Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A particle moves in a circle of diameter 1.0 cm under the action of a magnetic field of 0.40 T. An electric field of 200 V m−1 makes the path straight. Find the charge/mass ratio of the particle.
Solution
Given:
Diameter of the circle = 1.0 cm
Thus, radius of circle, r = = 0.5 × 10−2 m,
Magnetic field, B = 0.40 T
Electric field, E = 200 V m−1.
As per the question, the particle is moving in a circle under the action of a magnetic field. But when an electric field is applied on the particle, it moves in a straight line.
So, we can write:
Fe = Fm
qE = qvB, where q is the charge and v is the velocity of the particle.
⇒ `v = E/B = 200/0.4 = 500 m//s`
As r = `v/(rB)`
=`500/(0.5xx10^-2xx0.4)`
= 2.5 × 105 c /kg
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
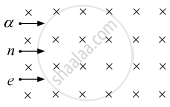
A neutron, an electron and an alpha particle, moving with equal velocities, enter a uniform magnetic field going into the plane of the paper, as shown. Trace their paths in the field and justify your answer.
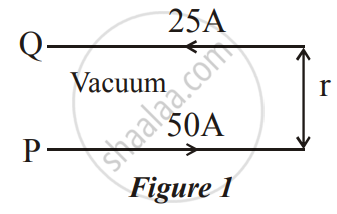
A long horizontal wire P carries a current of 50A. It is rigidly fixed. Another wire Q is placed directly above and parallel to P, as shown in Figure 1 below. The weight per unit length of the wire Q is 0.025 Nm-1 and it carries a current of 25A. Find the distance 'r' of the wire Q from the wire P so that the wire Q remains at rest
Write the expression for Lorentz magnetic force on a particle of charge ‘q’ moving with velocity `vecv` in a magnetic field`vecB`. Show that no work is done by this force on the charged particle.
A charged particle moves in a gravity-free space without change in velocity. Which of the following is/are possible?
(a) E = 0, B = 0
(b) E = 0, B ≠ 0
(c) E ≠ 0, B = 0
(d) E ≠ 0, B ≠ 0
If a charged particle moves unaccelerated in a region containing electric and magnetic fields
(a) `vecE "must be perpendicular" to vecB`
(b) `vecv "must be perpendicular" to vecE`
(c) must be perpendicular to v_B
A magnetic field of \[(4.0\times10^-3 \overrightarrow k)\] T exerts a force of \[(4.0 \overrightarrow i + 3.0 \overrightarrow j ) \times 10^{−10} N\] on a particle with a charge of 1.0 × 10−9 C and going in the x − y plane. Find the velocity of the particle.
A magnetic field of strength 1.0 T is produced by a strong electromagnet in a cylindrical region of radius 4.0 cm, as shown in the figure. A wire, carrying a current of 2.0 A, is placed perpendicular to and intersecting the axis of the cylindrical region. Find the magnitude of the force acting on the wire.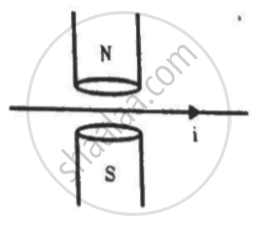
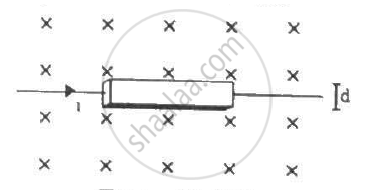
A current i is passed through a silver strip of width d and area of cross-section A. The number of free electrons per unit volume is n. (a) Find the drift velocity v of the electrons. (b) If a magnetic field B exists in the region, as shown in the figure, what is the average magnetic force on the free electrons? (c) Due to the magnetic force, the free electrons get accumulated on one side of the conductor along its length. This produces a transverse electric field in the conductor, which opposes the magnetic force on the electrons. Find the magnitude of the electric field which will stop further accumulation of electrons. (d) What will be the potential difference developed across the width of the conductor due to the electron-accumulation? The appearance of a transverse emf, when a current-carrying wire is placed in a magnetic field, is called Hall effect.
