically-downward magnetic field of magnitude 0.800 T exists in the space. The resistance of the circuit is slowly decreased and it is found that when the resistance goes below 20.0 Ω, the wire PQ starts sliding on the rails. Find the coefficient of friction.
Protons with kinetic energy K emerge from an accelerator as a narrow beam. The beam is bent by a perpendicular magnetic field, so that it just misses a plane target kept at a distance l in front of the accelerator. Find the magnetic field.
A square coil of edge l and with n turns carries a current i. It is kept on a smooth horizontal plate. A uniform magnetic field B exists parallel to an edge. The total mass of the coil is M. What should be the minimum value of B for which the coil will start tipping over?
A particle of mass m and charge q is projected into a region that has a perpendicular magnetic field B. Find the angle of deviation (figure) of the particle as it comes out of the magnetic field if the width d of the region is very slightly smaller than
(a) `(mv)/(qB)` (b)`(mv)/(2qB)` (c)`(2mv)/(qB)`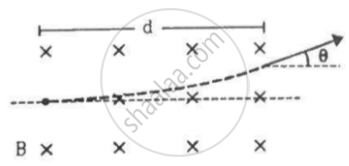
When does a moving charged particle nor experience any force while moving through a uniform magnetic field?
