Advertisements
Online Mock Tests
Chapters
2: Simple Machines
3: Refraction of Light
4: Refraction through Lenses and Optical Instruments
5: Spectrum
6: Echoes and Vibrations of Sound
7: Electricity
8: Electric Power and House hold Circuits
9: Magnetic Effect of Current
10: Specific Heat Capacity and Latent Heat
11: Thermionic Emission and Radioactivity
![ICSE solutions for Physics [English] Class 10 chapter 1 - Force, Work, Power and Energy ICSE solutions for Physics [English] Class 10 chapter 1 - Force, Work, Power and Energy - Shaalaa.com](/images/physics-english-class-10_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 1: Force, Work, Power and Energy
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 1 of CISCE ICSE for Physics [English] Class 10.
ICSE solutions for Physics [English] Class 10 1 Force, Work, Power and Energy Short Answers
Define force. Is force a scalar or a vector quantity?
State and define the unit of force in the S.I. system.
Define one newton. Write the relation between the S. I. unit and the C.G.S. unit of force.
Define 1 kgf., How is it related to the S.I. unit of force?
'The position of the centre of gravity of a body remains unchanged even when the body is deformed'.
True
False
Which of the following remains constant in a uniform circular motion, Speed or Velocity, or both?
Define 1 Dyne.
Define contact forces.
Define non-contact forces.
State the energy change in the following device while in use:
A loudspeaker
State the energy change in the following device while in use:
A glowing electric bulb.
Give any two effects of a force on a non-rigid body.
Where does the position of centre of gravity lie for a circular lamina
At which point is the centre of gravity situated in a triangular lamina?
What is Gravitational force? Give gravitational units of force.
What is the work done by the gravitational force on the moon that revolves around the earth?
A coolie, with a load of 30 kg on his head, walks on the platform. If he walks a distance of 60 m, what is the work done by him?
A bullet fired against a window glass pane makes a hole in it without any cracks while a stone striking the same glass pane smashes it; explain with reason.
State one factor on which the magnitude of a non-contact force depends. How does the magnitude of a non-contact force change along with distance?
Under what condition will a set of gears produce a gain in speed
Under what condition will a set of gears produce a gain in torque.
Name the force required for uniform circular motion. State its direction.
A force is applied on (i) a non-rigid body and (ii) a rigid body. How does the effect of the force differ in the above two cases?
How does the distance of separation between two bodies affect the magnitude of the non-contact force between them?
In what way does an ‘Ideal machine’ differ from a ‘Practical machine’?
Can a simple machine act as a force multiplier and a speed multiplier at the same time?
State two factors on which moment of the force about a point depends.
State the units of moment of force.
State the principle of moments.
State when the moment of force is positive and when it is negative.
Give the units of couple.
Two similar vehicles are moving with the same velocity on the road, such that one of thus is loaded and the other one is empty which of the two vehicles will require larger force to stop?
What is meant by the term ‘moment of force’? If the moment of force is assigned a negative sign then will the turning tendency of the force be clockwise or anti-clockwise?
Define Uniform circular motion.
Define Translational motion.
Define Centripetal force.
Define the term momentum.
How is force related to the momentum of a body?
State the condition when the change in the momentum of a body depends only on the change in its velocity.
With reference to the direction of action, how does a centripetal force differ from centrifugal force?
Can the CG be situated outside the material of the body? Give an example.
Explain why It is easier to knock down a boy who is standing on one foot than one who is standing on two.
Explain why One leans forward while climbing up a hill.
Explain why a tight rope-walker, often holds a long pole in his hands when in action.
Explain why a ship loaded with light goods is more liable to be overturned than the one loaded with heavy goods.
Explain why Standing passengers are not allowed on the upper deck of a double-decker bus.
Explain when we carry weight, on one hand, we bend on the other side.
What is the weight of a body placed at the centre of the earth?
What do you understand by work? Is work a scalar or a vector quantity?
In the following case write yes, if the work is being done and no if no work is being done.
A man trying to push a wall.
In the following case write yes, if the work is being done and no if no work is being done.
A man moving on the rough ground.
In the following case write yes, if the work is being done and no if no work is being done.
