Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
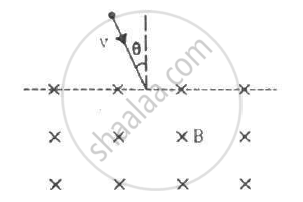
Assume that the magnetic field is uniform in a cubical region and zero outside. Can you project a charged particle from outside into the field, so that the particle describes a complete circle in the field?
उत्तर
Any charged particle from outside the cubical area can't be sent there in a way that makes it form a full circle inside the field. The particle will leave the cube before going all the way around because the magnetic field stops at the cube's edges.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A moving charged particle q travelling along the positive x-axis enters a uniform magnetic field B.
When will the force acting on q be maximum?
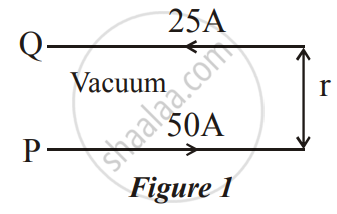
A long horizontal wire P carries a current of 50A. It is rigidly fixed. Another wire Q is placed directly above and parallel to P, as shown in Figure 1 below. The weight per unit length of the wire Q is 0.025 Nm-1 and it carries a current of 25A. Find the distance 'r' of the wire Q from the wire P so that the wire Q remains at rest
An electron moving horizontally with a velocity of 4 ✕ 104 m/s enters a region of uniform magnetic field of 10−5 T acting vertically upward as shown in the figure. Draw its trajectory and find out the time it takes to come out of the region of magnetic
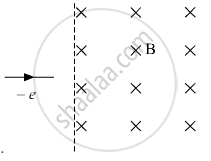
field.
A straight wire of mass 200 g and length 1.5 m carries a current of 2 A. It is suspended in mid air by a uniform magnetic field B. What is the magnitude of the magnetic field?
A charged particle moves in a uniform magnetic field. The velocity of the particle at some instant makes an acute angle with the magnetic field. The path of the particle will be
A charged particle moves along a circle under the action of possible constant electric and magnetic fields. Which of the following is possible?
(a) E = 0, B = 0
(b) E = 0, B ≠ 0
(c) E ≠ 0, B = 0
(d) E ≠ 0, B ≠ 0
If a charged particle moves unaccelerated in a region containing electric and magnetic fields
(a) `vecE "must be perpendicular" to vecB`
(b) `vecv "must be perpendicular" to vecE`
(c) must be perpendicular to v_B
Two ions have equal masses but one is singly-ionised and the other is doubly-ionised. They are projected from the same place in a uniform magnetic field with the same velocity perpendicular to the field.
(a) Both ions will move along circles of equal radii.
(b) The circle described by the singly-ionised charge will have a radius that is double that of the other circle.
(c) The two circles do not touch each other.
(d) The two circles touch each other.
A 10 g bullet with a charge of 4.00 μC is fired at a speed of 270 m s−1 in a horizontal direction. A vertical magnetic field of 500 µT exists in the space. Find the deflection of the bullet due to the magnetic field as it travels through 100 m. Make appropriate approximations.
A metal wire PQ of mass 10 g lies at rest on two horizontal metal rails separated by 4.90 cm (figure). A vertically-downward magnetic field of magnitude 0.800 T exists in the space. The resistance of the circuit is slowly decreased and it is found that when the resistance goes below 20.0 Ω, the wire PQ starts sliding on the rails. Find the coefficient of friction.
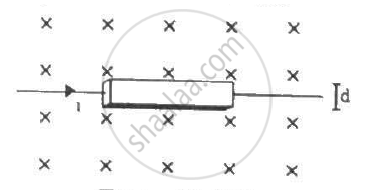
A current i is passed through a silver strip of width d and area of cross-section A. The number of free electrons per unit volume is n. (a) Find the drift velocity v of the electrons. (b) If a magnetic field B exists in the region, as shown in the figure, what is the average magnetic force on the free electrons? (c) Due to the magnetic force, the free electrons get accumulated on one side of the conductor along its length. This produces a transverse electric field in the conductor, which opposes the magnetic force on the electrons. Find the magnitude of the electric field which will stop further accumulation of electrons. (d) What will be the potential difference developed across the width of the conductor due to the electron-accumulation? The appearance of a transverse emf, when a current-carrying wire is placed in a magnetic field, is called Hall effect.
A proton describes a circle of radius 1 cm in a magnetic field of strength 0.10 T. What would be the radius of the circle described by an α-particle moving with the same speed in the same magnetic field?
A circular coil of radius 2.0 cm has 500 turns and carries a current of 1.0 A. Its axis makes an angle of 30° with the uniform magnetic field of magnitude 0.40 T that exists in the space. Find the torque acting on the coil.
A particle of mass m and positive charge q, moving with a uniform velocity v, enters a magnetic field B, as shown in the figure. (a) Find the radius of the circular arc it describes in the magnetic field. (b) Find the angle subtended by the arc at the centre. (c) How long does the particle stay inside the magnetic field? (d) Solve the three parts of the above problem if the charge q on the particle is negative.
The figure shows a convex lens of focal length 12 cm lying in a uniform magnetic field Bof magnitude 1.2 T parallel to its principal axis. A particle with charge 2.0 × 10−3 C and mass 2.0 × 10−5 kg is projected perpendicular to the plane of the diagram with a speed of 4.8 m s−1. The particle moves along a circle with its centre on the principal axis at a distance of 18 cm from the lens. Show that the image of the particle moves along a circle and find the radius of that circle.

A particle with a charge of 5.0 µC and a mass of 5.0 × 10−12 kg is projected with a speed of 1.0 km s−1 in a magnetic field of magnitude 5.0 mT. The angle between the magnetic field and the velocity is sin−1 (0.90). Show that the path of the particle will be a helix. Find the diameter of the helix and its pitch.
