Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The diagram shows the use of a lever.
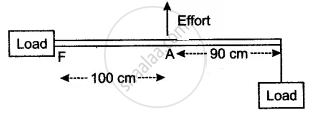
- State the principle of moments as applied to the above lever.
- Which class of lever is this? Give an example of this class of lever.
- If FA = 100 cm, AB = 90 cm, calculate the minimum effort required to lift the load.
उत्तर
(i) Sum of the clockwise moments about the fulcrum is equal to the sum of the anti-clockwise moments about the fulcrum.
(ii) Lever of class III,
Example: forceps or a pair of tongs.
(iii) E × 100 = 190 × 20
∴ E = 38 N.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A 4 m long rod of negligible weight is to be balanced about a point 125 cm from one end and a load of 18 kgf is suspended at a point 60 cm from the support on the shorter arm.
- If a weight W is placed at a distance of 250 cm from the support on the longer arm to balance the rod, find W.
- If a weight 5 kgf is kept to balance the rod, find its position.
- To which class of lever does it belong?
Fig 3.17 below shows a lever in use.

(a) To which class of lever does it belong?
(b) If FA = 80 cm, AB = 20 cm, find its mechanical advantage.
(c) Calculate the value of E.
Give three examples for leavers of 1st order.
The following belong to which class of lever?
A see-saw
The following belong to which class of lever?
A claw-hammer
The following belong to which class of lever?
A fire tongs
Draw a labelled sketch of a second class lever. Give one example of such a lever.
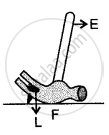
In the diagram shown alongside a claw hammer, mark the fulcrum (F) and indicate the directions of load (L) and effort (E) with arrows. What class of lever is it? Give one more example of this class of lever.
In the following diagram of a wheelbarrow, mark the fulcrum (F) and indicate the directions of load (L) and effort (E) with arrows.
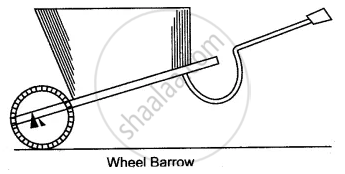
What class of lever is it? Give one more example of the same class of lever.
What is a first-order lever?
