Advertisements
Online Mock Tests
Chapters
2: Simple Machines
3: Refraction of Light
4: Refraction through Lenses and Optical Instruments
5: Spectrum
6: Echoes and Vibrations of Sound
7: Electricity
8: Electric Power and House hold Circuits
9: Magnetic Effect of Current
10: Specific Heat Capacity and Latent Heat
▶ 11: Thermionic Emission and Radioactivity
![ICSE solutions for Physics [English] Class 10 chapter 11 - Thermionic Emission and Radioactivity ICSE solutions for Physics [English] Class 10 chapter 11 - Thermionic Emission and Radioactivity - Shaalaa.com](/images/physics-english-class-10_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 11: Thermionic Emission and Radioactivity
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 11 of CISCE ICSE for Physics [English] Class 10.
ICSE solutions for Physics [English] Class 10 11 Thermionic Emission and Radioactivity Short Answers
Define bound electrons.
Define free electrons.
Define atomic number of an element.
Define mass number of an element.
Give one example of isotopes.
Give one example of isobars.
What do you mean by electron emission?
What are the types of emission?
What is thermionic emission?
State three factors on which the rate of emission of electrons from a metal surface depends
State two characteristics of the substance used as thermionic emitter.
What do you understand by the term nucleus?
What do you understand by the term nucleons?
State two properties that a substance should possess when used as a thermionic emitter.
How is a cathode ray beam affected while passing through a magnetic field?
How is a cathode ray beam affected while passing through an electric field?
What are cathode rays? Why are they called ‘cathode rays’? Name a material which exhibits fluorescence when cathode rays fall on it.
How is a zinc sulphide screen affected when a cathode ray beam strikes it?
State any two uses of cathode rays.
Why are materials of low work function preferred as thermionic cathode materials?
In a cathode ray tube state the purpose of covering cathode by thorium and carbon.
In a cathode ray tube state the purpose of the fluorescent screen.
In a cathode ray tube state. How is it possible to increase the rate of emission of electrons.
Name the three main parts of a Cathode Ray Tube.
How is a cathode ray tube used to convert an electrical signal into a visual signal?
Name a common device where a hot cathode ray tube is used.
What do you understand by the term radioactivity?
What are ‘Becquerel rays’?
What is meant by Radioactivity?
What is meant by radioactivity?
Name two radioactive substances.
Name the Different Radiations Which Are Emitted by the Radioactive Substances.
Are all the radiations mentioned by you, emitted in a single radioactive decay?
Are all the radiations viz. α, β and γ emitted in a single radioactive decay?
Compare the penetrating powers of α, β and γ-radiations.
Compare the ionising powers of α, β and γ radiations.
State the kind of nuclear reaction taking place in a nucleus during the emission of a β-particle.
A certain nucleus has a mass number 20 and atomic number 9. Find the number of neutrons and protons present in it.
Justify with reason, whether the following nuclear reactions are allowed or not.
\[\ce{^A_Z X -> ^A_{Z + 1}Y + ^0_{-1}β}\]
Justify with reason, whether the following nuclear reactions are allowed or not.
\[\ce{^A_Z X -> ^A_{Z - 2}X + ^4_{2}He}\]
An electrons emitter must have how much work function and melting point.
A radioactive nucleus undergoes a series of decays according to the sequence
\[\ce{X->[β] X1->[α] X2->[α]X3}\]
If the mass number and atomic number of X3 are 172 and 69 respectively, what is the mass number and atomic number of X?
A mixture of radioactive substances gives off three types of radiation name the radiation which travels with the speed of light.
A mixture of radioactive substances gives off three types of radiation name the radiation which has the highest ionizing power.
Complete the following nuclear change:
\[\ce{^24_11 Na -> ...Mg.... + ^0_-1β}\]
Complete the following nuclear change:
\[\ce{^238_92U -> ^234_90Th}\] + ______ + energy
Complete the following nuclear change:
\[\ce{_92P^238->[-α] ...P1 ... ->[-β]...P2 ... ->[-β] ... P3 ...}\]
An imaginary radioactive element `"_92X^235` decays to form X1; X2; X3; X4; X5 and X6 nuclides, by ejecting two β-particles, followed by α-particles and again two β-particles, followed by α-particle. Represent the various nuclear changes in the form of an equation. State the mass number and atomic number of X6. List the isotopes and isobars in the above nuclear equation.
