Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A man uses a crowbar of length 1.5 m to raise a load of 75 kgf by putting a sharp edge below the bar at a distance 1 m from his hand.
- Draw a diagram of the arrangement showing the fulcrum (F), load (L) and effort (E) with their directions.
- State the kind of lever.
- Calculate:
- load arm,
- effort arm,
- mechanical advantage and
- the effort needed.
उत्तर
(a)
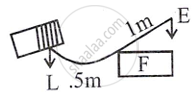
75 kgf. crow bar
Effort = ?
M.A. = `"L"/"E"`
2 = `("75 kgf")/"E"`
E = `75/2`
E = 37.5 kgf
(b) Class I lever
(c)
- Load arm 1.5 – 1.0 = 0.5 m
- Effort arm = 1 m
- Mechanical advantage = `1.0/0.5 = 2`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The lever for which the mechanical advantage is less than 1 has :
Give three examples for leavers of second order.
The following belong to which class of lever?
Pliers Tools
The following belong to which class of lever?
Rowing of a boat
The following belong to which class of lever?
Sugar tongs
The following belong to which class of lever?
A pair of scissors
Shears, used for cutting metals and scissors used for cutting clothes are both examples of levers of the first order. However, whereas the shears always have short blades and long handles, the scissors often have blades much longer than the handles. Explain, why this is so?
The length of a nut-cracker is 12 cm. A nut, when kept at a distance of 4 cm from its fulcrum, requires an effort of 100 gf to crack it. What force will be required to crack the nut without using the nut-cracker?
What is a first-order lever?
A lever is used to multiply the force.
