Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Show that in case of a body falling freely under gravity, total mechanical energy remains conserved (neglect air resistance).
Solution
Let a body of mass m fall freely under gravity from height h above the ground.
Let A, B, and C be the positions of the body.
Let x be the distance fallen from A to B.
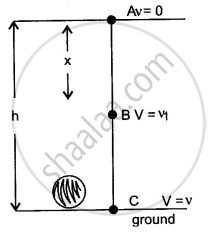
At position A :
KE = 0 .......(body is at rest)
and PE = mgh
∴ Total energy = 0 + mgh = mgh ..........(i)
At position B :
Let v1 be velocity of body, then u = 0, S = x.
From equation v2 = u2 + 2aS
v12 = 0 + 2gx = 2gx
Since KE =`1/2` mv2 = `1/2` m × 2gx = mgx
and PE = mg (h − x)
= mgh − mgx
∴ Total energy = mgx + mgh − mgx = mgh ..............(ii)
At position C :
Let velocity of body be v, then u = 0, S = h.
From equation v2 = u2 + 2gS
v2 = 0 + 2gh = 2gh
Since KE = `1/2` mv2 = `1/2` m × 2gh = mgh
and PE = 0
∴ Total energy = mgh + 0 = mgh ............(iii)
From (i), (ii) and (iii) it is clear that sum of mechanical energy remains same at any point in the path of free fall of a body.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
What do you understand by the kinetic energy of a body?
What is meant by the renewable and non-renewable sources of energy? Distinguish between them giving two examples of weach.
What is wind energy?
Write five forms of energy.
State the energy changes which take place in Electricity is obtained from solar energy.
State the energy changes which take place when:
A toy car spring is wound and car is made to run on level floor.
State the energy changes which take place when:
During electrolysis.
State the energy transformation on the following:
Electricity obtained from hydro energy.
A body of mass m falls from a height h1 to a height h2, above the ground (h1 > h2). What is the loss of potential energy?
