Advertisements
Online Mock Tests
Chapters
▶ 2: Simple Machines
3: Refraction of Light
4: Refraction through Lenses and Optical Instruments
5: Spectrum
6: Echoes and Vibrations of Sound
7: Electricity
8: Electric Power and House hold Circuits
9: Magnetic Effect of Current
10: Specific Heat Capacity and Latent Heat
11: Thermionic Emission and Radioactivity
![ICSE solutions for Physics [English] Class 10 chapter 2 - Simple Machines ICSE solutions for Physics [English] Class 10 chapter 2 - Simple Machines - Shaalaa.com](/images/physics-english-class-10_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 2: Simple Machines
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 2 of CISCE ICSE for Physics [English] Class 10.
ICSE solutions for Physics [English] Class 10 2 Simple Machines Short Answers
What is a machine?
State the principle of an ideal machine.
Give an example where a machine is used to obtain gain in speed.
What is the efficiency of an ideal machine?
Write an expression to show the relationship between mechanical advantage, velocity ratio, and efficiency for a simple machine.
Name a machine which can be used to multiply force and change the direction of force applied.
Define mechanical advantage (M.A.) of the machine.
Define Velocity Ratio
Comment on the statement ‘The mechanical advantage of a machine is greater than 1’. Give an example of a lever mechanical advantage is:
(i) greater than 1.
(ii) Equal to 1.
There is no gain in mechanical advantage in the case of a single fixed pulley. Explain, why the pulley is then used?
In the case of a block and tackle arrangement, the mechanical advantage increases with the number of pulleys. Explain.
Write an expression for the mechanical advantage of an inclined plane.
Write down a relation expressing the mechanical advantage of a lever.
What is the relationship between the mechanical advantage and the velocity ratio for:
(i) An ideal machine,
(ii) A practical machine.
State the principle of a lever?
Write down a relation expressing the mechanical advantage of a lever.
Which type of levers have mechanical advantage always more than 1? Give reasons.
Give three examples for leavers of 1st order.
Give three examples for leavers of second order.
Give three examples for leavers of the third order.
Which class of lever found in the human body is being used by a boy when he holds a load on the palm of his hand.
Which class of lever found in the human body is being used by a boy when he raises the weight of his body on his toes?
Which type of lever has a mechanical advantage always more than one? Give one example. What change can be made in this lever to increase its mechanical advantage?
State the class of levers and the relative positions of load (L) effort (E) and fulcrum (F) in a bottle opener?
State the class of levers and the relative positions of load (L), effort (E) and fulcrum (F) in sugar tongs.
What is a fixed pulley?
State two reasons, why the efficiency of a pulley system is not 100 percent?
A type of single pulley is very often used as a machine even though it does not give any gain in mechanical advantage. Name the type of pulley used.
A type of single pulley is very often used as a machine even though it does not give any gain in mechanical advantage. For what purpose is such a pulley used?
Give two reasons why the efficiency of a single movable pulley system is not 100%.
The following belong to which class of lever?
The Physical balance
The following belong to which class of lever?
A see-saw
The following belong to which class of lever?
An oar of a boat
The following belong to which class of lever?
Human-arm
The following belong to which class of lever?
Pliers Tools
The following belong to which class of lever?
A claw-hammer
The following belong to which class of lever?
Rowing of a boat
The following belong to which class of lever?
A fire tongs
The following belong to which class of lever?
Sugar tongs
The following belong to which class of lever?
A pair of scissors
The following belong to which class of lever?
Wheelbarrow
The following belong to which class of lever?
Nutcracker
Shows a lemon crusher. Name the class of lever.
The following belong to which class of lever?
Knife
The following belong to which class of lever?
Fore-arm
ICSE solutions for Physics [English] Class 10 2 Simple Machines Long Answers
How does a machine work?
Give an example of the following use of a machine to change the point of application of the force.
Give an example of the following use of a machine to obtain gain in force.
Give an example of the following use of a machine to change the direction of force.
State four ways in which machines are useful to us.
What is the efficiency of a machine?
Establish a relationship between efficiency, M.A., and V.R.
What is the relation between the mechanical advantage and the number of strands of string used to support the load, in a ‘block and tackle’ set-up?
Shears, used for cutting metals and scissors used for cutting clothes are both examples of levers of the first order. However, whereas the shears always have short blades and long handles, the scissors often have blades much longer than the handles. Explain, why this is so?
The following are an example of levers. State the class of lever to which each one belongs giving the relative positions of Load (L), Effort (E), Fulcrum (F):
(i) Scissors (ii) Sugar tongs (iii) Nutcracker (iv) Pliers.
What is a block and tackle system of pulleys? What precautions would you observe while rounding the string so that the effort is applied in the downward direction?
ICSE solutions for Physics [English] Class 10 2 Simple Machines Figure Based Short Answers
A crowbar of length 120 cm has its fulcrum situated at a distance of 20 cm from the load. Calculate the mechanical advantage of the crowbar.