State two factors upon which the rate of emission of thermions depends.
The isotope of 92U235 decays by alpha emission to an isotope of Thorium (Th). The Thorium isotope decays by beta emission to an isotope of Protactaminum (Pa). Write down the equations to represent these two nuclear changes.
A mixture of radioactive substance gives off three types of radiation name the radiations which are charged.
A mixture of radioactive substance gives off three types of radiation name the radiation similar in nature to cathode rays.
A mixture of radioactive substance gives off three types of radiation name the radiation similar in nature to X-rays.
A mixture of radioactive substance gives off three types of radiation name the radiation which is deviated most in a magnetic field.
A mixture of radioactive substance gives off three types of radiation name the radiation which is not affected by an electric field.
A mixture of radioactive substance gives off three types of radiation name the radiation which has the maximum penetrating power.
A mixture of radioactive substance gives off three types of radiation name the radiation which has the highest ionizing power.
A mixture of radioactive substance gives off three types of radiation name the radiation which has the highest speed.
A mixture of radioactive substance gives off three types of radiation name the radiation which when becomes neutral, become the atom of rare gas.
State, giving reason, whether the following nuclear decay is allowed or not?
\[\ce{_Z^AX -> _Z^AQ + γ}\]
State, giving reason, whether the following nuclear decay are allowed or not?
\[\ce{_Z^AP -> _{Z-2}^AY + _2^4He}\]
State, giving reason, whether the following nuclear decay are allowed or not?
\[\ce{_Z^AX ->_Z^{A-1}Y + _-1^0e}\]
A nucleus `"_11Na^24` emits a beta particle to change into Magnesium (Mg).
(i) Write the symbolic equation for the process.
(ii) What are numbers 24 and 11 called?
(iii) What is the general name `"_12^24Mg` with respect to `"_11^24Na`?
The nucleus 84X202emits an alpha particle and forms the nucleus Y. Represent this change in the form of an equation.
What changes will take place in the mass number and atomic number of the nucleus Y if it emits gamma radiations?
How does the position of an element change in the periodic table when it emits out an alpha particle?
What changes occur in the nucleus of a radioactive element when it emits an alpha particle? Show by an example?
What will an alpha particle change into when it absorb one electron.
What will an alpha particle change into when it absorb two electrons.
State three properties of α-rays.
What is the effect on the atomic mass and the atomic number of a radioactive element, after the emission of an α-particle?
When an alpha particle gains two electrons it becomes neutral and becomes an atom of an element which is a rare gas. What is the name of this rare gas?
An atomic nucleus A is composed of 84 protons and 128 neutrons. It emits an α-particle and is transformed into nucleus B. Write down the composition of B.
State charge and mass of α-particle.
State charge and mass of β-particle.
How does the position of an element change in the periodic table when it emits out a beta particle?
What are α-and β-radiations?
State three common properties of beta rays and cathode rays.
The nucleus of an atom does not contain electrons. Explain how is it possible for the nucleus to emit a beta particle which is fast moving electron.
What happens to the atomic number of an element when it emits an alpha particle.
What happens to the atomic number of an element when it emit a beta particle.
A radioactive carbon nucleus 6C14 emits a β-particle to form a nitrogen nucleus. Represent the change by an equation showing the atomic and mass number of each elements.
Two radioactive nuclei are represented by xAp and yAq and when p and q are mass numbers and x, y are the atomic number. How can the products be represented, i .e., what are the new values of p, q. x and y after the emission of an α-particle and a β-particle from A and B respectively.
A nucleus of an element has the symbol 84P202, and emits an α-particle and then a β-particle. The final nucleus is bQa Find a and b.
The nucleus B emit a β-particle and is transformed into nucleus C. What is the composition of C?
Explain briefly what changes take place within the nuclei when beta particles are emitted by a radioactive substance.
Which part of the atom undergoes a change in the process of radioactive decay?
How do infrared and γ-rays differ in wavelength.
How do infrared and γ-rays differ in penetrating power.
From α, β and γ-rays, name the one which travels with the speed of light?
From α, β and γ-rays, name the one which is not affected by electric or magnetic field?
