Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
If a charged particle at rest experiences no electromagnetic force,
(a) the electric field must be zero
(b) the magnetic field must be zero
(c) the electric field may or may not be zero
(d) the magnetic field may or may not be zero
Solution
(a) the electric field must be zero
(d) the magnetic field may or may not be zero
As the charged particle is at rest, its velocity, V = 0 and magnetic force, F = qVB = 0. Hence, we cannot determine whether a magnetic field is present or not.
But as the particle at rest experiences no electromagnetic force, the electric field must be zero. This is because electric force acts on a particle whether it is at rest or in motion.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
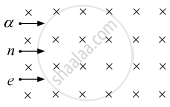
A neutron, an electron and an alpha particle, moving with equal velocities, enter a uniform magnetic field going into the plane of the paper, as shown. Trace their paths in the field and justify your answer.
A moving charged particle q travelling along the positive x-axis enters a uniform magnetic field B.
When will the force acting on q be maximum?
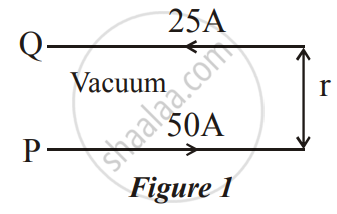
A long horizontal wire P carries a current of 50A. It is rigidly fixed. Another wire Q is placed directly above and parallel to P, as shown in Figure 1 below. The weight per unit length of the wire Q is 0.025 Nm-1 and it carries a current of 25A. Find the distance 'r' of the wire Q from the wire P so that the wire Q remains at rest
A proton and an α-particle move perpendicular to a magnetic field. Find the ratio of radii of circular paths described by them when both have (i) equal velocities, and (ii) equal kinetic energy.
Assume that the magnetic field is uniform in a cubical region and zero outside. Can you project a charged particle from outside into the field, so that the particle describes a complete circle in the field?
A positively-charged particle projected towards east is deflected towards north by a magnetic field. The field may be
An electric current i enters and leaves a uniform circular wire of radius a through diametrically opposite points. A charged particle q, moving along the axis of the circular wire, passes through its centre at speed v. The magnetic force acting on the particle, when it passes through the centre, has a magnitude equal to
When a proton is released from rest in a room, it starts with an initial acceleration a0towards west. When it is projected towards north with a speed v0, it moves with an initial acceleration 3a0 towards west. Find the electric field and the maximum possible magnetic field in the room.
A current of 2 A enters at the corner d of a square frame abcd of side 20 cm and leaves at the opposite corner b. A magnetic field B = 0.1 T exists in the space in a direction perpendicular to the plane of the frame, as shown in the figure. Find the magnitude and direction of the magnetic forces on the four sides of the frame.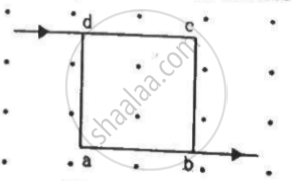
A magnetic field of strength 1.0 T is produced by a strong electromagnet in a cylindrical region of radius 4.0 cm, as shown in the figure. A wire, carrying a current of 2.0 A, is placed perpendicular to and intersecting the axis of the cylindrical region. Find the magnitude of the force acting on the wire.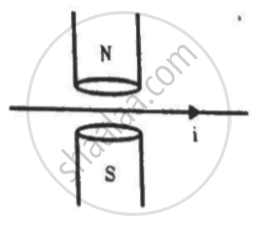
Prove that the force acting on a current-carrying wire, joining two fixed points a and b in a uniform magnetic field, is independent of the shape of the wire.
A wire, carrying a current i, is kept in the x−y plane along the curve y = A sin `((2x)/lamda x)`. magnetic field B exists in the z direction. Find the magnitude of the magnetic force on the portion of the wire between x = 0 and x = λ.
A proton is projected with a velocity of 3 × 106 m s−1 perpendicular to a uniform magnetic field of 0.6 T. Find the acceleration of the proton.
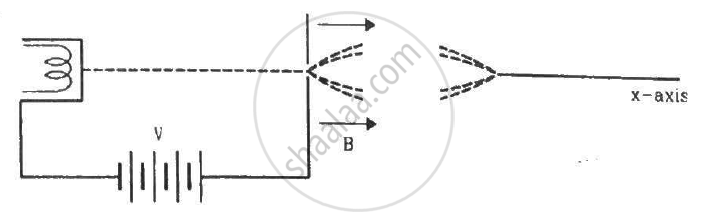
Electrons emitted with negligible speed from an electron gun are accelerated through a potential difference V along the x-axis. These electrons emerge from a narrow hole into a uniform magnetic field B directed along this axis. However, some of the electrons emerging from the hole make slightly divergent angles, as shown in the figure. Show that these paraxial electrons are refocussed on the x-axis at a distance `sqrt(8pi^2mV)/(eB^2).`
A uniform magnetic field of magnitude 0.20 T exists in space from east to west. With what speed should a particle of mass 0.010 g and with charge 1.0 × 10−5 C be projected from south to north so that it moves with uniform velocity?
A particle moves in a circle of diameter 1.0 cm under the action of a magnetic field of 0.40 T. An electric field of 200 V m−1 makes the path straight. Find the charge/mass ratio of the particle.
A proton projected in a magnetic field of 0.020 T travels along a helical path of radius 5.0 cm and pitch 20 cm. Find the components of the velocity of the proton along and perpendicular to the magnetic field. Take the mass of the proton = 1.6 × 10−27 kg
When does a moving charged particle nor experience any force while moving through a uniform magnetic field?
