Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Two ions have equal masses but one is singly-ionised and the other is doubly-ionised. They are projected from the same place in a uniform magnetic field with the same velocity perpendicular to the field.
(a) Both ions will move along circles of equal radii.
(b) The circle described by the singly-ionised charge will have a radius that is double that of the other circle.
(c) The two circles do not touch each other.
(d) The two circles touch each other.
उत्तर
(b) The circle described by the singly-ionised charge will have a radius that is double that of the other circle.
(d) The two circles touch each other.
The radius of the orbit of a charged particle in an external magnetic field,
`r = (mV)/(qB)`
where r is the radius of the circle, m is the mass of the ion, V is the velocity with which the ion is projected, q is the charge on the ion and B is the uniform magnetic field.
Since the mass m, the velocity V and the magnetic field B are same for both the ions, r is inversely proportional to the charge on the ion.
Hence, the radius of the circle described by the singly-charged ion will be twice the radius of the circle described by doubly-ionised ion.
Moreover, as both the charges are projected from the same place, the two circles described by them will touch each other at the point of projection.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
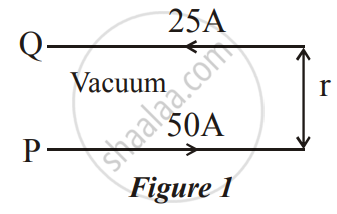
A long horizontal wire P carries a current of 50A. It is rigidly fixed. Another wire Q is placed directly above and parallel to P, as shown in Figure 1 below. The weight per unit length of the wire Q is 0.025 Nm-1 and it carries a current of 25A. Find the distance 'r' of the wire Q from the wire P so that the wire Q remains at rest
An electron moving horizontally with a velocity of 4 ✕ 104 m/s enters a region of uniform magnetic field of 10−5 T acting vertically upward as shown in the figure. Draw its trajectory and find out the time it takes to come out of the region of magnetic
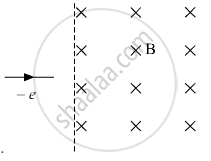
field.
Assume that the magnetic field is uniform in a cubical region and zero outside. Can you project a charged particle from outside into the field, so that the particle describes a complete circle in the field?
A charged particle moves in a gravity-free space without change in velocity. Which of the following is/are possible?
(a) E = 0, B = 0
(b) E = 0, B ≠ 0
(c) E ≠ 0, B = 0
(d) E ≠ 0, B ≠ 0
A 10 g bullet with a charge of 4.00 μC is fired at a speed of 270 m s−1 in a horizontal direction. A vertical magnetic field of 500 µT exists in the space. Find the deflection of the bullet due to the magnetic field as it travels through 100 m. Make appropriate approximations.
When a proton is released from rest in a room, it starts with an initial acceleration a0towards west. When it is projected towards north with a speed v0, it moves with an initial acceleration 3a0 towards west. Find the electric field and the maximum possible magnetic field in the room.
A magnetic field of strength 1.0 T is produced by a strong electromagnet in a cylindrical region of radius 4.0 cm, as shown in the figure. A wire, carrying a current of 2.0 A, is placed perpendicular to and intersecting the axis of the cylindrical region. Find the magnitude of the force acting on the wire.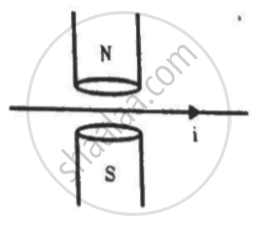
A semicircular wire of radius 5.0 cm carries a current of 5.0 A. A magnetic field B of magnitude 0.50 T exists along the perpendicular to the plane of the wire. Find the magnitude of the magnetic force acting on the wire.
A metal wire PQ of mass 10 g lies at rest on two horizontal metal rails separated by 4.90 cm (figure). A vertically-downward magnetic field of magnitude 0.800 T exists in the space. The resistance of the circuit is slowly decreased and it is found that when the resistance goes below 20.0 Ω, the wire PQ starts sliding on the rails. Find the coefficient of friction.
A square coil of edge l and with n turns carries a current i. It is kept on a smooth horizontal plate. A uniform magnetic field B exists parallel to an edge. The total mass of the coil is M. What should be the minimum value of B for which the coil will start tipping over?
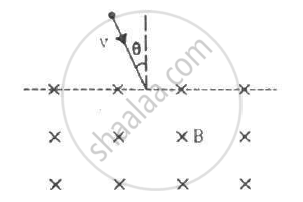
A particle of mass m and positive charge q, moving with a uniform velocity v, enters a magnetic field B, as shown in the figure. (a) Find the radius of the circular arc it describes in the magnetic field. (b) Find the angle subtended by the arc at the centre. (c) How long does the particle stay inside the magnetic field? (d) Solve the three parts of the above problem if the charge q on the particle is negative.
Doubly-ionised helium ions are projected with a speed of 10 km s−1 in a direction perpendicular to a uniform magnetic field of magnitude 1.0 T. Find (a) the force acting on an ion (b) the radius of the circle in which it circulates and (c) the time taken by an ion to complete the circle.
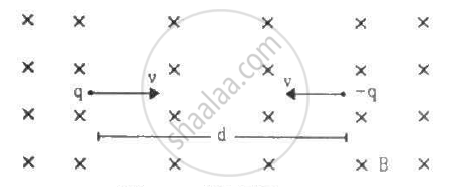
Two particles, each with mass m are placed at a separation d in a uniform magnetic field B, as shown in the figure. They have opposite charges of equal magnitude q. At time t = 0, the particles are projected towards each other, each with a speed v. Suppose the Coulomb force between the charges is switched off. (a) Find the maximum value vmof the projection speed, so that the two particles do not collide. (b) What would be the minimum and maximum separation between the particles if v = vm/2? (c) At what instant will a collision occur between the particles if v = 2vm? (d) Suppose v = 2vm and the collision between the particles is completely inelastic. Describe the motion after the collision.
A proton projected in a magnetic field of 0.020 T travels along a helical path of radius 5.0 cm and pitch 20 cm. Find the components of the velocity of the proton along and perpendicular to the magnetic field. Take the mass of the proton = 1.6 × 10−27 kg
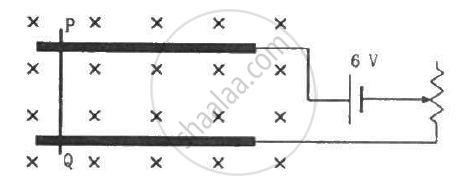
An electron is emitted with negligible speed from the negative plate of a parallel-plate capacitor charged to a potential difference V. The separation between the plates is dand a magnetic field B exists in the space, as shown in the figure. Show that the electron will fail to strike the upper plates if `d > ((2m_eV)/(eB_0^2))^(1/2)`
When does a moving charged particle nor experience any force while moving through a uniform magnetic field?
The velocity of a body of mass 2 kg as a function of time t is given by v(t) = 2t`hat"i" + "t"^2hat"j"`. The force acting on it, at time t = 2 s is given by ______.
