Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A circular coil of radius 2.0 cm has 500 turns and carries a current of 1.0 A. Its axis makes an angle of 30° with the uniform magnetic field of magnitude 0.40 T that exists in the space. Find the torque acting on the coil.
उत्तर
Given:
No. of turns of the coil, n = 500
Magnetic field intensity, B = 0.40 T = 4 × 10−1 T
Radius of the coil, r = 2 cm = 2 × 10−2 m
Magnitude of current, i = 1 A
Angle between the area vector and magnetic field, θ = 30°
Torque acting on the coil,
τ = niABsinθ
Here, A is the area of the coil.
τ = 500 × 1 × 3.14 × 4 × 10−4 ×4×10−1 × 1/2
= 12.56 × 10−2
= 0.1256 = 0.13 N-m
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Write the expression for the force `vecF` acting on a particle of mass m and charge q moving with velocity `vecV` in a magnetic field `vecB` , Under what conditions will it move in (i) a circular path and (ii) a helical path?
Show that the kinetic energy of the particle moving in a magnetic field remains constant.
A moving charged particle q travelling along the positive x-axis enters a uniform magnetic field B.
When will the force acting on q be maximum?
A straight wire of mass 200 g and length 1.5 m carries a current of 2 A. It is suspended in mid air by a uniform magnetic field B. What is the magnitude of the magnetic field?
Assume that the magnetic field is uniform in a cubical region and zero outside. Can you project a charged particle from outside into the field, so that the particle describes a complete circle in the field?
A positively-charged particle projected towards east is deflected towards north by a magnetic field. The field may be
A charged particle moves in a uniform magnetic field. The velocity of the particle at some instant makes an acute angle with the magnetic field. The path of the particle will be
An electric current i enters and leaves a uniform circular wire of radius a through diametrically opposite points. A charged particle q, moving along the axis of the circular wire, passes through its centre at speed v. The magnetic force acting on the particle, when it passes through the centre, has a magnitude equal to
A charged particle moves along a circle under the action of possible constant electric and magnetic fields. Which of the following is possible?
(a) E = 0, B = 0
(b) E = 0, B ≠ 0
(c) E ≠ 0, B = 0
(d) E ≠ 0, B ≠ 0
If a charged particle moves unaccelerated in a region containing electric and magnetic fields
(a) `vecE "must be perpendicular" to vecB`
(b) `vecv "must be perpendicular" to vecE`
(c) must be perpendicular to v_B
Two particles X and Y having equal charge, after being accelerated through the same potential difference enter a region of uniform magnetic field and describe circular paths of radii R1 and R2 respectively. The ratio of the mass of X to that of Y is ______.
Consider three quantities \[x = E/B, y = \sqrt{1/ \mu_0 \epsilon_0}\] and \[z = \frac{l}{CR}\] . Here, l is the length of a wire, C is a capacitance and R is a resistance. All other symbols have standard meanings.
(a) x, y have the same dimensions.
(b) y, z have the same dimensions.
(c) z, x have the same dimensions.
(d) None of the three pairs have the same dimensions.
A current of 2 A enters at the corner d of a square frame abcd of side 20 cm and leaves at the opposite corner b. A magnetic field B = 0.1 T exists in the space in a direction perpendicular to the plane of the frame, as shown in the figure. Find the magnitude and direction of the magnetic forces on the four sides of the frame.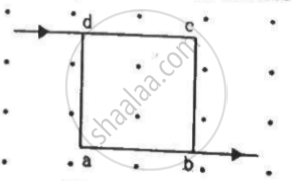
Prove that the force acting on a current-carrying wire, joining two fixed points a and b in a uniform magnetic field, is independent of the shape of the wire.
A narrow beam of singly-charged carbon ions, moving at a constant velocity of 6.0 × 104m s−1, is sent perpendicularly in a rectangular region of uniform magnetic field B = 0.5 T (figure). It is found that two beams emerge from the field in the backward direction, the separations from the incident beam being 3.0 cm and 3.5 cm. Identify the isotopes present in the ion beam. Take the mass of an ion = A(1.6 × 10−27) kg, where A is the mass number.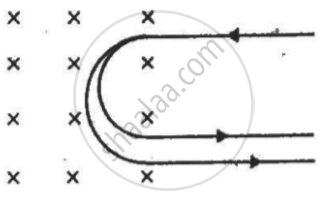
The figure shows a convex lens of focal length 12 cm lying in a uniform magnetic field Bof magnitude 1.2 T parallel to its principal axis. A particle with charge 2.0 × 10−3 C and mass 2.0 × 10−5 kg is projected perpendicular to the plane of the diagram with a speed of 4.8 m s−1. The particle moves along a circle with its centre on the principal axis at a distance of 18 cm from the lens. Show that the image of the particle moves along a circle and find the radius of that circle.

Current flows through uniform, square frames as shown in the figure. In which case is the magnetic field at the centre of the frame not zero?
The velocity of a body of mass 2 kg as a function of time t is given by v(t) = 2t`hat"i" + "t"^2hat"j"`. The force acting on it, at time t = 2 s is given by ______.
