Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Show that the kinetic energy of the particle moving in a magnetic field remains constant.
उत्तर
When a charged particle having charge q moves inside a magnetic field `vecB` with velocity v, it experiences a force `vecF =q(vecV ×vecB)`.
From the formula of the force we can see that, `vecF`is always perpendicular to both `vecV` and `vecB`, thus in this case work done by the force is always zero. From, the work energy theorem we know that the change in the kinetic energy of the body is equal to the work done.
Change in kinetic energy = 0
⇒Kinetic energy = A constant
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Write the expression for the force,`vecF` acting on a charged particle of charge ‘q’, moving with a velocity `vecV` in the presence of both electric field `vecF`and magnetic field `vecB` . Obtain the condition under which the particle moves undeflected through the fields.
A charged particle is whirled in a horizontal circle on a frictionless table by attaching it to a string fixed at one point. If a magnetic field is switched on in the vertical direction, the tension in the string
A charged particle moves along a circle under the action of possible constant electric and magnetic fields. Which of the following is possible?
(a) E = 0, B = 0
(b) E = 0, B ≠ 0
(c) E ≠ 0, B = 0
(d) E ≠ 0, B ≠ 0
A particle is projected in a plane perpendicular to a uniform magnetic field. The area bounded by the path described by the particle is proportional to
A magnetic field of strength 1.0 T is produced by a strong electromagnet in a cylindrical region of radius 4.0 cm, as shown in the figure. A wire, carrying a current of 2.0 A, is placed perpendicular to and intersecting the axis of the cylindrical region. Find the magnitude of the force acting on the wire.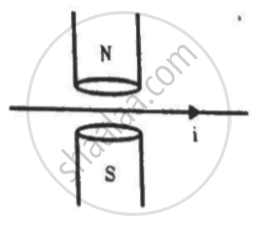
A charged particle is accelerated through a potential difference of 12 kV and acquires a speed of 1.0 × 106 m s−1. It is then injected perpendicularly into a magnetic field of strength 0.2 T. Find the radius of the circle described by it.
A proton is projected with a velocity of 3 × 106 m s−1 perpendicular to a uniform magnetic field of 0.6 T. Find the acceleration of the proton.
The figure shows a convex lens of focal length 12 cm lying in a uniform magnetic field Bof magnitude 1.2 T parallel to its principal axis. A particle with charge 2.0 × 10−3 C and mass 2.0 × 10−5 kg is projected perpendicular to the plane of the diagram with a speed of 4.8 m s−1. The particle moves along a circle with its centre on the principal axis at a distance of 18 cm from the lens. Show that the image of the particle moves along a circle and find the radius of that circle.

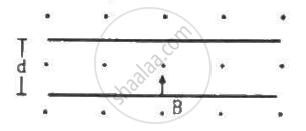
An electron is emitted with negligible speed from the negative plate of a parallel-plate capacitor charged to a potential difference V. The separation between the plates is dand a magnetic field B exists in the space, as shown in the figure. Show that the electron will fail to strike the upper plates if `d > ((2m_eV)/(eB_0^2))^(1/2)`
Current flows through uniform, square frames as shown in the figure. In which case is the magnetic field at the centre of the frame not zero?