A coolie standing with a heavy load on his head
Yes
No
In the following case write yes, if the work is being done and no if no work is being done.
A boy climbing up a staircase.
State two conditions when the work done by a force acting on a body is zero.
Define power.
Is power a scalar or a vector quantity?
State the condition when the work done by the force is positive
State the condition when the work done by the force is negative.
A force F when acts on a body, displace it by a distance d in a direction at an angle θ with the direction of the force. Write down the expression for the work done by the force.
Can two agents, doing the same work, have different power?
When does a force do work?
What is the work done by the moon when it revolves around the earth?
State the amount of work done by an object when it moves in a circular path for one complete rotation. Give a reason to justify your answer.
State two conditions for work to be done.
Why is less effort needed to lift a load over an inclined plane as compared to lifting the load directly?
What is the S.I. unit of work? Define it.
Justify the statement. “Power can be expressed as the product of force and velocity.”
State larger units of power.
State the practical unit mainly used in mechanical engineering and write down its equivalent in watt.
What happens to the power if the time for doing work is reduced from t second to t/10 second?
What do you understand by the term energy? Is energy a scalar or vector? How is the energy possessed by a body measured?
State the S.I. and C.G.S. units of energy. How are they related?
Write five forms of energy.
What do you understand by mechanical energy?
What are the two kinds of mechanical energy?
What do you understand by the potential energy of the body?
What do you understand by the kinetic energy of the body?
Give three examples of bodies possessing kinetic energy.
How is kinetic energy possessed by a moving body measured?
A man climbs a slope and another walks same distance on level road. Which of the two expends more energy and why?
Is it possible that a body may possess energy even when it is not in motion?
What kind of energy is possessed in a situation when?
A cocked up spring of air gun.
What kind of energy is possessed in a situation when?
A stone lying on the top of roof.
What kind of energy is possessed in a situation when?
A fish moving in the water.
What kind of energy is possessed in a situation when?
A horse running along a level road
What kind of energy is possessed in a situation when?
Water stored in dams.
What kind of energy is possessed in a situation when?
An electron spinning around the nucleus.
What kind of energy is possessed in a situation when?
A shooting arrow.
What kind of energy is possessed in a situation when?
A stone, in a stretched catapult.
Relate 1 KWh (kilowatt hour) with joule.
Obtain an expression for the potential energy of a body of mass m at a height h above the ground.
When an arrow is shot from a bow, it has kinetic energy in it. Explain briefly from where does it get its kinetic energy?
What happens to the K.E. when
(i) the mass of the body is doubled at a constant velocity and
(ii) the velocity of the body is doubled at constant mass?
Write the type of energy possessed in the following case:
A bent bow
Write the type of energy possessed in the following case:
A falling apple
Write the type of energy possessed in the following case:
A wound-up spring
Write the type of energy possessed in the following case:
A moving cricket ball.
Give three examples of bodies possessing potential energy.
What is dissipation of energy?
State the energy changes which take place in Electricity is obtained from solar energy.
What is the main energy transformation that occur in:
Photosynthesis in green leaves.
What is the main energy transformation that occur in:
Charging of a battery.
A man climbs a slope and another walks same distance on level road. Which of the two expends more energy and why?
Name the two groups in which various sources of energy are classified?
Give two examples each of renewable and non-renewable sources of energy?
Why using wood as fuel is not advisable although wood is a renewable source of energy?
Name a device in which solar energy is converted into electricity state its two uses.
Name the material commonly used for the manufacturing of solar cells.
Name two places in India where electricity is generated from nuclear power plants.
What should be the characteristic of a source of energy?
What is hydro energy?
Explain the principle of generating electricity from hydro energy.
How much hydro-electric power is generated in India?
State two advantages and two disadvantages of using hydro-energy for producing electricity.
What is wind energy?
Explain the principle of working of the windmill for generating electricity.
State two advantages and disadvantages of using wind energy for producing electricity.
State two advantages and disadvantages of using nuclear energy for producing electricity.
State four ways for the judicious use of energy.
Explain, why submarines are able to dive underwater as well as a sail on the surface of the water?
State the principle of conservation of energy.
