Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
The length of a nut-cracker is 12 cm. A nut, when kept at a distance of 4 cm from its fulcrum, requires an effort of 100 gf to crack it. What force will be required to crack the nut without using the nut-cracker?
Solution
Given : Effort arm = 12 cm, Load arm = 4 cm, Effort E = 100 gf, Load L = ?
(Nut-cracker is the lever of second order)
Since, `"Load"/"Effort"=("Effort arm")/("Load arm")`
∴ `"L"/100=12/4`
or L = 300 gf.
Thus, a force of 300 gf is required to crack the nut without using the nut-cracker.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Name a machine to obtain gain in speed ?
Draw a diagram of a lever which is always used as a force multiplier. How is the effort arm related to the load arm in such a lever?
A lever of length 9 cm has its load arm 5 cm long and the effort arm is 9 cm long.
- To which class does it belong?
- Draw a diagram of the lever showing the position of fulcrum F and directions of both the load L and effort E.
- What is the mechanical advantage and velocity ratio if the efficiency is 100%?
- What will be the mechanical advantage and velocity ratio if the efficiency becomes 50%?
Give three examples for leavers of 1st order.
The following belong to which class of lever?
A see-saw
The following belong to which class of lever?
Pliers Tools
The following belong to which class of lever?
Wheelbarrow
When we want to use a machine as a force multiplier, which class of lever should we preferably use? Give a simple diagram of such a lever.
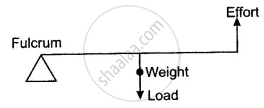
What is a lever?
The diagram shows the use of a lever.
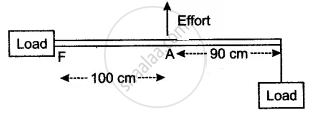
- State the principle of moments as applied to the above lever.
- Which class of lever is this? Give an example of this class of lever.
- If FA = 100 cm, AB = 90 cm, calculate the minimum effort required to lift the load.
