Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A lever of length 9 cm has its load arm 5 cm long and the effort arm is 9 cm long.
- To which class does it belong?
- Draw a diagram of the lever showing the position of fulcrum F and directions of both the load L and effort E.
- What is the mechanical advantage and velocity ratio if the efficiency is 100%?
- What will be the mechanical advantage and velocity ratio if the efficiency becomes 50%?
Solution
- The length of the lever is the same as the effort arm. Also, an effort arm is more than a load arm. So, this is a class II lever.

-
Mechanical advantage is
M.A. = `"effort arm"/"load arm" = (9 "cm")/(5 "cm")`
= 1.8
The relationship between MA, efficiency and V.R. is
M.A. = η × V.R.
V.R. = `(M.A)/η`V.R. = `(1.8 xx 100)/100`
V.R. = 1.8
-
When efficiency becomes 50%, i.e.,
`50/100 = 1/2`
M.A. < V.R.
Then V.R. will remain same 1.8
but its M.A. will become
M.A. = V.R. × η
M.A. = `(1.8 xx 50)/100 = 0.9`
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Give one example of a class I lever where mechanical advantage is more than one ?
Draw a diagram of a lever which is always used as a force multiplier. How is the effort arm related to the load arm in such a lever?
A man uses a crowbar of length 1.5 m to raise a load of 75 kgf by putting a sharp edge below the bar at a distance 1 m from his hand.
- Draw a diagram of the arrangement showing the fulcrum (F), load (L) and effort (E) with their directions.
- State the kind of lever.
- Calculate:
- load arm,
- effort arm,
- mechanical advantage and
- the effort needed.
The following belong to which class of lever?
Pliers Tools
The following belong to which class of lever?
Fore-arm
The following are an example of levers. State the class of lever to which each one belongs giving the relative positions of Load (L), Effort (E), Fulcrum (F):
(i) Scissors (ii) Sugar tongs (iii) Nutcracker (iv) Pliers.
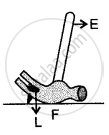
In the diagram shown alongside a claw hammer, mark the fulcrum (F) and indicate the directions of load (L) and effort (E) with arrows. What class of lever is it? Give one more example of this class of lever.
The diagram below shows a lever in use.
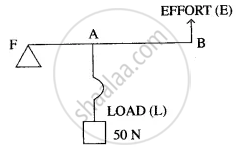
(i) To which class of lever does it belong?
(ii) If FA = 40 cm, AB = 60 cm, then find the mechanical advantage of the lever.
The diagram shows the use of a lever.
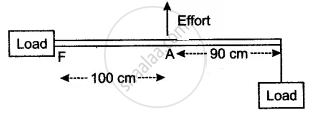
- State the principle of moments as applied to the above lever.
- Which class of lever is this? Give an example of this class of lever.
- If FA = 100 cm, AB = 90 cm, calculate the minimum effort required to lift the load.
What is a first-order lever?