A particle of charge 2.0 × 10−8 C and mass 2.0 × 10−10 g is projected with a speed of 2.0 × 103 m s−1 in a region with a uniform magnetic field of 0.10 T. The velocity is perpendicular to the field. Find the radius of the circle formed by the particle and also the time period.
A proton describes a circle of radius 1 cm in a magnetic field of strength 0.10 T. What would be the radius of the circle described by an α-particle moving with the same speed in the same magnetic field?
Protons with kinetic energy K emerge from an accelerator as a narrow beam. The beam is bent by a perpendicular magnetic field, so that it just misses a plane target kept at a distance l in front of the accelerator. Find the magnetic field.
A narrow beam of singly-charged carbon ions, moving at a constant velocity of 6.0 × 104m s−1, is sent perpendicularly in a rectangular region of uniform magnetic field B = 0.5 T (figure). It is found that two beams emerge from the field in the backward direction, the separations from the incident beam being 3.0 cm and 3.5 cm. Identify the isotopes present in the ion beam. Take the mass of an ion = A(1.6 × 10−27) kg, where A is the mass number.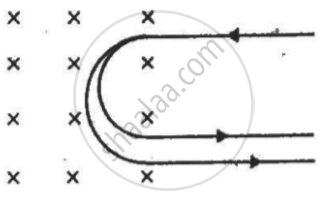
A narrow beam of singly charged potassium ions of kinetic energy 32 keV is injected into a region of width 1.00 cm with a magnetic field of strength 0.500 T, as shown in the figure. The ions are collected at a screen 95.5 cm away from the field region. If the beam contains isotopes of atomic weights 39 and 41, find the separation between the points where these isotopes strike the screen. Take the mass of a potassium ion = A (1.6 × 10−27) kg, where A is the mass number.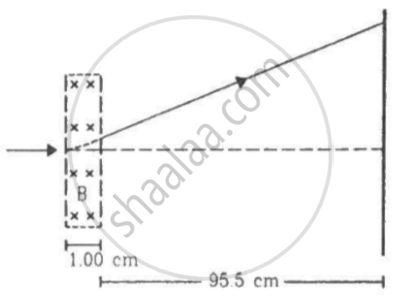
The figure shows a convex lens of focal length 12 cm lying in a uniform magnetic field Bof magnitude 1.2 T parallel to its principal axis. A particle with charge 2.0 × 10−3 C and mass 2.0 × 10−5 kg is projected perpendicular to the plane of the diagram with a speed of 4.8 m s−1. The particle moves along a circle with its centre on the principal axis at a distance of 18 cm from the lens. Show that the image of the particle moves along a circle and find the radius of that circle.

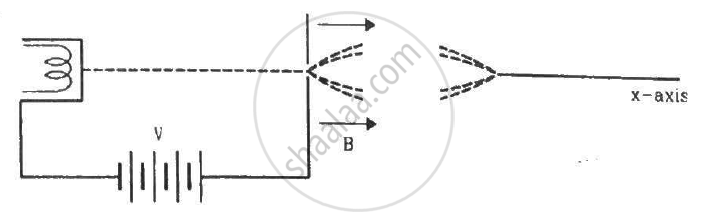
Electrons emitted with negligible speed from an electron gun are accelerated through a potential difference V along the x-axis. These electrons emerge from a narrow hole into a uniform magnetic field B directed along this axis. However, some of the electrons emerging from the hole make slightly divergent angles, as shown in the figure. Show that these paraxial electrons are refocussed on the x-axis at a distance `sqrt(8pi^2mV)/(eB^2).`
A particle of mass m and charge q is released from the origin in a region in which the electric field and magnetic field are given by
`vecB = -B_0 vecj and vecE = E_0 vecK `
Find the speed of the particle as a function of its z-coordinate.
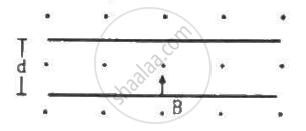
An electron is emitted with negligible speed from the negative plate of a parallel-plate capacitor charged to a potential difference V. The separation between the plates is dand a magnetic field B exists in the space, as shown in the figure. Show that the electron will fail to strike the upper plates if `d > ((2m_eV)/(eB_0^2))^(1/2)`
When does a moving charged particle nor experience any force while moving through a uniform magnetic field?
