Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A magnetic field of \[(4.0\times10^-3 \overrightarrow k)\] T exerts a force of \[(4.0 \overrightarrow i + 3.0 \overrightarrow j ) \times 10^{−10} N\] on a particle with a charge of 1.0 × 10−9 C and going in the x − y plane. Find the velocity of the particle.
Solution
Given:-
Magnetic field, B = `(4xx10xx^-3 hatK)`T
Force exerted by the magnetic field on the charged particle, F = `(4 hati + 3hatj )`× 10−10 N
Charge of the particle, q = 1 × 10−9 C
As per the question, the charge is going in the X-Y plane.
So, the x-component of force, Fx = 4 × 10−10 N
and the y-component of force, Fy = 3 × 10−10 N
Considering the motion along x-axis:-
Fx = qvy×B
On putting the respective values, we get:-
vy = 100 m/s
Motion along y-axis:-
Fy = qvx×B
⇒ vx = 75 m/s
Thus, total velocity =`( -75 vec i + 100 vec j) `m/s
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Write the expression for the force `vecF` acting on a particle of mass m and charge q moving with velocity `vecV` in a magnetic field `vecB` , Under what conditions will it move in (i) a circular path and (ii) a helical path?
A neutron, an electron and an alpha particle, moving with equal velocities, enter a uniform magnetic field going into the plane of the paper, as shown. Trace their paths in the field and justify your answer.
A moving charged particle q travelling along the positive x-axis enters a uniform magnetic field B.
When will the force acting on q be maximum?
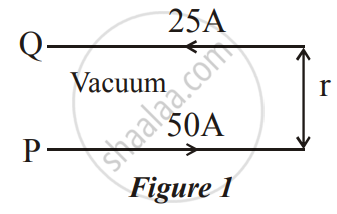
A long horizontal wire P carries a current of 50A. It is rigidly fixed. Another wire Q is placed directly above and parallel to P, as shown in Figure 1 below. The weight per unit length of the wire Q is 0.025 Nm-1 and it carries a current of 25A. Find the distance 'r' of the wire Q from the wire P so that the wire Q remains at rest
A straight wire of mass 200 g and length 1.5 m carries a current of 2 A. It is suspended in mid air by a uniform magnetic field B. What is the magnitude of the magnetic field?
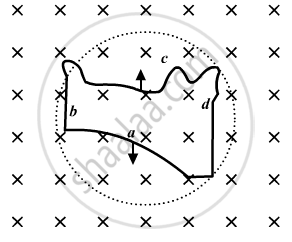
A flexible wire of irregular shape, abcd, as shown in the figure, turns into a circular shape when placed in a region of magnetic field which is directed normal to the plane of the loop away from the reader. Predict the direction of the induced current in the wire.
Two ions have equal masses but one is singly-ionised and the other is doubly-ionised. They are projected from the same place in a uniform magnetic field with the same velocity perpendicular to the field.
(a) Both ions will move along circles of equal radii.
(b) The circle described by the singly-ionised charge will have a radius that is double that of the other circle.
(c) The two circles do not touch each other.
(d) The two circles touch each other.
A 10 g bullet with a charge of 4.00 μC is fired at a speed of 270 m s−1 in a horizontal direction. A vertical magnetic field of 500 µT exists in the space. Find the deflection of the bullet due to the magnetic field as it travels through 100 m. Make appropriate approximations.
Prove that the force acting on a current-carrying wire, joining two fixed points a and b in a uniform magnetic field, is independent of the shape of the wire.
A semicircular wire of radius 5.0 cm carries a current of 5.0 A. A magnetic field B of magnitude 0.50 T exists along the perpendicular to the plane of the wire. Find the magnitude of the magnetic force acting on the wire.
A metal wire PQ of mass 10 g lies at rest on two horizontal metal rails separated by 4.90 cm (figure). A vertically-downward magnetic field of magnitude 0.800 T exists in the space. The resistance of the circuit is slowly decreased and it is found that when the resistance goes below 20.0 Ω, the wire PQ starts sliding on the rails. Find the coefficient of friction.
A particle of charge 2.0 × 10−8 C and mass 2.0 × 10−10 g is projected with a speed of 2.0 × 103 m s−1 in a region with a uniform magnetic field of 0.10 T. The velocity is perpendicular to the field. Find the radius of the circle formed by the particle and also the time period.
A proton describes a circle of radius 1 cm in a magnetic field of strength 0.10 T. What would be the radius of the circle described by an α-particle moving with the same speed in the same magnetic field?
A square coil of edge l and with n turns carries a current i. It is kept on a smooth horizontal plate. A uniform magnetic field B exists parallel to an edge. The total mass of the coil is M. What should be the minimum value of B for which the coil will start tipping over?
A proton is projected with a velocity of 3 × 106 m s−1 perpendicular to a uniform magnetic field of 0.6 T. Find the acceleration of the proton.
When does a moving charged particle nor experience any force while moving through a uniform magnetic field?
A particle of mass 10 mg and having a charge of 50 mC is projected with a speed of 15 m/s into a uniform magnetic field of 125 mT. Assuming that the particle is projected with its velocity perpendicular to the magnetic field, the time after which the particle reaches its original position for the first time is ______.
