Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Observe the segment of mRNA given below.

(a) Explain and illustrate the steps involved to make fully processed hnRNA?
(b) Gene encoding RNA Polymerase I and III have been affected by mutation in a cell. Explain its impact on the synthesis of a polypeptide, stating the reasons.
उत्तर
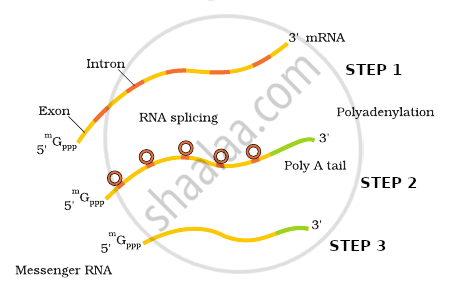
(a) The hnRNA undergoes processes called capping and tailing followed by splicing. In capping, an unusual nucleotide is added to the 5'-end of hnRNA methyl guanosine triphosphate. In tailing, adenylate residues (about 200 - 300) are added at the 3'-end in a template-independent manner. Now the hnRNA undergoes a process where the introns are removed and exons are joined to form mRNA called splicing.
(b) The process of translation will not happen, thus the polypeptide synthesis is stopped/hampered.
The reason for the above is:
RNA polymerase I transcribe rRNAs which is the cellular factory for protein synthesis.
RNA polymerase III helps in the transcription of tRNA which is the adaptor molecule that transfers amino acids to the site of protein synthesis.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Explain the process of transcription in Eukaryotes.
If the base sequence of a codon in mRNA is 5'-AUG-3', the sequence of tRNA pairing with it must be ______.
In eukaryotes, the process of processing of primary transcript involves ______.
Ribozyme is a/an:
Which of the following pair lack the unit membrane?
Which enzymes are responsible for the synthesis of tRNA?
Refer the given diagram. What does it represent?

What is the role of RNA polymerase III in the process of transcription in eukaryotes?
Which is the “Only enzyme” that has “Capability” to catalyse Initiation, Elongation and Termination in the process of transcription in prokaryotes?
Identify the correct statement.
