Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Doubly-ionised helium ions are projected with a speed of 10 km s−1 in a direction perpendicular to a uniform magnetic field of magnitude 1.0 T. Find (a) the force acting on an ion (b) the radius of the circle in which it circulates and (c) the time taken by an ion to complete the circle.
Solution
Given:
Speed of the helium ions, v = 10 km s−1 = 104 m/s
Uniform magnetic field, B = 1.0 T
Charge on the helium ions = 2e
Mass of the helium ions, m = 4 × 1.6 × 10-27 kg
(a) The force acting on an ion,
F = qvBsinθ
= 2 × 1.6 × 10−19 × 104 × 1.0
= 3.2 × 10−15 N
(b) The radius of the circle in which it circulates,
`r = (mv)/(qB)`
= `(4xx1.6xx10^27xx10^4)/(2xx1.6xx10^-9xx1)`
=`(2xx10^-23)/(10^-19)`
(c) The time taken by an ion to complete the circle,
`T = (2pir)/(v)`
= `(6.28xx2.1xx10^-4)/(10^4)`
= 1.31 × 10−7 s
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A straight wire of mass 200 g and length 1.5 m carries a current of 2 A. It is suspended in mid air by a uniform magnetic field B. What is the magnitude of the magnetic field?
Assume that the magnetic field is uniform in a cubical region and zero outside. Can you project a charged particle from outside into the field, so that the particle describes a complete circle in the field?
A positively-charged particle projected towards east is deflected towards north by a magnetic field. The field may be
A charged particle moves in a uniform magnetic field. The velocity of the particle at some instant makes an acute angle with the magnetic field. The path of the particle will be
A charged particle moves along a circle under the action of possible constant electric and magnetic fields. Which of the following is possible?
(a) E = 0, B = 0
(b) E = 0, B ≠ 0
(c) E ≠ 0, B = 0
(d) E ≠ 0, B ≠ 0
A magnetic field of \[(4.0\times10^-3 \overrightarrow k)\] T exerts a force of \[(4.0 \overrightarrow i + 3.0 \overrightarrow j ) \times 10^{−10} N\] on a particle with a charge of 1.0 × 10−9 C and going in the x − y plane. Find the velocity of the particle.
A 10 g bullet with a charge of 4.00 μC is fired at a speed of 270 m s−1 in a horizontal direction. A vertical magnetic field of 500 µT exists in the space. Find the deflection of the bullet due to the magnetic field as it travels through 100 m. Make appropriate approximations.
A magnetic field of strength 1.0 T is produced by a strong electromagnet in a cylindrical region of radius 4.0 cm, as shown in the figure. A wire, carrying a current of 2.0 A, is placed perpendicular to and intersecting the axis of the cylindrical region. Find the magnitude of the force acting on the wire.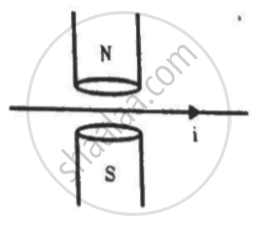
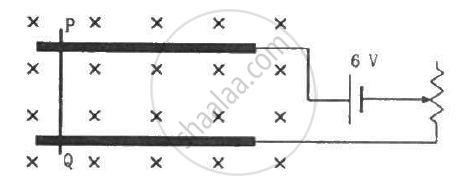
A metal wire PQ of mass 10 g lies at rest on two horizontal metal rails separated by 4.90 cm (figure). A vertically-downward magnetic field of magnitude 0.800 T exists in the space. The resistance of the circuit is slowly decreased and it is found that when the resistance goes below 20.0 Ω, the wire PQ starts sliding on the rails. Find the coefficient of friction.
A particle of charge 2.0 × 10−8 C and mass 2.0 × 10−10 g is projected with a speed of 2.0 × 103 m s−1 in a region with a uniform magnetic field of 0.10 T. The velocity is perpendicular to the field. Find the radius of the circle formed by the particle and also the time period.
An electron of kinetic energy 100 eV circulates in a path of radius 10 cm in a magnetic field. Find the magnetic field and the number of revolutions per second made by the electron.
Protons with kinetic energy K emerge from an accelerator as a narrow beam. The beam is bent by a perpendicular magnetic field, so that it just misses a plane target kept at a distance l in front of the accelerator. Find the magnetic field.
A charged particle is accelerated through a potential difference of 12 kV and acquires a speed of 1.0 × 106 m s−1. It is then injected perpendicularly into a magnetic field of strength 0.2 T. Find the radius of the circle described by it.
A narrow beam of singly-charged carbon ions, moving at a constant velocity of 6.0 × 104m s−1, is sent perpendicularly in a rectangular region of uniform magnetic field B = 0.5 T (figure). It is found that two beams emerge from the field in the backward direction, the separations from the incident beam being 3.0 cm and 3.5 cm. Identify the isotopes present in the ion beam. Take the mass of an ion = A(1.6 × 10−27) kg, where A is the mass number.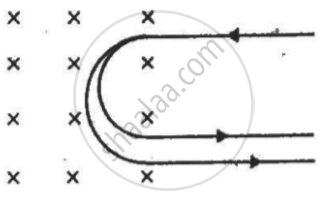
A proton is projected with a velocity of 3 × 106 m s−1 perpendicular to a uniform magnetic field of 0.6 T. Find the acceleration of the proton.
A particle moves in a circle of diameter 1.0 cm under the action of a magnetic field of 0.40 T. An electric field of 200 V m−1 makes the path straight. Find the charge/mass ratio of the particle.
A particle of mass m and charge q is released from the origin in a region in which the electric field and magnetic field are given by
`vecB = -B_0 vecj and vecE = E_0 vecK `
Find the speed of the particle as a function of its z-coordinate.
