Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
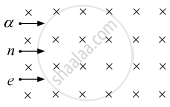
A neutron, an electron and an alpha particle, moving with equal velocities, enter a uniform magnetic field going into the plane of the paper, as shown. Trace their paths in the field and justify your answer.
Solution
We know that a charged particle will experience a force when it enters a magnetic field. The magnetic field will move the charged particle in a circular path, as the force is perpendicular to the velocity of particle. The radius of the circular path will be given by
`(mv^2)/r=Bqv`
`r=(mv)/(Bq)`
As B and v are constant, we can write
`rpropm/q`
The neutron will move along the straight line as it has no charge.
The electron will inscribe a circle of radius smaller than that of the alpha particle as the mass to charge ratio of the alpha particle is more than that of the electron.
So, the alpha particle will move in the clockwise direction and the electron will move in anticlockwise direction according to the right-hand rule.

RELATED QUESTIONS
Write the expression, in a vector form, for the Lorentz magnetic force \[\vec{F}\] due to a charge moving with velocity \[\vec{V}\] in a magnetic field \[\vec{B}\]. What is the direction of the magnetic force?
A straight wire of mass 200 g and length 1.5 m carries a current of 2 A. It is suspended in mid air by a uniform magnetic field B. What is the magnitude of the magnetic field?
A proton and a deuteron having equal momenta enter in a region of a uniform magnetic field at right angle to the direction of a the field. Depict their trajectories in the field.
A positively-charged particle projected towards east is deflected towards north by a magnetic field. The field may be
If a charged particle at rest experiences no electromagnetic force,
(a) the electric field must be zero
(b) the magnetic field must be zero
(c) the electric field may or may not be zero
(d) the magnetic field may or may not be zero
A charged particle moves along a circle under the action of possible constant electric and magnetic fields. Which of the following is possible?
(a) E = 0, B = 0
(b) E = 0, B ≠ 0
(c) E ≠ 0, B = 0
(d) E ≠ 0, B ≠ 0
Protons with kinetic energy K emerge from an accelerator as a narrow beam. The beam is bent by a perpendicular magnetic field, so that it just misses a plane target kept at a distance l in front of the accelerator. Find the magnetic field.
A square coil of edge l and with n turns carries a current i. It is kept on a smooth horizontal plate. A uniform magnetic field B exists parallel to an edge. The total mass of the coil is M. What should be the minimum value of B for which the coil will start tipping over?
A narrow beam of singly charged potassium ions of kinetic energy 32 keV is injected into a region of width 1.00 cm with a magnetic field of strength 0.500 T, as shown in the figure. The ions are collected at a screen 95.5 cm away from the field region. If the beam contains isotopes of atomic weights 39 and 41, find the separation between the points where these isotopes strike the screen. Take the mass of a potassium ion = A (1.6 × 10−27) kg, where A is the mass number.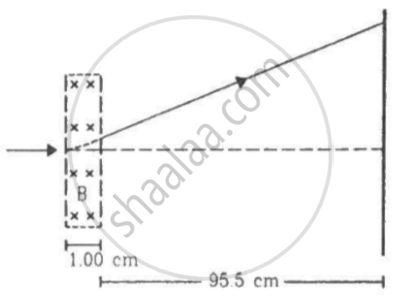
The figure shows a convex lens of focal length 12 cm lying in a uniform magnetic field Bof magnitude 1.2 T parallel to its principal axis. A particle with charge 2.0 × 10−3 C and mass 2.0 × 10−5 kg is projected perpendicular to the plane of the diagram with a speed of 4.8 m s−1. The particle moves along a circle with its centre on the principal axis at a distance of 18 cm from the lens. Show that the image of the particle moves along a circle and find the radius of that circle.

