Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Two particles X and Y having equal charge, after being accelerated through the same potential difference enter a region of uniform magnetic field and describe circular paths of radii R1 and R2 respectively. The ratio of the mass of X to that of Y is ______.
विकल्प
(R1/R2)1/2
R1/R2
(R1/R2)2
R1R2.
उत्तर
Two particles X and Y having equal charge, after being accelerated through the same potential difference enter a region of uniform magnetic field and describe circular paths of radii R1 and R2 respectively. The ratio of the mass of X to that of Y is (R1/R2)2.
Explanation:
`"R"_1^2/"R"_2^2`
Particles X and Y of respective masses m1 and m2 are carrying charge q describing circular paths with respective radii R1 and R2 such that
`"R"_1 = ("m"_1"v"_1)/"qB"`
`"R"_2 = ("m"_2"v"_2)/"qB"`
Since both the particles are accelerated through the same potential difference, both will have the same kinetic energy.
`therefore 1/2 "m"_1"v"_1^2 = 1/2 "m"_2"v"_2^2`
`because "R"_1 = ("m"_1"v"_1)/"qB" => "v"_1 = ("R"_1"qB")/"m"_1`
And
`because "R"_2 = ("m"_2"v"_2)/"qB" => "v"_2 = ("R"_2"qB")/"m"_2`
`therefore "m"_1 (("R"_1 "qB")/"m"_1)^2 = "m"_2 (("R"_1 "qB")/"m"_1)^2`
`=> "m"_1/"m"_2 = "R"_1^2/"R"_2^2`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Write the expression, in a vector form, for the Lorentz magnetic force \[\vec{F}\] due to a charge moving with velocity \[\vec{V}\] in a magnetic field \[\vec{B}\]. What is the direction of the magnetic force?
Show that the kinetic energy of the particle moving in a magnetic field remains constant.
A moving charged particle q travelling along the positive x-axis enters a uniform magnetic field B.
When will the force acting on q be maximum?
A proton and an α-particle move perpendicular to a magnetic field. Find the ratio of radii of circular paths described by them when both have (i) equal velocities, and (ii) equal kinetic energy.
If a charged particle projected in a gravity-free room deflects,
(a) there must be an electric field
(b) there must be a magnetic field
(c) both fields cannot be zero
(d) both fields can be non-zero
A charged particle moves in a gravity-free space without change in velocity. Which of the following is/are possible?
(a) E = 0, B = 0
(b) E = 0, B ≠ 0
(c) E ≠ 0, B = 0
(d) E ≠ 0, B ≠ 0
A charged particle moves along a circle under the action of possible constant electric and magnetic fields. Which of the following is possible?
(a) E = 0, B = 0
(b) E = 0, B ≠ 0
(c) E ≠ 0, B = 0
(d) E ≠ 0, B ≠ 0
Two ions have equal masses but one is singly-ionised and the other is doubly-ionised. They are projected from the same place in a uniform magnetic field with the same velocity perpendicular to the field.
(a) Both ions will move along circles of equal radii.
(b) The circle described by the singly-ionised charge will have a radius that is double that of the other circle.
(c) The two circles do not touch each other.
(d) The two circles touch each other.
Consider three quantities \[x = E/B, y = \sqrt{1/ \mu_0 \epsilon_0}\] and \[z = \frac{l}{CR}\] . Here, l is the length of a wire, C is a capacitance and R is a resistance. All other symbols have standard meanings.
(a) x, y have the same dimensions.
(b) y, z have the same dimensions.
(c) z, x have the same dimensions.
(d) None of the three pairs have the same dimensions.
A current of 2 A enters at the corner d of a square frame abcd of side 20 cm and leaves at the opposite corner b. A magnetic field B = 0.1 T exists in the space in a direction perpendicular to the plane of the frame, as shown in the figure. Find the magnitude and direction of the magnetic forces on the four sides of the frame.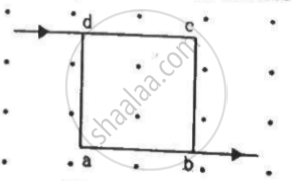
A magnetic field of strength 1.0 T is produced by a strong electromagnet in a cylindrical region of radius 4.0 cm, as shown in the figure. A wire, carrying a current of 2.0 A, is placed perpendicular to and intersecting the axis of the cylindrical region. Find the magnitude of the force acting on the wire.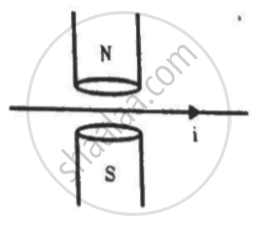
Prove that the force acting on a current-carrying wire, joining two fixed points a and b in a uniform magnetic field, is independent of the shape of the wire.
A proton describes a circle of radius 1 cm in a magnetic field of strength 0.10 T. What would be the radius of the circle described by an α-particle moving with the same speed in the same magnetic field?
An electron of kinetic energy 100 eV circulates in a path of radius 10 cm in a magnetic field. Find the magnetic field and the number of revolutions per second made by the electron.
A circular coil of radius 2.0 cm has 500 turns and carries a current of 1.0 A. Its axis makes an angle of 30° with the uniform magnetic field of magnitude 0.40 T that exists in the space. Find the torque acting on the coil.
A particle of mass m and charge q is projected into a region that has a perpendicular magnetic field B. Find the angle of deviation (figure) of the particle as it comes out of the magnetic field if the width d of the region is very slightly smaller than
(a) `(mv)/(qB)` (b)`(mv)/(2qB)` (c)`(2mv)/(qB)`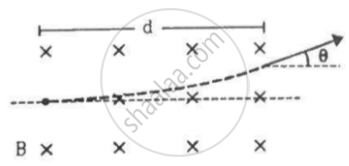
Doubly-ionised helium ions are projected with a speed of 10 km s−1 in a direction perpendicular to a uniform magnetic field of magnitude 1.0 T. Find (a) the force acting on an ion (b) the radius of the circle in which it circulates and (c) the time taken by an ion to complete the circle.
An electron is emitted with negligible speed from the negative plate of a parallel-plate capacitor charged to a potential difference V. The separation between the plates is dand a magnetic field B exists in the space, as shown in the figure. Show that the electron will fail to strike the upper plates if `d > ((2m_eV)/(eB_0^2))^(1/2)`