Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A particle of mass m and positive charge q, moving with a uniform velocity v, enters a magnetic field B, as shown in the figure. (a) Find the radius of the circular arc it describes in the magnetic field. (b) Find the angle subtended by the arc at the centre. (c) How long does the particle stay inside the magnetic field? (d) Solve the three parts of the above problem if the charge q on the particle is negative.
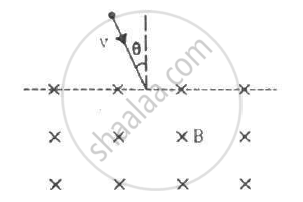
उत्तर
Given:-
Mass of the particle = m
Positive charge on the particle = q
Uniform velocity of the particle = v
Magnetic field = B
(a) The radius of the circular arc described by the particle in the magnetic field:-
We know
`r = (mv)/(qB)`
(b) 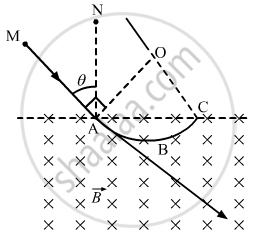
The angle subtended by the arc at the centre:-
Line MAB is tangent to arc ABC, so the angle described by the charged particle,
∠MAO = 90°
Now, ∠NAC = 90°
OAC = OCA = θ
[by geometry]
Then, AOC = 180° − (θ + θ) (By angle-sum property of a triangle)
= π − 2θ
(c) The time for which the particle stay inside the magnetic field:-
Distance covered by the particle inside the magnetic field,
l = rθ
`t = 1/v = m/(qB)(pi - 2theta)(U sing r = (mv)/(qB))`
(d) If the charge q on the particle is negative, then
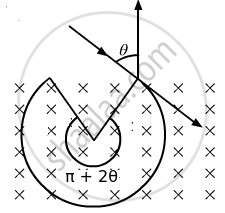
(i) Radius of circular arc, `r = (mv)/(qB)`
(ii) The centre of the arc will lie within the magnetic field. Therefore, the angle subtended by the arc = π + 2θ
(iii) Similarly, the time taken by the particle to cover the path inside the magnetic field = `m/(qB)(pi + 2theta)`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A moving charged particle q travelling along the positive x-axis enters a uniform magnetic field B.
When will the force acting on q be maximum?
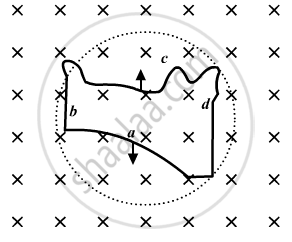
A flexible wire of irregular shape, abcd, as shown in the figure, turns into a circular shape when placed in a region of magnetic field which is directed normal to the plane of the loop away from the reader. Predict the direction of the induced current in the wire.
Write the expression for the force,`vecF` acting on a charged particle of charge ‘q’, moving with a velocity `vecV` in the presence of both electric field `vecF`and magnetic field `vecB` . Obtain the condition under which the particle moves undeflected through the fields.
A positively-charged particle projected towards east is deflected towards north by a magnetic field. The field may be
A charged particle is whirled in a horizontal circle on a frictionless table by attaching it to a string fixed at one point. If a magnetic field is switched on in the vertical direction, the tension in the string
A particle is projected in a plane perpendicular to a uniform magnetic field. The area bounded by the path described by the particle is proportional to
Two particles X and Y having equal charge, after being accelerated through the same potential difference enter a region of uniform magnetic field and describe circular paths of radii R1 and R2 respectively. The ratio of the mass of X to that of Y is ______.
Consider three quantities \[x = E/B, y = \sqrt{1/ \mu_0 \epsilon_0}\] and \[z = \frac{l}{CR}\] . Here, l is the length of a wire, C is a capacitance and R is a resistance. All other symbols have standard meanings.
(a) x, y have the same dimensions.
(b) y, z have the same dimensions.
(c) z, x have the same dimensions.
(d) None of the three pairs have the same dimensions.
An experimenter's diary reads as follows: "A charged particle is projected in a magnetic field of `(7.0 vec i - 3.0 vecj)xx 10^-3 `T. The acceleration of the particle is found to be `(x veci + 7.0 vecj )` The number to the left of i in the last expression was not readable. What can this number be?