Arrange α, β, and γ rays in ascending order with respect to their
1) Penetrating power.
2) Ionising power
3) Biological effect
What changes occur in the nucleus of a radioactive element when it emits gamma radiation? Give one example, in support of your answer.
What is the value of the speed of gamma radiations in air or vacuum?
What are beta rays and gamma rays?
Which one α, β and γ has the least penetrating power?
Explain why alpha and beta particles are deflected in an electric or a magnetic field, but gamma rays are not deflected in such a field.
A radioactive substance is oxidized. What changes would you expect to take place in the nature of radioactivity? Explain your answer.
State the medical use of radioactivity.
Explain, why radium paint, consisting of zinc sulphide and a trace of radium salt, glows in the dark?
State one use of radio-isotopes.
State three safety precautions that you would take while handling the radioactive substances.
It is advised not to touch a radioactive substance by hand. Give reason.
Which of the radioactive radiations can cause severe genetical disorders and are deflected by an electric field?
Give any two important sources of background radiation.
What is mean by background radiation?
What is nuclear energy? Name the process used for producing electricity using the nuclear energy.
State one important advantage and disadvantage each of using nuclear energy for producing electricity.
State the energy conversion taking place in a solar cell.
What is meant by nuclear waste?
Suggest one effective way for the safe disposal of nuclear waste.
ICSE solutions for Physics [English] Class 10 11 Thermionic Emission and Radioactivity Long Answers
State three ways of obtaining an electron-beam.
Name the particles that constitute the cathode rays. State some properties of cathode rays.
Mention four properties of Becquerel rays.
Name the three main parts of a Cathode Ray Tube.
Mention one important function of ear main parts:
State the principle on which the functioning of a nuclear reactor is based.
What precautions must be taken for the safe disposal of nuclear waste?
How many alpha and beta particles are emitted when Uranium nucleus 9U238 decays to Lead If 82Pb206 ?
State three safety precautions that you would take while handling the radioactive substances.
What safety measures and needed in a nuclear power plant?
ICSE solutions for Physics [English] Class 10 11 Thermionic Emission and Radioactivity Figure Based Short Answers
Draw a simplified labelled diagram of a hot cathode ray tube.
The figure shows a radioactive source S placed in a thick-walled lead container. The radiations given off pass through a magnetic field acting in direction perpendicular to the plane of paper inwards as shown by X. Copy the diagram and show the path of radiations. Explain why the source is kept in a thick-walled lead container.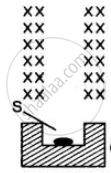
ICSE solutions for Physics [English] Class 10 11 Thermionic Emission and Radioactivity Figure Based Long Answers
Answer the question with respect to the following diagram:
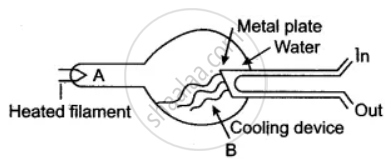
Name the charged particles emitted from the heated filament? Name the phenomenon of emission of these particles.
Answer the question with respect to the following diagram:
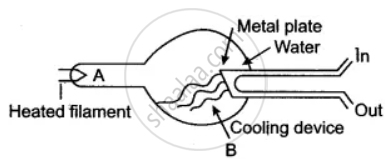
A beam of such particles, after acceleration is allowed to strike a metal plate C. Radiation B is given off. Name the radiation B.
Answer the question with respect to the following diagram:

Name the material of target C.
Answer the question with respect to the following diagram:

State two properties of radiation B different from those of visible light.
Answer the question with respect to the following diagram:
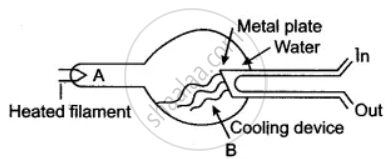
State two factors on which the wavelength of radiation B depends.
Answer the question with respect to the following diagram:

State two uses of radiation B.
Answer the question with respect to the following diagram:

Why is it necessary to cool the tube?
A certain nucleus X has a mass number 14 and atomic number 6. The nucleus X changes to `"_7Y^14` after the loss of a particle. Name the particle emitted.
A certain nucleus X has a mass number 14 and atomic number 6. The nucleus X changes to `"_7Y^14` after the loss of a particle. Represent this change in the form of an equation.
