Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
In the diagram shown alongside a claw hammer, mark the fulcrum (F) and indicate the directions of load (L) and effort (E) with arrows. What class of lever is it? Give one more example of this class of lever.
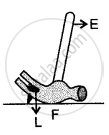
Solution
Claw-hammer is the lever of the first order. One more example of this class of lever is a see-saw. In the following diagram, F indicates the position of the fulcrum. The arrows labelled L and E respectively indicate the directions of load and effort.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Draw a diagram of a lever which is always used as a force multiplier. How is the effort arm related to the load arm in such a lever?
The lever for which the mechanical advantage is less than 1 has :
A man uses a crowbar of length 1.5 m to raise a load of 75 kgf by putting a sharp edge below the bar at a distance 1 m from his hand.
- Draw a diagram of the arrangement showing the fulcrum (F), load (L) and effort (E) with their directions.
- State the kind of lever.
- Calculate:
- load arm,
- effort arm,
- mechanical advantage and
- the effort needed.
Which class of lever found in the human body is being used by a boy when he raises the weight of his body on his toes?
The following belong to which class of lever?
A pair of scissors
The following belong to which class of lever?
Wheelbarrow
The following belong to which class of lever?
Fore-arm
Shears, used for cutting metals and scissors used for cutting clothes are both examples of levers of the first order. However, whereas the shears always have short blades and long handles, the scissors often have blades much longer than the handles. Explain, why this is so?
The diagram shows the use of a lever.
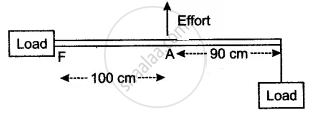
- State the principle of moments as applied to the above lever.
- Which class of lever is this? Give an example of this class of lever.
- If FA = 100 cm, AB = 90 cm, calculate the minimum effort required to lift the load.
The length of a nut-cracker is 12 cm. A nut, when kept at a distance of 4 cm from its fulcrum, requires an effort of 100 gf to crack it. What force will be required to crack the nut without using the nut-cracker?