Distinguish between work and power.
State the energy changes which take place when:
A body released from rest from the top of a building.
State the energy changes which take place when:
A body thrown vertically upwards from the ground.
State the energy changes which take place when:
In a heat engine.
State the energy changes which take place when:
A bulb glows, when torchlight is switched on.
State the energy changes which take place when:
A car moves up a hill.
State the energy changes which take place when:
A toy car spring is wound and car is made to run on level floor.
State the energy changes which take place when:
Water stored in dams rotates turbine connected to a dynamo.
State the energy changes which take place when:
An air gun is loaded and then fired.
State the energy changes which take place when:
A magnesium ribbon burns in air.
State the energy changes which take place when:
A stone projected vertically upwards, returns back to the thrower.
State the energy changes which take place when:
Water freezes in the freezing chamber of a fridge.
State the energy changes which take place when:
Photographic film is exposed to sunlight.
State the energy changes which take place when:
Food is digested by animals.
State the energy changes which take place when:
During electrolysis.
State the energy changes which take place when:
Burning of coal.
State the energy changes in the following case while in use:
A petrol engine of a running car
State the energy changes which take place when:
A battery lighting up a bulb.
State the energy changes which take place when:
Electricity obtained from nuclear energy.
State the energy changes which take place in Electricity is obtained from solar energy.
State the energy transformation on the following:
Electricity is obtained from wind energy.
State the energy transformation on the following:
Electricity obtained from hydro energy.
Give one example when:
Heat energy changes to kinetic energy.
Give one example when:
Kinetic energy changes to heat energy.
Give one example when:
Sound energy changes to electric energy.
Give one example when:
Electric energy changes to sound energy.
Give one example when:
Light energy changes to chemical energy.
Give one example when:
Chemical energy changes to light energy.
Give one example when:
Electric energy changes to mechanical energy.
Give one example when:
Mechanical energy changes to electric energy.
Give one example when:
Potential energy changes to electric energy.
Give one example when:
Electric energy changes to potential energy.
Give one example when:
Mechanical energy to heat energy.
Give one example when:
Kinetic energy to potential energy.
Give one example when:
Electrical energy to heat energy.
Give one example when:
Chemical energy to electrical energy.
ICSE solutions for Physics [English] Class 10 1 Force, Work, Power and Energy Long Answers
Give two examples each of contact and non-contact forces.
Why is it easier to open a door by applying the force at the free end of it?
Explain the term ‘centre of gravity’ of a body.
State the effects that a force can produce. Given one example of each.
What is meant by equilibrium and state the conditions of equilibrium of a body?
What do you mean by dynamic and static equilibrium? Give one example of each.
State two methods of increasing the stability of the body.
What is the difference between renewable and non-renewable resources?
What are the advantages and disadvantages of using solar cells for producing electricity?
ICSE solutions for Physics [English] Class 10 1 Force, Work, Power and Energy Figure Based Short Answers
What is a couple?
Is it possible to have an accelerated motion with a constant speed? Explain.
One end of a spring is kept fixed while the other end is stretched by a force as shown in the diagram.
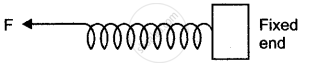
(i) Copy the diagram and mark on it the direction of the restoring force.
(ii) Name one instrument which works on the above principle.
A boy of mass 30 kg is fitting at a distance of 2 m from the middle of a see-saw. Where should a boy of mass 40 kg sit so as to balance the see-saw?
Write the expression for calculating the moment of force about a given point.
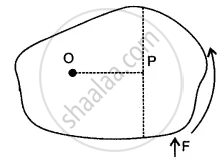
The moment of a force of 10 N about a fixed point O is 5 N m. Calculate the distance of the point O from the line of action of the force.
A boy sits and stands repeatedly. Draw a graph showing the variation of potential energy with time.
A ball is placed on a compressed spring. When the spring is released, the ball is observed to fly away.
(i) What form of energy does the compressed spring possess?
(ii) Why does the ball fly away?
Draw a diagram to show the energy changes in an oscillating simple pendulum. Indicate in your diagram how the total mechanical energy in it remains constant during the oscillation.