In the alongside the figure of two pulleys shown a system in which one pulley is fixed and the other is movable. What is the velocity ratio of the system?
An effort of 600 N is needed to lift a weight of 1000 N. What are the mechanical advantage and efficiency of the pulley system?
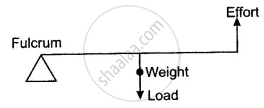
Draw a labelled sketch of a second class lever. Give one example of such a lever.
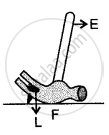
In the diagram shown alongside a claw hammer, mark the fulcrum (F) and indicate the directions of load (L) and effort (E) with arrows. What class of lever is it? Give one more example of this class of lever.
In the following diagram of a wheelbarrow, mark the fulcrum (F) and indicate the directions of load (L) and effort (E) with arrows.
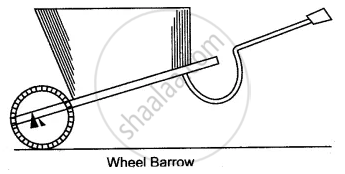
What class of lever is it? Give one more example of the same class of lever.
When we want to use a machine as a force multiplier, which class of lever should we preferably use? Give a simple diagram of such a lever.
The diagram below shows a lever in use.
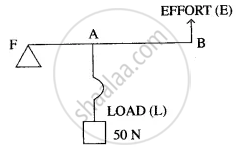
(i) To which class of lever does it belong?
(ii) If FA = 40 cm, AB = 60 cm, then find the mechanical advantage of the lever.
What is a pulley?
Name the type of single pulley that can act as a force multiplier. Draw a labeled diagram of the pulley mentioned by you.
Draw a diagram to show how a single pulley can be used so as to have its ideal M.A= 2.
ICSE solutions for Physics [English] Class 10 2 Simple Machines Figure Based Long Answers
(i) Calculate the mechanical advantage of the lever shown in the figure.
(ii) How do you define the mechanical advantage of a machine?

A uniform metre scale is kept in equilibrium when supported at the 60 cm mark and a mass M is suspended from the 90 cm mark as shown in the figure. State with reasons, whether the weight of the scale is greater than, less than or equal to the weight of mass M.

What is a lever?
The diagram shows the use of a lever.
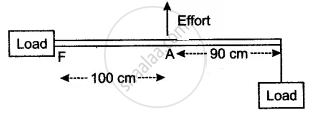
- State the principle of moments as applied to the above lever.
- Which class of lever is this? Give an example of this class of lever.
- If FA = 100 cm, AB = 90 cm, calculate the minimum effort required to lift the load.
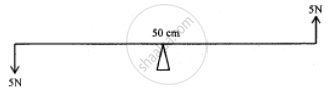
Two forces each of 5N act vertically upwards and downwards respectively on the two ends of a uniform metre rule which is placed at its mid-point as shown in the diagram. Determine the magnitude of the resultant moment of these forces about the midpoint.
State the types (or kinds) of lever, and give two examples of each kind.
Draw the diagram of a single movable pulley and obtain its mechanical advantage, velocity ratio, and efficiency.
Draw a diagram of a single fixed pulley and obtain expressions for its:
(i) Mechanical advantage,
(ii) Velocity ratio, and
(iii) Efficiency, in the ideal case.
The pulley system shown in the figure is to be used to lift a load W. If the man applying the effort cannot apply a force exceeding 1000 N, what is the maximum load that can be lifted?
The actual load that the man is finally able to lift turns out to be 2700 N. What are the values of the actual M.A., obtained, and the efficiency of the actual set-up?
The alongside figure shows the combination of a movable pulley P1 with a fixed pulley P2 used for lifting up a load W.

(i) State the function of the fixed pulley P2.
(ii) If the free end of the string moves through a distance x, find the distance by which the load W is raised.
(iii) Calculate the force to be applied at C to just raise the load W = 20 kgf, neglecting the weight of the pulley P1 and friction.
Draw a diagram showing a block and tackle system of 4 pulleys.

(i) State, how many strands of tackle support the load?
(ii) Draw arrows to represent tension in each strand.
(iii) Find the mechanical advantage of the system, stating the assumptions made.
(iv) If the load is pulled up by a distance 1m, how much does the effort end move?
A block and tackle system of pulleys has a velocity ratio of 4.
- Draw a labelled diagram of the system indicating clearly the points of application and directions of load and effort.
- What is the value of the mechanical advantage of the given pulley system if it is an ideal pulley system?
Diagram given below shows an arrangement of four pulleys. A load L is attached to the movable lower block and effort E is applied at the free end of the string.
