Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
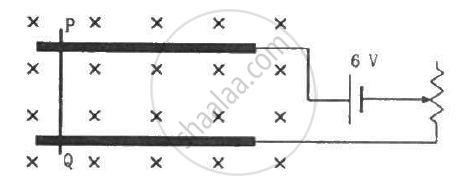
A metal wire PQ of mass 10 g lies at rest on two horizontal metal rails separated by 4.90 cm (figure). A vertically-downward magnetic field of magnitude 0.800 T exists in the space. The resistance of the circuit is slowly decreased and it is found that when the resistance goes below 20.0 Ω, the wire PQ starts sliding on the rails. Find the coefficient of friction.
उत्तर
Given:-
Mass of the metal wire, M = 10 g
Distance between the two horizontal metal rails, l = 4.90 cm
Vertically-downward magnetic field, B = 0.800 T
As per the question, when the resistance of the circuit is slowly decreased below 20.0 Ω, the wire PQ starts sliding on the rails. At that moment,
current in the wire, i = `V/R =6/20A `Using Fleming's left-hand rule, the magnetic force will act towards the right. So, due to this magnetic force, the wire will try to slide on the rails.The frictional force will try to oppose this motion of the wire.
When the wire just starts sliding on the rails, the frictional force acting on the wire will just balance the magnetic force acting on the wire.This implies
µR = F, where
µ is the coffiecent of friction
R is the normal reaction force and
F is the magnetic force
`⇒mu xx M xx g = ilB`
`muxx10xx10^-3xx9.8 = 6/20xx 4.9 xx 10^-2xx0.8`
`mu = (6xx4.9xx10^-2xx0.8)/(20xx10xx10^-3xx9.8)`
µ = 0.12
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Write the expression, in a vector form, for the Lorentz magnetic force \[\vec{F}\] due to a charge moving with velocity \[\vec{V}\] in a magnetic field \[\vec{B}\]. What is the direction of the magnetic force?
Write the expression for the force,`vecF` acting on a charged particle of charge ‘q’, moving with a velocity `vecV` in the presence of both electric field `vecF`and magnetic field `vecB` . Obtain the condition under which the particle moves undeflected through the fields.
A positively-charged particle projected towards east is deflected towards north by a magnetic field. The field may be
A charged particle moves in a uniform magnetic field. The velocity of the particle at some instant makes an acute angle with the magnetic field. The path of the particle will be
An electric current i enters and leaves a uniform circular wire of radius a through diametrically opposite points. A charged particle q, moving along the axis of the circular wire, passes through its centre at speed v. The magnetic force acting on the particle, when it passes through the centre, has a magnitude equal to
If a charged particle at rest experiences no electromagnetic force,
(a) the electric field must be zero
(b) the magnetic field must be zero
(c) the electric field may or may not be zero
(d) the magnetic field may or may not be zero
A particle is projected in a plane perpendicular to a uniform magnetic field. The area bounded by the path described by the particle is proportional to
Two particles X and Y having equal charge, after being accelerated through the same potential difference enter a region of uniform magnetic field and describe circular paths of radii R1 and R2 respectively. The ratio of the mass of X to that of Y is ______.
A current of 2 A enters at the corner d of a square frame abcd of side 20 cm and leaves at the opposite corner b. A magnetic field B = 0.1 T exists in the space in a direction perpendicular to the plane of the frame, as shown in the figure. Find the magnitude and direction of the magnetic forces on the four sides of the frame.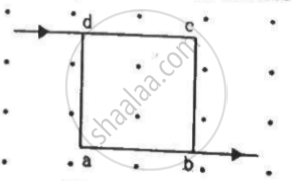
A square coil of edge l and with n turns carries a current i. It is kept on a smooth horizontal plate. A uniform magnetic field B exists parallel to an edge. The total mass of the coil is M. What should be the minimum value of B for which the coil will start tipping over?
A narrow beam of singly-charged carbon ions, moving at a constant velocity of 6.0 × 104m s−1, is sent perpendicularly in a rectangular region of uniform magnetic field B = 0.5 T (figure). It is found that two beams emerge from the field in the backward direction, the separations from the incident beam being 3.0 cm and 3.5 cm. Identify the isotopes present in the ion beam. Take the mass of an ion = A(1.6 × 10−27) kg, where A is the mass number.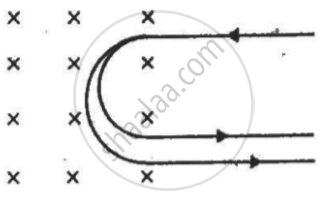
A proton is projected with a velocity of 3 × 106 m s−1 perpendicular to a uniform magnetic field of 0.6 T. Find the acceleration of the proton.
The figure shows a convex lens of focal length 12 cm lying in a uniform magnetic field Bof magnitude 1.2 T parallel to its principal axis. A particle with charge 2.0 × 10−3 C and mass 2.0 × 10−5 kg is projected perpendicular to the plane of the diagram with a speed of 4.8 m s−1. The particle moves along a circle with its centre on the principal axis at a distance of 18 cm from the lens. Show that the image of the particle moves along a circle and find the radius of that circle.

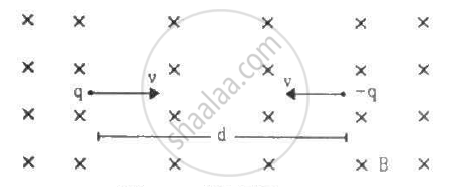
Two particles, each with mass m are placed at a separation d in a uniform magnetic field B, as shown in the figure. They have opposite charges of equal magnitude q. At time t = 0, the particles are projected towards each other, each with a speed v. Suppose the Coulomb force between the charges is switched off. (a) Find the maximum value vmof the projection speed, so that the two particles do not collide. (b) What would be the minimum and maximum separation between the particles if v = vm/2? (c) At what instant will a collision occur between the particles if v = 2vm? (d) Suppose v = 2vm and the collision between the particles is completely inelastic. Describe the motion after the collision.
A particle moves in a circle of diameter 1.0 cm under the action of a magnetic field of 0.40 T. An electric field of 200 V m−1 makes the path straight. Find the charge/mass ratio of the particle.
When does a moving charged particle nor experience any force while moving through a uniform magnetic field?
Current flows through uniform, square frames as shown in the figure. In which case is the magnetic field at the centre of the frame not zero?