What is the form of that graph between
(i) K.E. and velocity for a constant mass?
(ii) K.E. and mass for a constant velocity?
Define an Inclined plane.
ICSE solutions for Physics [English] Class 10 1 Force, Work, Power and Energy Figure Based Long Answers
Two unlike forces (parallel) of 10 N and 25 N act at a distance of 12 cm. from each other. Find the point about which the body balance.
A uniform metre scale is balanced at a 40 cm mark when weights of 20 gf and 5 gf are suspended at 5 cm mark and 75 cm mark respectively. Calculate the weight of metre scale.
Give an experiment to verify the principle of moments.
A uniform metre rule rests horizontally on a knife-edge at the 60 cm mark when a mass of 10 gram is suspended from one end. At which end must this mass be suspended? What is the mass of the rule?
A uniform metre scale can be balanced at the 70.0 cm mark when a mark when a mass 0.05 kg is hung from the 94.0 cm mark
1) draw a diagram of the arrangement
2) Find the mass of the metre scale
A block of mass 30 kg is pulled up a slope, as shown in diagram with a constant speed, by applying a force of 200 N parallel to slope.
A and B are initial and final positions of block.
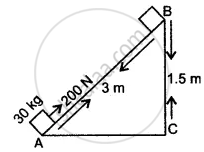
(i) Calculate the work done by force in moving the block from A to B.
(ii) Calculate P.E. gained by block. [g=10ms-2]
(i) A 200g ball is thrown vertically upward with an initial velocity of 30 ms-1. Draw a velocity-time graph for the motion of ball.
(ii) How long will the ball take to reach the highest point?
(iii) What will be the kinetic energy of ball, when it returns to the starting point, neglecting the air resistance?
(iv) What will be the potential energy of ball at highest point?
A truck driver can load oil drums into the back of the truck by pushing them up a sloping plank, or by lifting them directly. Each drum has a mass of 80 kg, the plank is 3 m long, and the back of the truck is 0.8 m above the ground.

(i) How much force would be needed to lift a drum into the truck directly/without using the plank? (Take g = 10 m/s2)
(ii) How much energy would be required in lifting the drum into the truck without the plank?
(iii) If the force needed to push the drum up the plank is 300 N, why is this less than the answer to part (i)?
(iv) When the truck is loaded, the driver drives off. List the major energy changes that take place in moving the truck.
(v) The driver has to stop at the factory gates. What happens to the kinetic energy of the truck?
Show that in case of a body falling freely under gravity, total mechanical energy remains conserved (neglect air resistance).
What is nuclear energy? Explain the principle of producing electricity using nuclear energy is a nuclear reactor.
ICSE solutions for Physics [English] Class 10 1 Force, Work, Power and Energy Short Numerical
Derive a relation between the S.I. and C.G.S. unit of force.
A man can open a nut by applying a force of 150 N by using a lever handle of length 0.4 m. What should be the length of the handle if he is able to open it by applying a force of 60 N?
The perpendicular distance between the point of application of force and turning point is 1.75 m when a force of 80 N acts on a rigid body. Calculate the moment of force.
Calculate the minimum distance between point of application of force and axis of rotation of a rigid body, if a force 125 N produces a moment of force of 25.75 Nm.
A couple of 15 N force acts on a rigid body, such that arm of couple is 85 cm. Calculate moment of couple in the SI system.
Calculate the magnitude of the force of a couple, when the arm of the couple is 63 cm and the moment of the couple is 21 Nm.
Calculate the change in the Kinetic energy of a moving body if its velocity is reduced to 1/3rd of the initial velocity.
The power of a motor is 40 kW. At what speed can the motor raise a load of 20,000 N?
Calculate the length of arm of couple, if a force of 13 N produces a moment of couple of 14.3 Nm.
Calculate the work done when:
A 5 kg weight is lifted 10 m vertically. (g = 9.8 m/s2)
Calculate the work done when:
A car is moved on a rough road through 30 m against a frictional resistance of 75 N.
A coolie carrying a load on his head and moving on a frictionless horizontal platform does no work. Explain the reason why.
