Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Show that in case of a body falling freely under gravity, total mechanical energy remains conserved (neglect air resistance).
उत्तर
Let a body of mass m fall freely under gravity from height h above the ground.
Let A, B, and C be the positions of the body.
Let x be the distance fallen from A to B.
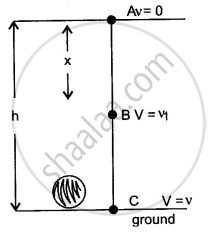
At position A :
KE = 0 .......(body is at rest)
and PE = mgh
∴ Total energy = 0 + mgh = mgh ..........(i)
At position B :
Let v1 be velocity of body, then u = 0, S = x.
From equation v2 = u2 + 2aS
v12 = 0 + 2gx = 2gx
Since KE =`1/2` mv2 = `1/2` m × 2gx = mgx
and PE = mg (h − x)
= mgh − mgx
∴ Total energy = mgx + mgh − mgx = mgh ..............(ii)
At position C :
Let velocity of body be v, then u = 0, S = h.
From equation v2 = u2 + 2gS
v2 = 0 + 2gh = 2gh
Since KE = `1/2` mv2 = `1/2` m × 2gh = mgh
and PE = 0
∴ Total energy = mgh + 0 = mgh ............(iii)
From (i), (ii) and (iii) it is clear that sum of mechanical energy remains same at any point in the path of free fall of a body.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Fill in the blank
The energy possessed by a body due to its position is called ________ energy.
Fill in the blank
An object falling freely from the roof of a multistorey building has ________ and _________ energy when halfway down the building.
Give one relevant example for the following transformation of energy :
Chemical energy to light energy.
Write an expression for the potential energy of a body of mass m placed at a height h above the earth's surface. State the assumptions made, if any.
Write the type of energy possessed in the following case:
A wound-up spring
What is the main energy transformation that occur in:
Photosynthesis in green leaves.
A ball of mass 50 g falls from a height of 2m and rebounds from the ground to 1.6 m. Find:
(i) The potential energy possessed by the ball when initially at rest.
(ii) The kinetic energy of the ball before it hits the ground.
(iii) The final potential energy of the ball.
(iv) The loss in kinetic energy of the ball on collision. (Take: g = 10N kg−1)
The solar cooker is an application of the ______ energy of the sun, while solar cells, solar lamps are applications of the ______ energy of the sun.
Energy from various sources is considered to have been derived from the sun. Do you agree? Justify your answer.
Name the type of energy (kinetic energy K or potential energy U) possessed in the following case:
A moving cricket ball
