Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A proton is projected with a velocity of 3 × 106 m s−1 perpendicular to a uniform magnetic field of 0.6 T. Find the acceleration of the proton.
उत्तर
Given:
Velocity of the proton, v = 3 × 106 m s−1
Uniform magnetic field, B = 0.6 T
As per the question, the proton is projected perpendicular to a uniform magnetic field.
We know,
F = mpa ....(i)
and
F = evBsinθ ....(ii)
On equating (i) and (ii), we get:
ma = evBsinθ (As θ = 90˚)
`a = (evB)/(m)`
`(1.6xx10^-19xx3xx10^6xx0.6)/(1.67xx10^-27)`
= 1.72 × 1014 m/s2
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Write the expression, in a vector form, for the Lorentz magnetic force \[\vec{F}\] due to a charge moving with velocity \[\vec{V}\] in a magnetic field \[\vec{B}\]. What is the direction of the magnetic force?
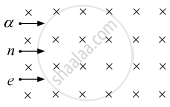
A neutron, an electron and an alpha particle, moving with equal velocities, enter a uniform magnetic field going into the plane of the paper, as shown. Trace their paths in the field and justify your answer.
An electron moving horizontally with a velocity of 4 ✕ 104 m/s enters a region of uniform magnetic field of 10−5 T acting vertically upward as shown in the figure. Draw its trajectory and find out the time it takes to come out of the region of magnetic
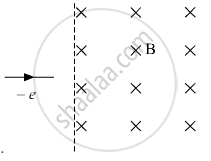
field.
A proton and a deuteron having equal momenta enter in a region of a uniform magnetic field at right angle to the direction of a the field. Depict their trajectories in the field.
A charged particle is whirled in a horizontal circle on a frictionless table by attaching it to a string fixed at one point. If a magnetic field is switched on in the vertical direction, the tension in the string
If a charged particle at rest experiences no electromagnetic force,
(a) the electric field must be zero
(b) the magnetic field must be zero
(c) the electric field may or may not be zero
(d) the magnetic field may or may not be zero
A charged particle moves along a circle under the action of possible constant electric and magnetic fields. Which of the following is possible?
(a) E = 0, B = 0
(b) E = 0, B ≠ 0
(c) E ≠ 0, B = 0
(d) E ≠ 0, B ≠ 0
If a charged particle moves unaccelerated in a region containing electric and magnetic fields
(a) `vecE "must be perpendicular" to vecB`
(b) `vecv "must be perpendicular" to vecE`
(c) must be perpendicular to v_B
Using the formula \[\vec{F} = q \vec{v} \times \vec{B} \text{ and } B = \frac{\mu_0 i}{2\pi r}\]show that the SI units of the magnetic field B and the permeability constant µ0 may be written as N mA−1 and NA−2 respectively.
Consider a non-conducting ring of radius r and mass m that has a total charge qdistributed uniformly on it. The ring is rotated about its axis with an angular speed ω. (a) Find the equivalent electric current in the ring. (b) Find the magnetic moment µ of the ring. (c) Show that `pi = (q)/(2m)` l, where l is the angular momentum of the ring about its axis of rotation.
A charged particle is accelerated through a potential difference of 12 kV and acquires a speed of 1.0 × 106 m s−1. It is then injected perpendicularly into a magnetic field of strength 0.2 T. Find the radius of the circle described by it.
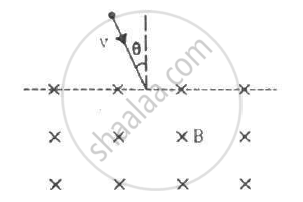
A particle of mass m and positive charge q, moving with a uniform velocity v, enters a magnetic field B, as shown in the figure. (a) Find the radius of the circular arc it describes in the magnetic field. (b) Find the angle subtended by the arc at the centre. (c) How long does the particle stay inside the magnetic field? (d) Solve the three parts of the above problem if the charge q on the particle is negative.
A particle of mass m and charge q is released from the origin in a region in which the electric field and magnetic field are given by
`vecB = -B_0 vecj and vecE = E_0 vecK `
Find the speed of the particle as a function of its z-coordinate.
A uniform magnetic field of 1.5 T exists in a cylindrical region of radius 10.0 cm, its direction parallel to the axis along east to west. A wire carrying current of 7.0 A in the north to south direction passes through this region. What is the magnitude and direction of the force on the wire if,
(a) the wire intersects the axis,
(b) the wire is turned from N-S to northeast-northwest direction,
(c) the wire in the N-S direction is lowered from the axis by a distance of 6.0 cm?
The velocity of a body of mass 2 kg as a function of time t is given by v(t) = 2t`hat"i" + "t"^2hat"j"`. The force acting on it, at time t = 2 s is given by ______.
A particle of mass 10 mg and having a charge of 50 mC is projected with a speed of 15 m/s into a uniform magnetic field of 125 mT. Assuming that the particle is projected with its velocity perpendicular to the magnetic field, the time after which the particle reaches its original position for the first time is ______.
