Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Write the expression, in a vector form, for the Lorentz magnetic force \[\vec{F}\] due to a charge moving with velocity \[\vec{V}\] in a magnetic field \[\vec{B}\]. What is the direction of the magnetic force?
उत्तर
The Lorentz magnetic force is given by the following relation:
`vecF=q(vecVxxvecB)`
Here, q is the magnitude of the moving charge.
The direction of the magnetic force is perpendicular to the plane containing the velocity vector `(vecV)`and the magnetic field vector `(vecB)`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A proton and an α-particle move perpendicular to a magnetic field. Find the ratio of radii of circular paths described by them when both have (i) equal velocities, and (ii) equal kinetic energy.
A beam consisting of protons and electrons moving at the same speed goes through a thin region in which there is a magnetic field perpendicular to the beam. The protons and the electrons
If a charged particle moves unaccelerated in a region containing electric and magnetic fields
(a) `vecE "must be perpendicular" to vecB`
(b) `vecv "must be perpendicular" to vecE`
(c) must be perpendicular to v_B
Two ions have equal masses but one is singly-ionised and the other is doubly-ionised. They are projected from the same place in a uniform magnetic field with the same velocity perpendicular to the field.
(a) Both ions will move along circles of equal radii.
(b) The circle described by the singly-ionised charge will have a radius that is double that of the other circle.
(c) The two circles do not touch each other.
(d) The two circles touch each other.
A semicircular wire of radius 5.0 cm carries a current of 5.0 A. A magnetic field B of magnitude 0.50 T exists along the perpendicular to the plane of the wire. Find the magnitude of the magnetic force acting on the wire.
A wire, carrying a current i, is kept in the x−y plane along the curve y = A sin `((2x)/lamda x)`. magnetic field B exists in the z direction. Find the magnitude of the magnetic force on the portion of the wire between x = 0 and x = λ.
A proton is projected with a velocity of 3 × 106 m s−1 perpendicular to a uniform magnetic field of 0.6 T. Find the acceleration of the proton.
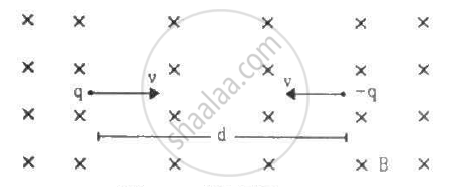
Two particles, each with mass m are placed at a separation d in a uniform magnetic field B, as shown in the figure. They have opposite charges of equal magnitude q. At time t = 0, the particles are projected towards each other, each with a speed v. Suppose the Coulomb force between the charges is switched off. (a) Find the maximum value vmof the projection speed, so that the two particles do not collide. (b) What would be the minimum and maximum separation between the particles if v = vm/2? (c) At what instant will a collision occur between the particles if v = 2vm? (d) Suppose v = 2vm and the collision between the particles is completely inelastic. Describe the motion after the collision.
A particle with a charge of 5.0 µC and a mass of 5.0 × 10−12 kg is projected with a speed of 1.0 km s−1 in a magnetic field of magnitude 5.0 mT. The angle between the magnetic field and the velocity is sin−1 (0.90). Show that the path of the particle will be a helix. Find the diameter of the helix and its pitch.
A uniform magnetic field of 1.5 T exists in a cylindrical region of radius 10.0 cm, its direction parallel to the axis along east to west. A wire carrying current of 7.0 A in the north to south direction passes through this region. What is the magnitude and direction of the force on the wire if,
(a) the wire intersects the axis,
(b) the wire is turned from N-S to northeast-northwest direction,
(c) the wire in the N-S direction is lowered from the axis by a distance of 6.0 cm?