A certain nucleus X has a mass number 14 and atomic number 6. The nucleus X changes to `"_7Y^14` after the loss of a particle. A radioactive substance is oxidized. What change would you expect to take place in the nature of its radioactivity? Give a reason for your answer.
ICSE solutions for Physics [English] Class 10 11 Thermionic Emission and Radioactivity Short Numericals
An element P disintegrates by α-emission and the new element suffers two further disintegration, both by β-emission, to form an element Q. Explain that fact P and Q are isotopes.
An element X has the symbol 84X202. It emits an alpha-particle and then a beta-particle. The final nucleus is bYa. Find a and b.
Complete the following fission reaction:
\[\ce{_92U^235 _0n^1 -> _aSb^133 + _41Co^b + 4_0n_1 + energy}\]
Write down the values of a and b.
ICSE solutions for Physics [English] Class 10 11 Thermionic Emission and Radioactivity Long Numericals
A certain nucleus X has a mass number 15 and atomic number 7. Find the number of neutrons. The nucleus X losses one proton and Express the change and write the symbol of the new nucleus.
A certain nucleus X has a mass number 15 and atomic number 7. Find the number of neutrons. The nucleus X losses one β-particle and Express the change and write the symbol of the new nucleus.
A certain nucleus X has a mass number 15 and atomic number 7. Find the number of neutrons. The nucleus X losses one α-particle and Express the change and write the symbol of the new nucleus.
An element 92U238 losses one alpha particle, and then one β-particle and then again one β- particle to get the final nucleus bQa.
(i) Write down the values of a and b.
(ii) State the relationship between the nuclei P and Q.
An isotope of uranium is 92Y238, i.e., it has mass number 235 and atomic number 92.
Find the number of electrons in the neutral atom of this isotope.
An isotope of uranium is 92Y238, i.e., it has mass number 235 and atomic number 92.
Find the number of protons and neutrons in its nucleus.
An isotope of uranium is 92Y238, i.e., it has mass number 235 and atomic number 92.
Do all isotopes have the same number of neutrons?
An isotope of uranium is 92Y238, i.e., it has mass number 235 and atomic number 92.
What is the number of protons in 92U238?
An isotope of uranium is 92Y238, i.e., it has mass number 235 and atomic number 92.
Mention the relationship between 92U235 and 92U238.
Solutions for 11: Thermionic Emission and Radioactivity
![ICSE solutions for Physics [English] Class 10 chapter 11 - Thermionic Emission and Radioactivity ICSE solutions for Physics [English] Class 10 chapter 11 - Thermionic Emission and Radioactivity - Shaalaa.com](/images/physics-english-class-10_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
ICSE solutions for Physics [English] Class 10 chapter 11 - Thermionic Emission and Radioactivity
Shaalaa.com has the CISCE Mathematics Physics [English] Class 10 CISCE solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. ICSE solutions for Mathematics Physics [English] Class 10 CISCE 11 (Thermionic Emission and Radioactivity) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. ICSE textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Physics [English] Class 10 chapter 11 Thermionic Emission and Radioactivity are Isotopes, Isobars, Isotones or Isoneutronic, Radioactivity, Radioactivity as Emission of Alpha, Beta, and Gamma Radiations, Properties of Alpha Particles, Properties of Beta Particles, Properties of Gamma Radiations, Changes Within the Nucleus in Alpha, Beta and Gamma Emission, Alpha Decay (Alpha Emission), Beta Decay (Beta Emission), Gamma Decay (Gamma Emission), Uses of Radioactive Isotopes, Nuclear Energy, Safety Precautions While Using Nuclear Energy, Nuclear Fission, Nuclear Fusion, Distinction Between the Radioactive Decay and Nuclear Fission, Distinction Between the Nuclear Fission and Nuclear Fusion, Structure of the Atom and Nucleus, Atomic Model, Sources of Harmful Radiations, Hazards of Radioactive Substances and Radiation, Background Radiations.
Using ICSE Physics [English] Class 10 solutions Thermionic Emission and Radioactivity exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in ICSE Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum CISCE Physics [English] Class 10 students prefer ICSE Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 11, Thermionic Emission and Radioactivity Physics [English] Class 10 additional questions for Mathematics Physics [English] Class 10 CISCE, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
