Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
The diagram shows the use of a lever.
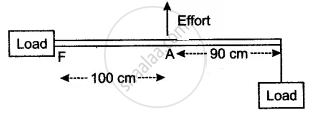
- State the principle of moments as applied to the above lever.
- Which class of lever is this? Give an example of this class of lever.
- If FA = 100 cm, AB = 90 cm, calculate the minimum effort required to lift the load.
Solution
(i) Sum of the clockwise moments about the fulcrum is equal to the sum of the anti-clockwise moments about the fulcrum.
(ii) Lever of class III,
Example: forceps or a pair of tongs.
(iii) E × 100 = 190 × 20
∴ E = 38 N.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Which class of lever will always have MA > 1 and why?
State the principle of a lever?
A lever of length 9 cm has its load arm 5 cm long and the effort arm is 9 cm long.
- To which class does it belong?
- Draw a diagram of the lever showing the position of fulcrum F and directions of both the load L and effort E.
- What is the mechanical advantage and velocity ratio if the efficiency is 100%?
- What will be the mechanical advantage and velocity ratio if the efficiency becomes 50%?
Which class of lever found in the human body is being used by a boy when he holds a load on the palm of his hand.
The following belong to which class of lever?
Pliers Tools
The following belong to which class of lever?
A pair of scissors
The following belong to which class of lever?
Wheelbarrow
State the types (or kinds) of lever, and give two examples of each kind.
A crowbar of length 100 cm is used to lift a load of 5 kgf. It has its fulcrum at a distance of 20 cm from the load. Calculate:
(i) the mechanical advantage of a crowbar and,
(ii) the effort applied at the other end.
A lever is used to multiply the force.
