Advertisements
Online Mock Tests
Chapters
2: Simple Machines
3: Refraction of Light
4: Refraction through Lenses and Optical Instruments
5: Spectrum
6: Echoes and Vibrations of Sound
7: Electricity
▶ 8: Electric Power and House hold Circuits
9: Magnetic Effect of Current
10: Specific Heat Capacity and Latent Heat
11: Thermionic Emission and Radioactivity
![ICSE solutions for Physics [English] Class 10 chapter 8 - Electric Power and House hold Circuits ICSE solutions for Physics [English] Class 10 chapter 8 - Electric Power and House hold Circuits - Shaalaa.com](/images/physics-english-class-10_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 8: Electric Power and House hold Circuits
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 8 of CISCE ICSE for Physics [English] Class 10.
ICSE solutions for Physics [English] Class 10 8 Electric Power and House hold Circuits Short Answers
What does the unit kilowatt hour measure? Define it.
Define watt-hour. How many joules are equal to 1 watt-hour?
Define Kilo watt hour.
Express watt hour and kilowatt hour in joule.
What is the energy conversion when an electric current passes through a metallic wire?
State one advantage of using a.c. over d.c.
Which cable, one rated 15A and the other rated 5A will be thicker? Give a reason.
What is electric power? State and define its S.I. unit.
State three factors on which the heat produced in a metallic wire due to passage of current in it depends.
Explain the meaning of the statement 'the power of an appliance is 100 W'.
An electric current is passed through a metallic wire. The wire gets heated up. Give the reason. Is it possible to melt the wire by passing a heavy current?
Why is heating coil wound in the form of a helix in electric stove?
Why is the heating coil placed in a circular porcelain plate in an electric stove?
What are the two main systems of wiring commonly used in houses? Which of these systems mentioned by you is better and why?
Point out two main disadvantages of ‘Tree System’.
State two advantages of ‘the ring system of house wiring’.
Two sets A and B of four bulbs each are glowing in two separate rooms. When one of the bulbs in set A is fused, the other three bulbs also cease to glow. But in set B, when one bulb fuses, the other bulbs continue to glow. Explain the difference in the two sets.
How should the electric lamps in a house be connected so that the switching ON or OFF in a room has no effect on other lamps in the same building?
State the colour coding of wires in the flexible lead used for connecting the appliances to the mains in a house circuiting.
Name three main characteristics of an heating element.
Mention three uses of the carbon arc.
Name two common material used for heating elements.
In an electric radiator or room heater, state with reason, why the porcelain tube wound with a nichrome wire is placed between the pole and principal focus of the parabolic concave reflector.
Why is heating element wound on a long porcelain rod in a room heater.
Why is a concave reflector placed behind the heating element in a room heater.
State the position of heating element with respect to principal focus of concave reflector and give reason for choosing this position.
Household wiring for lamp connections can either be done in parallel or in series.Which one would you prefer? Give a reason for your answer.
What is meant by earthing of an electrical appliance? Why is it essential?
What precaution do you observe while connecting a plug top into a socket?
In a three-pin plug top, one of the pins is thicker and longer than the other two, Give reason. Name this pin.
Why is that the same current flowing through the bulb heats up the filament, while the leads are not heated up?
A lady working in her kitchen received a shock from an electric hot plate. What could be the reason for the shock?
Why is the filament in an electric bulb coiled?
Why is the heating element of an electric oven wound on a helix? State the reason.
The electric bulbs used these days have a coil-coiled filament. State its reason.
What changes in energy occur in an electric bulb?
What changes in energy occur in an electric heater?
Why mica is preferred to other insulators in an electric iron?
What is meant by ‘MCB’? Which part of the domestic electric circuit does it replace?
Name the markings of a three-pin plug. Give the colour codes of the connecting leads.
What is a switch? State its function in an electric circuit.
What will happen if switch is connected in ‘neutral wire’?
