Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A circular coil of radius 2.0 cm has 500 turns and carries a current of 1.0 A. Its axis makes an angle of 30° with the uniform magnetic field of magnitude 0.40 T that exists in the space. Find the torque acting on the coil.
Solution
Given:
No. of turns of the coil, n = 500
Magnetic field intensity, B = 0.40 T = 4 × 10−1 T
Radius of the coil, r = 2 cm = 2 × 10−2 m
Magnitude of current, i = 1 A
Angle between the area vector and magnetic field, θ = 30°
Torque acting on the coil,
τ = niABsinθ
Here, A is the area of the coil.
τ = 500 × 1 × 3.14 × 4 × 10−4 ×4×10−1 × 1/2
= 12.56 × 10−2
= 0.1256 = 0.13 N-m
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Write the expression for the force `vecF` acting on a particle of mass m and charge q moving with velocity `vecV` in a magnetic field `vecB` , Under what conditions will it move in (i) a circular path and (ii) a helical path?
A straight wire of mass 200 g and length 1.5 m carries a current of 2 A. It is suspended in mid air by a uniform magnetic field B. What is the magnitude of the magnetic field?
A proton and a deuteron having equal momenta enter in a region of a uniform magnetic field at right angle to the direction of a the field. Depict their trajectories in the field.
Write the expression for the force,`vecF` acting on a charged particle of charge ‘q’, moving with a velocity `vecV` in the presence of both electric field `vecF`and magnetic field `vecB` . Obtain the condition under which the particle moves undeflected through the fields.
A beam consisting of protons and electrons moving at the same speed goes through a thin region in which there is a magnetic field perpendicular to the beam. The protons and the electrons
If a charged particle projected in a gravity-free room deflects,
(a) there must be an electric field
(b) there must be a magnetic field
(c) both fields cannot be zero
(d) both fields can be non-zero
An experimenter's diary reads as follows: "A charged particle is projected in a magnetic field of `(7.0 vec i - 3.0 vecj)xx 10^-3 `T. The acceleration of the particle is found to be `(x veci + 7.0 vecj )` The number to the left of i in the last expression was not readable. What can this number be?
A 10 g bullet with a charge of 4.00 μC is fired at a speed of 270 m s−1 in a horizontal direction. A vertical magnetic field of 500 µT exists in the space. Find the deflection of the bullet due to the magnetic field as it travels through 100 m. Make appropriate approximations.
When a proton is released from rest in a room, it starts with an initial acceleration a0towards west. When it is projected towards north with a speed v0, it moves with an initial acceleration 3a0 towards west. Find the electric field and the maximum possible magnetic field in the room.
A magnetic field of strength 1.0 T is produced by a strong electromagnet in a cylindrical region of radius 4.0 cm, as shown in the figure. A wire, carrying a current of 2.0 A, is placed perpendicular to and intersecting the axis of the cylindrical region. Find the magnitude of the force acting on the wire.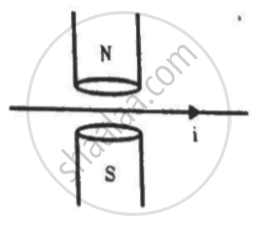
A semicircular wire of radius 5.0 cm carries a current of 5.0 A. A magnetic field B of magnitude 0.50 T exists along the perpendicular to the plane of the wire. Find the magnitude of the magnetic force acting on the wire.
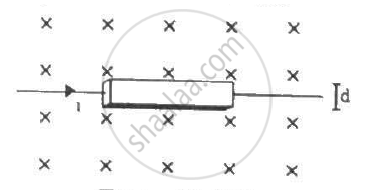
A current i is passed through a silver strip of width d and area of cross-section A. The number of free electrons per unit volume is n. (a) Find the drift velocity v of the electrons. (b) If a magnetic field B exists in the region, as shown in the figure, what is the average magnetic force on the free electrons? (c) Due to the magnetic force, the free electrons get accumulated on one side of the conductor along its length. This produces a transverse electric field in the conductor, which opposes the magnetic force on the electrons. Find the magnitude of the electric field which will stop further accumulation of electrons. (d) What will be the potential difference developed across the width of the conductor due to the electron-accumulation? The appearance of a transverse emf, when a current-carrying wire is placed in a magnetic field, is called Hall effect.
A charged particle is accelerated through a potential difference of 12 kV and acquires a speed of 1.0 × 106 m s−1. It is then injected perpendicularly into a magnetic field of strength 0.2 T. Find the radius of the circle described by it.
A particle of mass m and charge q is projected into a region that has a perpendicular magnetic field B. Find the angle of deviation (figure) of the particle as it comes out of the magnetic field if the width d of the region is very slightly smaller than
(a) `(mv)/(qB)` (b)`(mv)/(2qB)` (c)`(2mv)/(qB)`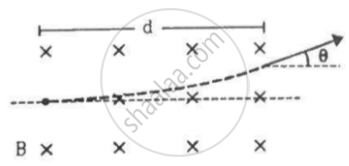
A narrow beam of singly charged potassium ions of kinetic energy 32 keV is injected into a region of width 1.00 cm with a magnetic field of strength 0.500 T, as shown in the figure. The ions are collected at a screen 95.5 cm away from the field region. If the beam contains isotopes of atomic weights 39 and 41, find the separation between the points where these isotopes strike the screen. Take the mass of a potassium ion = A (1.6 × 10−27) kg, where A is the mass number.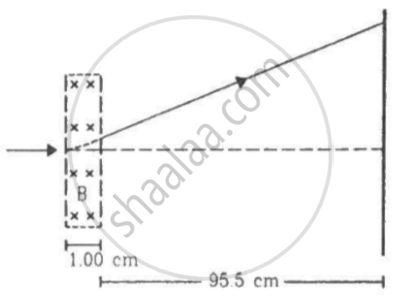
Doubly-ionised helium ions are projected with a speed of 10 km s−1 in a direction perpendicular to a uniform magnetic field of magnitude 1.0 T. Find (a) the force acting on an ion (b) the radius of the circle in which it circulates and (c) the time taken by an ion to complete the circle.
A proton is projected with a velocity of 3 × 106 m s−1 perpendicular to a uniform magnetic field of 0.6 T. Find the acceleration of the proton.
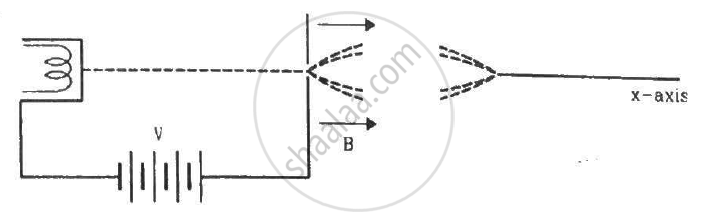
Electrons emitted with negligible speed from an electron gun are accelerated through a potential difference V along the x-axis. These electrons emerge from a narrow hole into a uniform magnetic field B directed along this axis. However, some of the electrons emerging from the hole make slightly divergent angles, as shown in the figure. Show that these paraxial electrons are refocussed on the x-axis at a distance `sqrt(8pi^2mV)/(eB^2).`
A proton projected in a magnetic field of 0.020 T travels along a helical path of radius 5.0 cm and pitch 20 cm. Find the components of the velocity of the proton along and perpendicular to the magnetic field. Take the mass of the proton = 1.6 × 10−27 kg
A long, straight wire carrying a current of 30 A is placed in an external, uniform magnetic field of 4.0 × 10−4 T parallel to the current. Find the magnitude of the resultant magnetic field at a point 2.0 cm away from the wire.