A girl of mass 35 kg climbs up from the first floor of a building at a height 4 m above the ground to the third floor at a height 12 m above the ground. What will be the increase in her gravitational potential energy? [g = 10 ms-2]
A force is applied on a body of mass 20 kg moving with a velocity of 40 ms−1. The body attains a velocity of 50 ms−1 in 2 seconds. Calculate the work done by the body.
The world record for weight lifting was held by Sergei Didyk of the USSR. He lifted 261 kg to a height of 2.3 m in 4s; find:
(a) Weight lifted by him
(b) Work done by him
(c) Power developed by him. (g = 10m/s2)
The work done by the heart is 1 Joule per beat. Calculate the power of the heart if it beats 72 times in one
How long should an electric motor, of power 2 H.P. operate, so as to pump 5 m3 of water from a depth of 15m. [Take g = 10 N kg−1]
A man having a box on his head, climbs up a slope and another man having an identical box walks the same distance on a levelled road.
Who does more work against the force of gravity and why?
A machine raises a load of 750 N through a height of 16 m in 5 seconds. Calculate the power at which the machine works.
State the C.G.S. unit of work. How it is related to its S.I. unit?
A body of mass 0.2 kg falls from a height of 10 m to a height of 6 m above the ground. Find the loss in potential energy taking place in the body. [g = 10ms−2]
A ball of mass 200 g falls from a height of 5 m. What will be its kinetic energy when it just reaches the ground? (g = 9.8 m s−2)
Two bodies, A and B of equal mass are kept at heights 20 m and 30 m respectively. Calculate the ratio of their potential energies.
A ball of mass 0.20 kg is thrown vertically upwards with an initial velocity of 20 m s-1. Calculate the maximum potential energy it gains as it goes up.
A body is thrown vertically upwards. Its velocity keeps on decreasing. What happens to its kinetic energy as its velocity becomes zero?
A moving body weighing 400 N possesses 500 J of kinetic energy. Calculate the velocity with which the body is moving. (g = 10 ms2)
ICSE solutions for Physics [English] Class 10 1 Force, Work, Power and Energy Long Numerical
How do you define force? What are the forces acting on a man standing in a lift? If the lift moves down with an acceleration of 2 ms−2, what is the net force on the man if his mass is 50 kg?
A boy of mass 40 kg runs up a height of 30 steps, each 20 cm high. Find:
(i) The force of gravity acting on the boy.
(ii) The work done by the boy against gravity. (Take g = 9.8 ms−2)
A coolie is pushing a box weighing 1500 N up an inclined plane 7.5 m long on to a platform, 2.5 m above the ground.
(i) Calculate the mechanical advantage of the inclined plane. (ii) Calculate the effort applied by the coolie.
(iii) In actual practice, the coolie needs to apply more effort than what is calculated. Give one reason why you think the coolie needs to apply more effort.
Calculate the work done when:
A 5 kg weight is lifted 10 m vertically. (g = 9.8 m/s2)
Calculate the work done when:
A car is moved on a rough road through 30 m against a frictional resistance of 75 N.
An electric motor of power 100 W is used to drive the stirrer in a water bath. If 50% of the energy supplied to the motor is spent in stirring the water. Calculate the work done on the water in one minute.
The weights of two bodies are 2.0 N and 2.0 kgf respectively what is the mass of each body?
A truck weighing 1000 kgf changes its speed from 36 km h-1 to 72 km h-1 in 2 minutes. Calculate:
- the work done by the engine and
- its power (g = 10 m s-2)
A coolie carries a load of 30 kgf through a distance of 500 m in 5 minutes while another coolie B carries the same load through the same distance in 10 minutes. Compare the
(i) work done, and
(ii) power developed. (Take: g = 10md−2)
A girl of mass 40 kg runs a height of 80 stairs, each 25 cm high with a load of 20 kg on her head in 25 sec. If g is 10 m/s2, find:
(i) Gravitational force acting on the girl.
(ii) Work done by her.
(iii) Useful work done by her.
(iv) Her power in watt.
A man weighing 700 N runs up a flight of 15 steps, each 20 cm high, in 5 seconds. Calculate the power of the man.