A switch is not touched with wet hands while putting it on or off. Give a reason for your answer.
State the purpose served by the terminals of a three pin plug.
What are ‘dual switches’? Mention their one main use.
Where is a fuse placed in an electrical circuit? Name a material suitable for making a fuse wire.
An electric filament lamp is connected to a supply of voltage higher than the recommended value. Give reasons, why compared with a normal performance, the lamp emits a brighter light and its life is shortened.
Two fuse wires of the same lengths are rated 5A and 20A. Which of the two fuse wires is thick and why?
Why fuse wire must always be connected in ‘live’ wire? Explain.
Where are the cartridge type fuse used?
‘The current rating of a fuse is 5A’. Comment on this statement.
What is the rating of fuse used in light and fan circuits?
What is the rating of fuse used in power circuits, in domestic use?
Two lamps are rated 220V, 50W and the other rated 220V, 100W are connected in series with the mains of 220 V. Explain, why the 50W lamp glows more?
Why does not the heating coil produce any visible light? in an electric stove.
Of the three connecting wires in a household circuit: Which two of the three wires are at the same potential? In which of the three wires should the switch be connected?
Name two precautions to be observed while using an immersion heater.
State two advantages of filling an inert gas in an evacuated electric filament lamp.
A device is used to transform 12 V a.c. to 200 V a.c. What is the name of this device? Name the principle on which it works.
Which material is the calorimeter commonly made of? Give one reason for using this material.
Name a metal that is used as an electron emitter. Give one reason for using this metal.
What is ‘Rating’ of an electric appliance?
If the rating of an electric bulb is 100W – 230V, Explain its meaning.
What would happen and why, to an electric bulb when it is connected across a supply of voltage (i) lower (ii) higher than its proper rating?
An electric bulb is marked 100 W, 230 V. What does this mean?
Two electric lamps each rating 100 W, 110 V are connected in series to a 220 V power supply and two other electric lamps each of marking 100 W, 220 V are connected in parallel to the same power supply. Will anyone of the two combinations give more light than the other? Give a reason for your answer.
Why should switches always be connected to the live wire? Give one precaution that should be taken while handling switches.
What is the order of current drawn by appliances connected to the ‘light circuit’ of a household?
What is the order of current drawn by appliances connected to the ‘power circuit’ of a household?
Give two precautious that you would take while putting off an electric switch.
What is the function of the split rings in a d.c. motor?
Why is the electric power from the generating station transmitted at high voltage?
How does the heat produced by die passage of current in a metallic wire depend on the current in the wire?
How does the heat produced by die passage of current in a metallic wire depend on the resistance of the wire.
How does the heat produced by die passage of current in a metallic wire depend on the time of passage of current in the wire?
ICSE solutions for Physics [English] Class 10 8 Electric Power and House hold Circuits Long Answers
What do you understand by ‘earthing’? What are the advantages of earthing in a household electric circuit? Explain, how it is done?
State relative advantages and disadvantages of ring system of wiring over the tree system.
An electric heater is rated 220 V, 550 W. What does this statement mean?
An electric heater is rated 220 V, 550 W. Calculate the electrical energy consumed in 3 hours?
An electric heater is rated 220 V, 550 W. Electrical energy is also measured in kWh. What do you understand by a kilo-watt-hour?
(i) Two sets A and B, of three bulbs each, are glowing in two separate rooms. When one of the bulbs in set A is fused, the other two bulbs also cease to glow. But in set B, when one bulb fuses, the other two bulbs continue to glow. Explain why this phenomenon occurs.
(ii) Why do we prefer arrangements of Set B for house circuiting?
State the reason why, in a three pin plug, the earth pin is longer and thicker than the other two.
Give the role of each of the three terminals of a three way pin plug.
Why is the fuse wire fitted in a porcelain casing?
How does earthing prevent electrical shock?
