Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
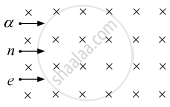
A beam consisting of protons and electrons moving at the same speed goes through a thin region in which there is a magnetic field perpendicular to the beam. The protons and the electrons
Options
will go undeviated
will be deviated by the same angle and will not separate
will be deviated by different angles and hence will separate
will be deviated by the same angle but will separate
Solution
will be deviated by different angles and hence will separate
Force on a charged particle, F = qVB
For an electron, this force is F = -eVB, whereas on a proton this force is F = eVB.
Here, 'e' is the charge of the electron. So, from the above formulas, we can see that electrons and protons will experience equal force but in opposite directions; so they separate out. In other words, we can say that they are deviated by different angles and causes them to separate.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A neutron, an electron and an alpha particle, moving with equal velocities, enter a uniform magnetic field going into the plane of the paper, as shown. Trace their paths in the field and justify your answer.
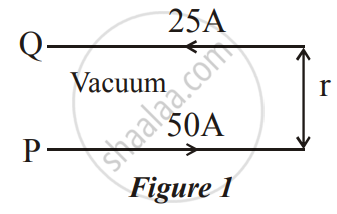
A long horizontal wire P carries a current of 50A. It is rigidly fixed. Another wire Q is placed directly above and parallel to P, as shown in Figure 1 below. The weight per unit length of the wire Q is 0.025 Nm-1 and it carries a current of 25A. Find the distance 'r' of the wire Q from the wire P so that the wire Q remains at rest
An electron moving horizontally with a velocity of 4 ✕ 104 m/s enters a region of uniform magnetic field of 10−5 T acting vertically upward as shown in the figure. Draw its trajectory and find out the time it takes to come out of the region of magnetic
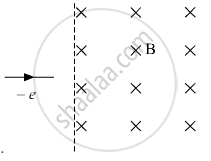
field.
A straight wire of mass 200 g and length 1.5 m carries a current of 2 A. It is suspended in mid air by a uniform magnetic field B. What is the magnitude of the magnetic field?
Write the expression for the force,`vecF` acting on a charged particle of charge ‘q’, moving with a velocity `vecV` in the presence of both electric field `vecF`and magnetic field `vecB` . Obtain the condition under which the particle moves undeflected through the fields.
An electric current i enters and leaves a uniform circular wire of radius a through diametrically opposite points. A charged particle q, moving along the axis of the circular wire, passes through its centre at speed v. The magnetic force acting on the particle, when it passes through the centre, has a magnitude equal to
If a charged particle at rest experiences no electromagnetic force,
(a) the electric field must be zero
(b) the magnetic field must be zero
(c) the electric field may or may not be zero
(d) the magnetic field may or may not be zero
A charged particle moves in a gravity-free space without change in velocity. Which of the following is/are possible?
(a) E = 0, B = 0
(b) E = 0, B ≠ 0
(c) E ≠ 0, B = 0
(d) E ≠ 0, B ≠ 0
A charged particle moves along a circle under the action of possible constant electric and magnetic fields. Which of the following is possible?
(a) E = 0, B = 0
(b) E = 0, B ≠ 0
(c) E ≠ 0, B = 0
(d) E ≠ 0, B ≠ 0
Two ions have equal masses but one is singly-ionised and the other is doubly-ionised. They are projected from the same place in a uniform magnetic field with the same velocity perpendicular to the field.
(a) Both ions will move along circles of equal radii.
(b) The circle described by the singly-ionised charge will have a radius that is double that of the other circle.
(c) The two circles do not touch each other.
(d) The two circles touch each other.
A particle is projected in a plane perpendicular to a uniform magnetic field. The area bounded by the path described by the particle is proportional to
Consider three quantities \[x = E/B, y = \sqrt{1/ \mu_0 \epsilon_0}\] and \[z = \frac{l}{CR}\] . Here, l is the length of a wire, C is a capacitance and R is a resistance. All other symbols have standard meanings.
(a) x, y have the same dimensions.
(b) y, z have the same dimensions.
(c) z, x have the same dimensions.
(d) None of the three pairs have the same dimensions.
Using the formula \[\vec{F} = q \vec{v} \times \vec{B} \text{ and } B = \frac{\mu_0 i}{2\pi r}\]show that the SI units of the magnetic field B and the permeability constant µ0 may be written as N mA−1 and NA−2 respectively.
A square coil of edge l and with n turns carries a current i. It is kept on a smooth horizontal plate. A uniform magnetic field B exists parallel to an edge. The total mass of the coil is M. What should be the minimum value of B for which the coil will start tipping over?
A particle moves in a circle of diameter 1.0 cm under the action of a magnetic field of 0.40 T. An electric field of 200 V m−1 makes the path straight. Find the charge/mass ratio of the particle.
A proton projected in a magnetic field of 0.020 T travels along a helical path of radius 5.0 cm and pitch 20 cm. Find the components of the velocity of the proton along and perpendicular to the magnetic field. Take the mass of the proton = 1.6 × 10−27 kg
When does a moving charged particle nor experience any force while moving through a uniform magnetic field?
Current flows through uniform, square frames as shown in the figure. In which case is the magnetic field at the centre of the frame not zero?