A current of 2 A enters at the corner d of a square frame abcd of side 20 cm and leaves at the opposite corner b. A magnetic field B = 0.1 T exists in the space in a direction perpendicular to the plane of the frame, as shown in the figure. Find the magnitude and direction of the magnetic forces on the four sides of the frame.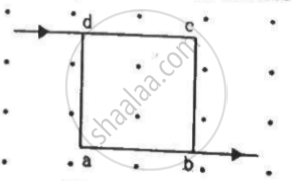
Using the formula \[\vec{F} = q \vec{v} \times \vec{B} \text{ and } B = \frac{\mu_0 i}{2\pi r}\]show that the SI units of the magnetic field B and the permeability constant µ0 may be written as N mA−1 and NA−2 respectively.
Consider a non-conducting ring of radius r and mass m that has a total charge qdistributed uniformly on it. The ring is rotated about its axis with an angular speed ω. (a) Find the equivalent electric current in the ring. (b) Find the magnetic moment µ of the ring. (c) Show that `pi = (q)/(2m)` l, where l is the angular momentum of the ring about its axis of rotation.
A narrow beam of singly charged potassium ions of kinetic energy 32 keV is injected into a region of width 1.00 cm with a magnetic field of strength 0.500 T, as shown in the figure. The ions are collected at a screen 95.5 cm away from the field region. If the beam contains isotopes of atomic weights 39 and 41, find the separation between the points where these isotopes strike the screen. Take the mass of a potassium ion = A (1.6 × 10−27) kg, where A is the mass number.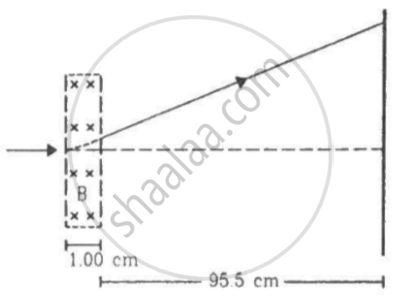
A proton is projected with a velocity of 3 × 106 m s−1 perpendicular to a uniform magnetic field of 0.6 T. Find the acceleration of the proton.
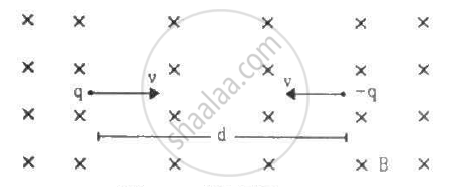
Two particles, each with mass m are placed at a separation d in a uniform magnetic field B, as shown in the figure. They have opposite charges of equal magnitude q. At time t = 0, the particles are projected towards each other, each with a speed v. Suppose the Coulomb force between the charges is switched off. (a) Find the maximum value vmof the projection speed, so that the two particles do not collide. (b) What would be the minimum and maximum separation between the particles if v = vm/2? (c) At what instant will a collision occur between the particles if v = 2vm? (d) Suppose v = 2vm and the collision between the particles is completely inelastic. Describe the motion after the collision.
A uniform magnetic field of magnitude 0.20 T exists in space from east to west. With what speed should a particle of mass 0.010 g and with charge 1.0 × 10−5 C be projected from south to north so that it moves with uniform velocity?
A proton projected in a magnetic field of 0.020 T travels along a helical path of radius 5.0 cm and pitch 20 cm. Find the components of the velocity of the proton along and perpendicular to the magnetic field. Take the mass of the proton = 1.6 × 10−27 kg
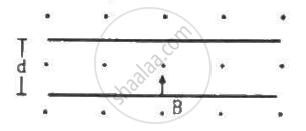
An electron is emitted with negligible speed from the negative plate of a parallel-plate capacitor charged to a potential difference V. The separation between the plates is dand a magnetic field B exists in the space, as shown in the figure. Show that the electron will fail to strike the upper plates if `d > ((2m_eV)/(eB_0^2))^(1/2)`
When does a moving charged particle nor experience any force while moving through a uniform magnetic field?
Current flows through uniform, square frames as shown in the figure. In which case is the magnetic field at the centre of the frame not zero?