You are required to connect a bulb, a fan and a socket outlet to the mains in one set A and an air-conditioner and a refrigerator to the mains in other set B. Will you recommend the wire of same thickness and same insulation in both? explain your answer.
An electric filament lamp is connected to a supply of voltage higher than the recommended value. Give reasons, why compared with a normal performance, the lamp emits a brighter light and its life is shortened.
What is an ‘electric fuse’? State its two characteristics of electric fuse.
At what voltage is the electric power generated at the generating station? Explain the transmission of this power to your house.
How is the amount of heat produced calculated due to the passage of current in a metallic conductor? Derive an expression for it.
ICSE solutions for Physics [English] Class 10 8 Electric Power and House hold Circuits Figure Based Short Answers
Draw diagram of a three pin socket outlet and state the connections made to them.
Draw a diagram of a three pin plug top. Mark the pins used for live, neutral and earth connections as L, N and E respectively. To which part of the appliance is the pin marked as E connected. To which line L or N is the fuse connected?
Draw a labelled diagram with necessary switch, regulator etc. to connect a bulb, a plug socket outlet and a fan with the mains. In what arrangement have you connected these to the mains?
ICSE solutions for Physics [English] Class 10 8 Electric Power and House hold Circuits Figure Based Long Answers
Explain the significance of kWh meter, main switch and main fuse in house-circuiting.
Draw a circuit diagram using the dual control switches to light a staircase electric light and explain its working.
The diagram shows two ways of connecting three lamps P, Q and R to A.C. supply of 220 V.
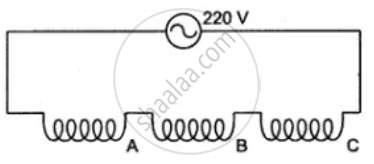
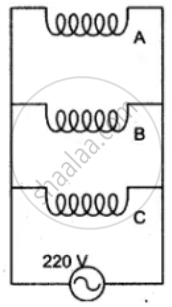
Three 250 W heaters are connected in parallel to a 100 V supply, Calculate total current taken from the supply.
Three 250 W heaters are connected in parallel to a 100 V supply, Calculate the resistance of each heater.
Three 250 W heaters are connected in parallel to a 100 V supply, Calculate the energy supply in kWh to the three heaters in 5 hour.
An electric bulb is rated 240V-60W and is working at 100% efficiency.
(i) Calculate the resistance of bulb.
(ii) (a) Draw the circuit diagram.
(b) What is the rate of conversion of energy in each bulb?
(c) Total power used by the bulbs.
With reference to the diagram shown below calculate:
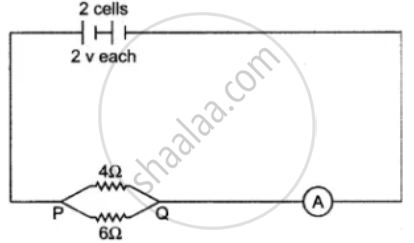
(i) The equivalent resistance between P and Q.
(ii) The reading of ammeter.
(iii) The electrical power between P and Q.
ICSE solutions for Physics [English] Class 10 8 Electric Power and House hold Circuits Short Numericals
State other bigger units of electric power and express them in watt.
State (i) the S. I. unit, (ii) the household unit, of electrical energy. How are these units related?
An electric kettle is rated 3kW, 250V. What should be the current capacity of the fuse with it?
I ampere of current is passed through a resistor of resistance R ohm for time t second. Obtain expression for
(i) the electrical energy, and
(ii) the electrical power spent.
How can electric energy consumed by an electric appliance be calculated in kilowatt hour (kWh)?
What is the resistance of an appliance rated at V volt, P watt?
A family uses a light bulb of 100W, a fan of 100W, and a heater of 1000W, each for 8 hours a day. If the cost of electricity is Rs. 2 per unit, what is the expenditure to the family per day, on electricity?
