Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The lever for which the mechanical advantage is less than 1 has :
विकल्प
Fulcrum at mid-point between load and effort.
Load between effort and fulcrum.
Effort between fulcrum and load.
Load and effort acting at the same point.
उत्तर
Effort between fulcrum and load.
Reason:
Levers, for which the mechanical advantage is less than 1, always have the effort arm shorter than the load arm.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The diagram below shows a lever in use:
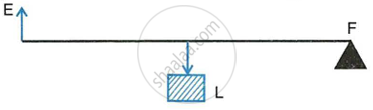
- To which class of levers does it belong?
- Without changing the dimensions of the lever, if the load is shifted towards the fulcrum what happens to the mechanical advantage of the lever?
What is a lever?
shows a nut cracker name the class of lever ?
A man uses a crowbar of length 1.5 m to raise a load of 75 kgf by putting a sharp edge below the bar at a distance 1 m from his hand.
- Draw a diagram of the arrangement showing the fulcrum (F), load (L) and effort (E) with their directions.
- State the kind of lever.
- Calculate:
- load arm,
- effort arm,
- mechanical advantage and
- the effort needed.
The following belong to which class of lever?
Sugar tongs
In the following diagram of a wheelbarrow, mark the fulcrum (F) and indicate the directions of load (L) and effort (E) with arrows.
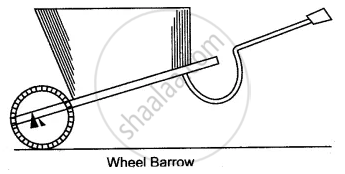
What class of lever is it? Give one more example of the same class of lever.
The diagram below shows a lever in use.
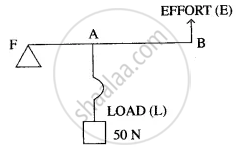
(i) To which class of lever does it belong?
(ii) If FA = 40 cm, AB = 60 cm, then find the mechanical advantage of the lever.
The diagram shows the use of a lever.
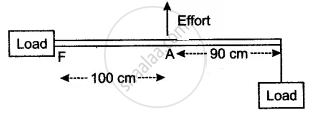
- State the principle of moments as applied to the above lever.
- Which class of lever is this? Give an example of this class of lever.
- If FA = 100 cm, AB = 90 cm, calculate the minimum effort required to lift the load.
A crowbar of length 100 cm is used to lift a load of 5 kgf. It has its fulcrum at a distance of 20 cm from the load. Calculate:
(i) the mechanical advantage of a crowbar and,
(ii) the effort applied at the other end.
What is a first-order lever?