Copy the diagram; and
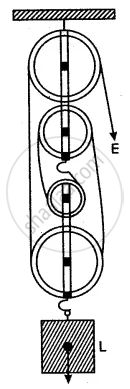
(i) Draw arrows to indicate tension in each part of the string; and
(ii) Calculate the mechanical advantage of the system.
ICSE solutions for Physics [English] Class 10 2 Simple Machines Short Numerical
The length of a nut-cracker is 12 cm. A nut, when kept at a distance of 4 cm from its fulcrum, requires an effort of 100 gf to crack it. What force will be required to crack the nut without using the nut-cracker?
A crowbar of length 100 cm is used to lift a load of 5 kgf. It has its fulcrum at a distance of 20 cm from the load. Calculate:
(i) the mechanical advantage of a crowbar and,
(ii) the effort applied at the other end.
In a single movable pulley system, a load of 125 kgf is lifted by an effort of 75 kgf. Find the percentage efficiency of system.
A woman draws water from a well using a fixed pulley. The mass of the bucket and water together is 60 kg. The force applied by the woman is 70 N. Calculate the mechanical advantage. [Take g = 10 m/s2].
A man raises a load of 360 kgf using a block and tackle system of 3 pulleys. If the efficiency of the pulley system is 60%, what effort is applied by the man?
ICSE solutions for Physics [English] Class 10 2 Simple Machines Long Numerical
A machine is driven by a 50 kg mass falling at a rate of 10.0 m in 5s. It lifts n load of 250 kgf. Taking the force of gravity on 1 kg mass as 10 N. Calculate the power input to the machine. If the efficiency of the machine is 60%, find the height to which the load is raised in 5s.
The mechanical advantage of a machine is 5 and its efficiency is 80%. It is used to lift a load of 200 kgf to a height of 20 m. Calculate:
(i) The effort required, and
(ii) The work done on the machine (g = 10 ms−2).
The mechanical advantage of a machine is 5 and its efficiency is 80%. It is used to lift a load of 200 kgf to a height of 20 m. Calculate:
(i) The effort required, and
(ii) The work done on the machine (g = 10 ms−2).
A cook used a ‘fire tong pair’ of length 32 cm. to lift a piece of burning coal of mass 500 g. If he applies his effort at a distance of 8 cm from the fulcrum, what is his effort? Assume friction etc. to be absent. Also, obtain values of the M.A. and the V.R. of this ‘machine’.
If the weight of the movable pulley is W, obtain the expression for MA, VR, and efficiency.
A simple machine enables us to lift a load of 10,000 N by the application of an effort of 500 N. However, when the point of application of the effort moves through 2.5 m, the load gets raised through 10 cm only. What are the values of the:
(i) M.A.
(ii) V.R. and
(iii) Efficiency of the machine?
A pulley system has a velocity ratio of 4 and an efficiency of 90%. Calculate:
(i) the mechanical advantage of the system.
(ii) the effort required to raise a load of 300 N by the system.
A ‘block and tackle’ system used 3 pulleys in the lower block and 4 pulleys in the upper block. What is the ‘velocity ratio’ of this system? If the load is to be lifted by a person capable of applying a maximum effort of 1000 N, what is the maximum load than can be lifted under ideal conditions?
The actual maximum load that gets lifted turns out to be 6300 N. What are the values of the actual M.A. and efficiency of the set-up?
A boy lifts a load of 40 kgf through a vertical height of 2m in 5s by using a single fixed pulley when he applies an effort of 48 kgf. Calculate:
(i) the mechanical advantage, and
(ii) the efficiency of the pulley. Why is the efficiency of the pulley is not 100%?
(iii) the energy gained by the load in 5s, and
(iv) the power developed by the boy in raising the load.
Solutions for 2: Simple Machines
![ICSE solutions for Physics [English] Class 10 chapter 2 - Simple Machines ICSE solutions for Physics [English] Class 10 chapter 2 - Simple Machines - Shaalaa.com](/images/physics-english-class-10_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
ICSE solutions for Physics [English] Class 10 chapter 2 - Simple Machines
Shaalaa.com has the CISCE Mathematics Physics [English] Class 10 CISCE solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. ICSE solutions for Mathematics Physics [English] Class 10 CISCE 2 (Simple Machines) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. ICSE textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Physics [English] Class 10 chapter 2 Simple Machines are Machines, Simple Machines, Machines (Numerical), A Lever, A Pulley, Principle of Machine, Relationship between efficiency (ղ), mechanical advantage (M.A.) and velocity ratio (VR), Types of Levers, Single Fixed Pulley, Technical Terms Related to a Machine, Single Movable Pulley, Combination of Pulleys, Examples of Each Class of Levers as Found in the Human Body.
Using ICSE Physics [English] Class 10 solutions Simple Machines exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in ICSE Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum CISCE Physics [English] Class 10 students prefer ICSE Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 2, Simple Machines Physics [English] Class 10 additional questions for Mathematics Physics [English] Class 10 CISCE, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