Establish the relation that heat produced in a metallic conductor due to the flow of current is V2t/R joules, where V is the potential difference across the ends of the conductor, R its resistance and t is the time in second for which current flows.
Find the heat produced in joules when a current of 10 amperes flows through a connecting wire of resistance 2 × 10-2 ohms and heating element of resistance 250 ohms for 2 seconds.
An electric lamp A of 40 W and another electric lamp B of 100 W are connected to 220 V supply. Calculate the ratio of their filament resistances?
In what unit does the electric meter in a house measure the electrical energy consumed? What is its value in S.I unit?
Find the energy released by a current of 0.25 amperes flowing through a heater for 5 minutes. The p.d. is 230 V.
An electric iron is rated at 230 V, 750 W. What is its resistance? What maximum current can be passed through it?
An electric bulb is rated as 100W – 250V. What information does it convey? Calculate the resistance of its filament while glowing.
An electric bulb is rated as 100W – 250V. What information does it convey? Calculate the current through the filament of the bulb.
An Electric bulb is marked 100 W, 230 V. What find the energy consumed by the bulb in one hour.
An Electric bulb is marked 100 W, 230 V. What current does it take?
An Electric bulb is marked 100 W, 230 V. What how long would this lamp take to consume one unit of electricity?
Out of the three fuses with current ratings 5A, 10A, 15A, which one is to be connected in a geyser circuit marked 3 kW, 220V? Give reason for your answer.
The equation I2R seems to suggest that the rate of heating in a resistor is reduced if resistance decreases, whereas equation P = V2/R suggests just the opposite. How do you reconcile this problem?
ICSE solutions for Physics [English] Class 10 8 Electric Power and House hold Circuits Long Numericals
An electric bulb is rated as 100W – 250V. What information does it convey? Calculate the resistance of its filament while glowing.
An electric bulb is rated as 100W – 250V. What information does it convey? Calculate the current through the filament of the bulb.
Two resistances R1 = 4Ω and R2 = 6Ω are connected in series. The combination is connected with a battery of e.m.f. 6V and negligible resistance. Calculate:
(i) the heat produced per minute in each resistor,
(ii) the power supplied by the battery.
A bulb is connected to a battery of e.m.f. 6V and internal resistance 2Ω A steady current of 0.5A flows through the bulb. Calculate the total energy supplied by the battery in 10 minutes.
A bulb is connected to a battery of e.m.f. 6V and internal resistance 2Ω A steady current of 0.5A flows through the bulb. Calculate the resistance of the bulb.
A bulb is connected to a battery of e.m.f. 6V and internal resistance 2Ω A steady current of 0.5A flows through the bulb. Calculate the heat energy dissipated in the bulb in 10 minutes.
A battery of e.m.f. 12V and internal resistance 1.6 Ω is connected to two resistors of 4Ω and 6Ω connected in parallel. Calculate:
(i) the current drawn from the battery,
(ii) the power dissipated in each resistor,
(ii)the total power supplied by the battery.
A bulb is marked 100W, 220V and an electric heater is marked 2000 W, 220 V.
(i) What is the ratio between the resistances of these two devices?
(ii) How does the power-voltage rating of a device help us to decide about the type of leads (connecting wires) to be used for it?
(iii) In which of the above two devices, a thicker connecting wire of lead is required?
An immersion rod having resistance of 50 Ω is connected to 220V main supply. Assuming that all the energy generated goes to heat the water, calculate the time taken to heat 5 kg water from 30°C to 100°C.
A house is provided with 15 bulbs of 40W, 5 bulbs of 100W, 5 fans of 80 W, and one heater of 1.0 kW. Each day bulbs are used for 4h, fans for lOh, and heater for 2h. The voltage of mains is 220 V. Calculate:
(i) Maximum power of the circuit in the house,
(ii) maximum current capacity of the main fuse in the house,
(iii) the electrical energy consumed in a week,
(iv) cost of electricity consumed at 1.25 Rs. per kWh.