A water pump raises 50 kg of water through a height of 25 m in 5s. Calculate the power supplied by the pump (Take: g = 10 N kg−1).
An electric motor pump is 60% efficient and is rated 2.5 H.P. Calculate the maximum load it can lift through a height of 10m in 8 sec. (1 H.P. = 750 W).
For the same kinetic energy of a body, what should be the change in its velocity if its mass is increased nine times?
Calculate the kinetic energy of a body of mass 0.1 kg. and momentum 40kg m/s.
A body of mass 50 kg has a momentum of 3000 kg−1 ms. Calculate:
(j) the kinetic energy of the body.
(ii) the velocity of the body.
A body of mass m falls from a height h1 to a height h2, above the ground (h1 > h2). What is the loss of potential energy?
Obtain an expression for the kinetic energy of a body of mass m moving with a velocity v?
A body of mass m is taken from a height h to 2h. What is the increase in its potential energy?
A ball of mass 50 g falls from a height of 2m and rebounds from the ground to 1.6 m. Find:
(i) The potential energy possessed by the ball when initially at rest.
(ii) The kinetic energy of the ball before it hits the ground.
(iii) The final potential energy of the ball.
(iv) The loss in kinetic energy of the ball on collision. (Take: g = 10N kg−1)
In a hydroelectric power station, 1000 kg of water is allowed to drop through a height of 100 m in 1 sec. If the conversion of potential energy to electric energy is 60%. Calculate the power output. [Take: g = 10m/sec2]
On a see-saw, two children of masses 30 kg and 50 kg are sitting on one side of it at distance 2 m and 2.5 m respectively, from its middle, where should a man of mass 74 kg sit to balance it?
A force of 1 kgf displaces a body by a distance of 10 cm
(i) in direction of force,
(ii) normal to the force
(iii) at an angle of 60° to the direction of the force.
Calculate the amount of work done in each case. (Take: g = 9.8 ms−2 )
Solutions for 1: Force, Work, Power and Energy
![ICSE solutions for Physics [English] Class 10 chapter 1 - Force, Work, Power and Energy ICSE solutions for Physics [English] Class 10 chapter 1 - Force, Work, Power and Energy - Shaalaa.com](/images/physics-english-class-10_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
ICSE solutions for Physics [English] Class 10 chapter 1 - Force, Work, Power and Energy
Shaalaa.com has the CISCE Mathematics Physics [English] Class 10 CISCE solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. ICSE solutions for Mathematics Physics [English] Class 10 CISCE 1 (Force, Work, Power and Energy) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. ICSE textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Physics [English] Class 10 chapter 1 Force, Work, Power and Energy are Work Done by the Force of Gravity (W = mgh), Forms of Energy, Gravitational Potential Energy at a Height (U = mgh), Concept of Work, Measurement of Work, Power, Energy, Mechanical Energy, Potential Energy (U), Types of Potential Energy, Kinetic Energy (K), Types of Kinetic Energy, Conversion of Potential Energy into Kinetic Energy, Transformation of Energy, Principle of Conservation of Energy, Theoretical verification of K + U = Constant for a freely falling body, Application of Principle of Conservation of Energy to a Simple Pendulum, Concept of Work, Force, Translational and Rotational Motions, Couple, Principle of Moments, Uniform Circular Motion (UCM), Centrifugal Forces, Centripetal Force, Moment (Turning Effect) of a Force Or Torque, Equilibrium of Bodies and Its Types, Centre of Gravity, Machines, Simple Machines, Machines (Numerical), A Lever, A Pulley, Principle of Machine, Relationship between efficiency (ղ), mechanical advantage (M.A.) and velocity ratio (VR), Types of Levers, Single Fixed Pulley, Technical Terms Related to a Machine, Single Movable Pulley, Combination of Pulleys, Examples of Each Class of Levers as Found in the Human Body.
Using ICSE Physics [English] Class 10 solutions Force, Work, Power and Energy exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in ICSE Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum CISCE Physics [English] Class 10 students prefer ICSE Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 1, Force, Work, Power and Energy Physics [English] Class 10 additional questions for Mathematics Physics [English] Class 10 CISCE, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
