Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Draw a diagram of a single fixed pulley and obtain expressions for its:
(i) Mechanical advantage,
(ii) Velocity ratio, and
(iii) Efficiency, in the ideal case.
Solution
The diagram of a single fixed pulley is shown alongside. If T is the tension in each strand of the string and in the ideal case string is massless and there is no friction in the pulley bearings, then in equilibrium, E = T and L = T

(i) Mechanical advantage = `"L"/"E"="T"/"T"=1`
(ii) If the effort E moves a distance d downwards, the load L moves the same distance d upwards.
So, velocity ratio = `"d"_"E"/"d"_"L"="d"/"d"=1`
(iii) Efficiency =`"M.A."/"V.R."=1/1` = 1 (or 100%).
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Differentiate between a single fixed pulley and a single movable pulley.
Explain how a gear system can be used to obtain gain in torque? Given one example.
Define the following term in reference to a gear system for Gear ratio ?
Name the type of single pulley that can act as a force multiplier. Draw a labelled diagram of the pulley mentioned by you.
A block and tackle pulley system has a velocity ratio 5. Draw a labelled diagram of this system. In your diagram, indicate clearly the points of application and the directions of the load and effort.
Give reason for the following:
In a single fixed pulley, the velocity ratio is always more than the mechanical advantage.
What is a block and tackle system of pulleys? What precautions would you observe while rounding the string so that the effort is applied in the downward direction?
What is a pulley?
Diagram given below shows an arrangement of four pulleys. A load L is attached to the movable lower block and effort E is applied at the free end of the string.
Copy the diagram; and
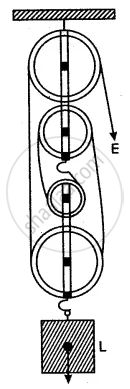
(i) Draw arrows to indicate tension in each part of the string; and
(ii) Calculate the mechanical advantage of the system.
Name the type of single pulley that has an ideal mechanical advantage equal to 2. Draw a labelled diagram of the pulley mentioned by you.
