Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The diagram shows the use of a lever.
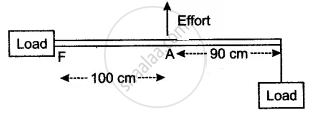
- State the principle of moments as applied to the above lever.
- Which class of lever is this? Give an example of this class of lever.
- If FA = 100 cm, AB = 90 cm, calculate the minimum effort required to lift the load.
उत्तर
(i) Sum of the clockwise moments about the fulcrum is equal to the sum of the anti-clockwise moments about the fulcrum.
(ii) Lever of class III,
Example: forceps or a pair of tongs.
(iii) E × 100 = 190 × 20
∴ E = 38 N.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
State the principle of a lever?
Write down a relation expressing the mechanical advantage of a lever.
Give one example of a class I lever where mechanical advantage is more than one ?
shows a nut cracker name the class of lever ?
Class II levers are designed to have ______.
The following belong to which class of lever?
Pliers Tools
The following belong to which class of lever?
Fore-arm
The following are an example of levers. State the class of lever to which each one belongs giving the relative positions of Load (L), Effort (E), Fulcrum (F):
(i) Scissors (ii) Sugar tongs (iii) Nutcracker (iv) Pliers.
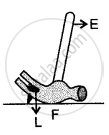
In the diagram shown alongside a claw hammer, mark the fulcrum (F) and indicate the directions of load (L) and effort (E) with arrows. What class of lever is it? Give one more example of this class of lever.
In the following diagram of a wheelbarrow, mark the fulcrum (F) and indicate the directions of load (L) and effort (E) with arrows.
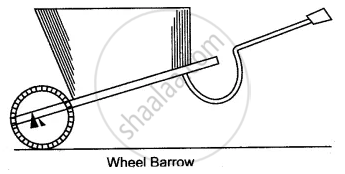
What class of lever is it? Give one more example of the same class of lever.
