Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A current of 2 A enters at the corner d of a square frame abcd of side 20 cm and leaves at the opposite corner b. A magnetic field B = 0.1 T exists in the space in a direction perpendicular to the plane of the frame, as shown in the figure. Find the magnitude and direction of the magnetic forces on the four sides of the frame.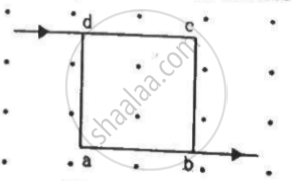
Solution
Given:
A square frame abcd of side, l = 20 cm
Electric current through the wire, I = 2 A
Magnetic field, B = 0.1 T
The direction of magnetic field is perpendicular to the plane of the frame, coming out of the plane.
As per the question, current enters at the corner d of the square frame and leaves at the opposite corner b.
Angle between the frame and magnetic field, θ = 90˚
Magnetic force,
`vecF = i vecl xx vecB`
For wire da and cb,
`|vecF| = ilBsin theta`
`|vecF| = ilBsin90°`
`= 2/2 xx 20 xx 10^-2xx 0.1`
= 0.02 N
The direction of force can be found using Fleming's left-hand rule.
Thus, the direction of magnetic force is towards the left.
For wires dc and ab,
`|vecF| = ilBsintheta`
∴ `|vecF| = ilBsin90^circ`
`= 2/2 xx 20 xx 10^-2xx0.1`
`= 0.02 N`
The direction of force can be found using Fleming's left-hand rule.
Thus, the direction of magnetic force is downwards.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Show that the kinetic energy of the particle moving in a magnetic field remains constant.
A proton and an α-particle move perpendicular to a magnetic field. Find the ratio of radii of circular paths described by them when both have (i) equal velocities, and (ii) equal kinetic energy.
Write the expression for Lorentz magnetic force on a particle of charge ‘q’ moving with velocity `vecv` in a magnetic field`vecB`. Show that no work is done by this force on the charged particle.
A charged particle is whirled in a horizontal circle on a frictionless table by attaching it to a string fixed at one point. If a magnetic field is switched on in the vertical direction, the tension in the string
A charged particle moves along a circle under the action of possible constant electric and magnetic fields. Which of the following is possible?
(a) E = 0, B = 0
(b) E = 0, B ≠ 0
(c) E ≠ 0, B = 0
(d) E ≠ 0, B ≠ 0
A particle is projected in a plane perpendicular to a uniform magnetic field. The area bounded by the path described by the particle is proportional to
Two particles X and Y having equal charge, after being accelerated through the same potential difference enter a region of uniform magnetic field and describe circular paths of radii R1 and R2 respectively. The ratio of the mass of X to that of Y is ______.
A magnetic field of \[(4.0\times10^-3 \overrightarrow k)\] T exerts a force of \[(4.0 \overrightarrow i + 3.0 \overrightarrow j ) \times 10^{−10} N\] on a particle with a charge of 1.0 × 10−9 C and going in the x − y plane. Find the velocity of the particle.
An experimenter's diary reads as follows: "A charged particle is projected in a magnetic field of `(7.0 vec i - 3.0 vecj)xx 10^-3 `T. The acceleration of the particle is found to be `(x veci + 7.0 vecj )` The number to the left of i in the last expression was not readable. What can this number be?
A wire, carrying a current i, is kept in the x−y plane along the curve y = A sin `((2x)/lamda x)`. magnetic field B exists in the z direction. Find the magnitude of the magnetic force on the portion of the wire between x = 0 and x = λ.
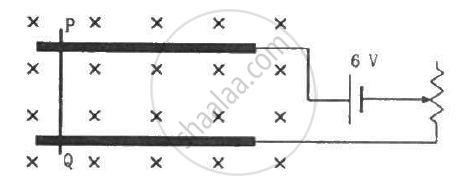
A metal wire PQ of mass 10 g lies at rest on two horizontal metal rails separated by 4.90 cm (figure). A vertically-downward magnetic field of magnitude 0.800 T exists in the space. The resistance of the circuit is slowly decreased and it is found that when the resistance goes below 20.0 Ω, the wire PQ starts sliding on the rails. Find the coefficient of friction.
A proton describes a circle of radius 1 cm in a magnetic field of strength 0.10 T. What would be the radius of the circle described by an α-particle moving with the same speed in the same magnetic field?
An electron of kinetic energy 100 eV circulates in a path of radius 10 cm in a magnetic field. Find the magnetic field and the number of revolutions per second made by the electron.
A circular coil of radius 2.0 cm has 500 turns and carries a current of 1.0 A. Its axis makes an angle of 30° with the uniform magnetic field of magnitude 0.40 T that exists in the space. Find the torque acting on the coil.
Consider a non-conducting ring of radius r and mass m that has a total charge qdistributed uniformly on it. The ring is rotated about its axis with an angular speed ω. (a) Find the equivalent electric current in the ring. (b) Find the magnetic moment µ of the ring. (c) Show that `pi = (q)/(2m)` l, where l is the angular momentum of the ring about its axis of rotation.
A uniform magnetic field of magnitude 0.20 T exists in space from east to west. With what speed should a particle of mass 0.010 g and with charge 1.0 × 10−5 C be projected from south to north so that it moves with uniform velocity?
A proton projected in a magnetic field of 0.020 T travels along a helical path of radius 5.0 cm and pitch 20 cm. Find the components of the velocity of the proton along and perpendicular to the magnetic field. Take the mass of the proton = 1.6 × 10−27 kg
A uniform magnetic field of 1.5 T exists in a cylindrical region of radius 10.0 cm, its direction parallel to the axis along east to west. A wire carrying current of 7.0 A in the north to south direction passes through this region. What is the magnitude and direction of the force on the wire if,
(a) the wire intersects the axis,
(b) the wire is turned from N-S to northeast-northwest direction,
(c) the wire in the N-S direction is lowered from the axis by a distance of 6.0 cm?
