Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A particle moves in a circle of diameter 1.0 cm under the action of a magnetic field of 0.40 T. An electric field of 200 V m−1 makes the path straight. Find the charge/mass ratio of the particle.
उत्तर
Given:
Diameter of the circle = 1.0 cm
Thus, radius of circle, r = = 0.5 × 10−2 m,
Magnetic field, B = 0.40 T
Electric field, E = 200 V m−1.
As per the question, the particle is moving in a circle under the action of a magnetic field. But when an electric field is applied on the particle, it moves in a straight line.
So, we can write:
Fe = Fm
qE = qvB, where q is the charge and v is the velocity of the particle.
⇒ `v = E/B = 200/0.4 = 500 m//s`
As r = `v/(rB)`
=`500/(0.5xx10^-2xx0.4)`
= 2.5 × 105 c /kg
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Write the expression, in a vector form, for the Lorentz magnetic force \[\vec{F}\] due to a charge moving with velocity \[\vec{V}\] in a magnetic field \[\vec{B}\]. What is the direction of the magnetic force?
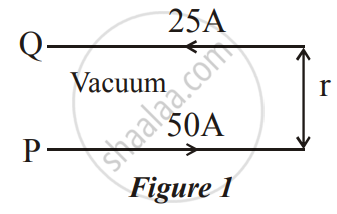
A long horizontal wire P carries a current of 50A. It is rigidly fixed. Another wire Q is placed directly above and parallel to P, as shown in Figure 1 below. The weight per unit length of the wire Q is 0.025 Nm-1 and it carries a current of 25A. Find the distance 'r' of the wire Q from the wire P so that the wire Q remains at rest
Write the expression for the force,`vecF` acting on a charged particle of charge ‘q’, moving with a velocity `vecV` in the presence of both electric field `vecF`and magnetic field `vecB` . Obtain the condition under which the particle moves undeflected through the fields.
Assume that the magnetic field is uniform in a cubical region and zero outside. Can you project a charged particle from outside into the field, so that the particle describes a complete circle in the field?
A positively-charged particle projected towards east is deflected towards north by a magnetic field. The field may be
A charged particle is whirled in a horizontal circle on a frictionless table by attaching it to a string fixed at one point. If a magnetic field is switched on in the vertical direction, the tension in the string
A charged particle moves along a circle under the action of possible constant electric and magnetic fields. Which of the following is possible?
(a) E = 0, B = 0
(b) E = 0, B ≠ 0
(c) E ≠ 0, B = 0
(d) E ≠ 0, B ≠ 0
If a charged particle moves unaccelerated in a region containing electric and magnetic fields
(a) `vecE "must be perpendicular" to vecB`
(b) `vecv "must be perpendicular" to vecE`
(c) must be perpendicular to v_B
Two particles X and Y having equal charge, after being accelerated through the same potential difference enter a region of uniform magnetic field and describe circular paths of radii R1 and R2 respectively. The ratio of the mass of X to that of Y is ______.
When a proton is released from rest in a room, it starts with an initial acceleration a0towards west. When it is projected towards north with a speed v0, it moves with an initial acceleration 3a0 towards west. Find the electric field and the maximum possible magnetic field in the room.
A semicircular wire of radius 5.0 cm carries a current of 5.0 A. A magnetic field B of magnitude 0.50 T exists along the perpendicular to the plane of the wire. Find the magnitude of the magnetic force acting on the wire.
Consider a non-conducting ring of radius r and mass m that has a total charge qdistributed uniformly on it. The ring is rotated about its axis with an angular speed ω. (a) Find the equivalent electric current in the ring. (b) Find the magnetic moment µ of the ring. (c) Show that `pi = (q)/(2m)` l, where l is the angular momentum of the ring about its axis of rotation.
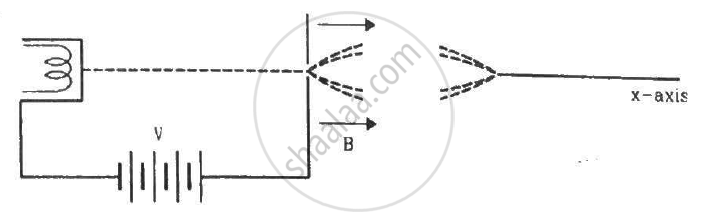
Electrons emitted with negligible speed from an electron gun are accelerated through a potential difference V along the x-axis. These electrons emerge from a narrow hole into a uniform magnetic field B directed along this axis. However, some of the electrons emerging from the hole make slightly divergent angles, as shown in the figure. Show that these paraxial electrons are refocussed on the x-axis at a distance `sqrt(8pi^2mV)/(eB^2).`
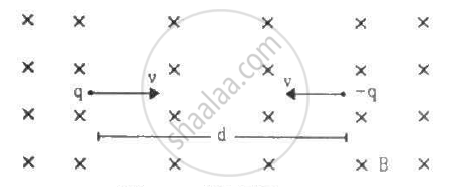
Two particles, each with mass m are placed at a separation d in a uniform magnetic field B, as shown in the figure. They have opposite charges of equal magnitude q. At time t = 0, the particles are projected towards each other, each with a speed v. Suppose the Coulomb force between the charges is switched off. (a) Find the maximum value vmof the projection speed, so that the two particles do not collide. (b) What would be the minimum and maximum separation between the particles if v = vm/2? (c) At what instant will a collision occur between the particles if v = 2vm? (d) Suppose v = 2vm and the collision between the particles is completely inelastic. Describe the motion after the collision.
A particle of mass m and charge q is released from the origin in a region in which the electric field and magnetic field are given by
`vecB = -B_0 vecj and vecE = E_0 vecK `
Find the speed of the particle as a function of its z-coordinate.
A long, straight wire carrying a current of 30 A is placed in an external, uniform magnetic field of 4.0 × 10−4 T parallel to the current. Find the magnitude of the resultant magnetic field at a point 2.0 cm away from the wire.
Current flows through uniform, square frames as shown in the figure. In which case is the magnetic field at the centre of the frame not zero?
The velocity of a body of mass 2 kg as a function of time t is given by v(t) = 2t`hat"i" + "t"^2hat"j"`. The force acting on it, at time t = 2 s is given by ______.