Two bulbs are rated: bulb A 100W, 120 V bulb B 10W, 120 V. If both are connected across a 120V supply, which bulb will consume more energy, When in series? Also calculate the current through each bulb in above cases.
Two bulbs are rated: bulb A 100W, 120 V bulb B 10 W, 120 V. If both are connected across a 120V supply, which bulb will consume more energy, When in parallel? Also calculate the current through each bulb in the above cases.
A. bulb is rated at 100W, 250V and another one at 60W, 250V. What is the current flowing in the circuit if the two bulbs are put in series across a 220 V mains supply?
The resistance of filament of an electric heater is 500 Ω It is operated at 200V for 1 hour daily. Calculate the current drawn by the heater and the energy consumed in joule.
The resistance of filament of an electric heater is 500 Ω It is operated at 200V for 1 hour daily. Calculate the current drawn by the heater and the energy consumed in kWh, by the heater in a month of 30 days.
An electrical appliance is rated 1500 W, 250 V. This appliance is connected to 250 V mains. Calculate:
(i) the current drawn,
(ii) the electrical energy consumed in 60 hours,
(iii) the cost of electrical energy consumed at Rs. 2.50 per kWh.
An electric appliance is rated at 1000 W, 250V. Calculate:
(i) The electrical energy consumed by the appliance in 12 hour.
(ii) The cost of energy consumed at Rs. 1.20 per kWh.
How long would this appliance take to use 1 kWh energy when operated at 250 V?
The following table gives the electrical appliances used, their power and the average time for which they are used each day in a home. Estimate the monthly electricity bill if the rate is 60 paise per unit.
| Sr.no. | Name | Nos. | Power rating | Time/day |
| 1 | Bulb | 4 | 100 W | 7.5 hr |
| 2 | Fans | 2 | 50 W | 10 hr |
| 3 | T.V. | 1 | 100 W | 2 hr |
| 4 | Iron | 1 | 500 W | 1 hr |
| 5 | Electric stove | 1 | 750 W | 2 hr |
A consumer uses 4 lamps of 60 watt, 2 lamps of 40 watt, and 2 lamps of 100 watt. All these are used for 6 hour daily. Find the total bill for 30 days when the rate of energy is 75 paise per unit and the meter rent is Rs. 1.
Find the cost of operating an electric toaster for two hours if it draws 8 A current on a 110 volt circuit. The cost of electrical energy is Rs. 2.50 per kWh.
Solutions for 8: Electric Power and House hold Circuits
![ICSE solutions for Physics [English] Class 10 chapter 8 - Electric Power and House hold Circuits ICSE solutions for Physics [English] Class 10 chapter 8 - Electric Power and House hold Circuits - Shaalaa.com](/images/physics-english-class-10_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
ICSE solutions for Physics [English] Class 10 chapter 8 - Electric Power and House hold Circuits
Shaalaa.com has the CISCE Mathematics Physics [English] Class 10 CISCE solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. ICSE solutions for Mathematics Physics [English] Class 10 CISCE 8 (Electric Power and House hold Circuits) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. ICSE textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Physics [English] Class 10 chapter 8 Electric Power and House hold Circuits are Miniature Circuit Breaker (MCB), Electric Switch, Three-pin Plug and Socket, Circuits with Dual Control Switches (Staircase Wire), Colour Coding of Live, Neutral, and Earth Wires, Precautions to Be Taken While Using Electricity, House Wiring (Ring System), Power Distribution to a House, Earthing (Grounding), High Tension Wires, Transmission of Power from the Power Generating Station to the Consumer, Electric Fuse.
Using ICSE Physics [English] Class 10 solutions Electric Power and House hold Circuits exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in ICSE Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum CISCE Physics [English] Class 10 students prefer ICSE Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 8, Electric Power and House hold Circuits Physics [English] Class 10 additional questions for Mathematics Physics [English] Class 10 CISCE, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
