Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Observe the segment of mRNA given below.

(a) Explain and illustrate the steps involved to make fully processed hnRNA?
(b) Gene encoding RNA Polymerase I and III have been affected by mutation in a cell. Explain its impact on the synthesis of a polypeptide, stating the reasons.
उत्तर
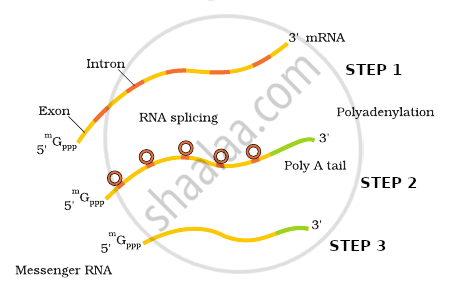
(a) The hnRNA undergoes processes called capping and tailing followed by splicing. In capping, an unusual nucleotide is added to the 5'-end of hnRNA methyl guanosine triphosphate. In tailing, adenylate residues (about 200 - 300) are added at the 3'-end in a template-independent manner. Now the hnRNA undergoes a process where the introns are removed and exons are joined to form mRNA called splicing.
(b) The process of translation will not happen, thus the polypeptide synthesis is stopped/hampered.
The reason for the above is:
RNA polymerase I transcribe rRNAs which is the cellular factory for protein synthesis.
RNA polymerase III helps in the transcription of tRNA which is the adaptor molecule that transfers amino acids to the site of protein synthesis.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
On the ribosome, mRNA binds ______ and two sites in the ______ for subsequent amino acids to bind to be close enough to each other for the formation of a peptide bond.
A special feature of viruses is that they:
The most likely method, used to determine the structural details of the cell organelle is ______.
Sigma factor is a component of ______.
Which enzymes are responsible for the synthesis of tRNA?
A ribozyme is an:
The exon part of mRNA has code for ______
Refer the given diagram. What does it represent?

Which is the “Only enzyme” that has “Capability” to catalyse Initiation, Elongation and Termination in the process of transcription in prokaryotes?
What are the functions of methylated guanasine cap?
