Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
What is meant by radioactivity?
Solution
Elements with a high atomic number such as uranium, thorium, radium have a property of spontaneously emitting invisible, highly penetrating and high energy radiation. This property is called radioactivity. The nucleus of radioactive elements is unstable.
RELATED QUESTIONS
How can they be made to leave the metal surface? (State any two ways)
An element `""_ZS^A` decays to `""_85R^222` after emitting 2 α particles and 1 β particle.
Find the atomic number and atomic mass of the element S.
Arrange α, β, and γ rays in ascending order with respect to their
1) Penetrating power.
2) Ionising power
3) Biological effect
A nucleus `""_11^24Na` emits a beta particle to change into Magnesium (Mg)
(i) Write the symbolic equation for the process.
(ii) What are numbers 24 and 11 called?
(iii) What is the general name of `""_12^24Mg `with respect to `""_11^24Na` ?
A radioactive source emits three types of radiations. Name them.
(i) Name the radiations which are charged.
(ii) Name the radiations which are most penetrating.
(iii) Name the radiations which travel with the speed of light.
(iv) Name the radiations which have the largest mass.
In the following fig. shows a radioactive source S in a thick lead container. The radiations pass through an electric field between the plates P and Q. Complete the diagram to show the paths of α , β and γ radiations.
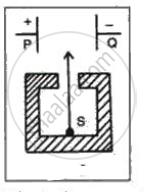
Why is the source S placed in a thick lead container?
Draw a diagram of a simple atom showing the nucleus and electrons. In this atom:
(a) What type of charge will there be on the nucleus?
(b) What is the value of this charge?
A nucleus is \[\ce{^24_11 Na}\] β-radioactive.
Write the equation represent β-decay.
Why should a radioactive substance not be touched by hands?
What do you mean by electron emission?
State two properties that a substance should possess when used as a thermionic emitter.
How is a cathode ray beam affected while passing through a magnetic field?
What do you understand by the term radioactivity?
Name the Different Radiations Which Are Emitted by the Radioactive Substances.
Are all the radiations mentioned by you, emitted in a single radioactive decay?
From α, β and γ-rays, name the one which travels with the speed of light?
What is the value of the speed of gamma radiations in air or vacuum?
Explain, why radium paint, consisting of zinc sulphide and a trace of radium salt, glows in the dark?
State one use of radio-isotopes.
State three ways of obtaining an electron-beam.
Mention four properties of Becquerel rays.
The half-life of a radioactive nuclide is 100 hours. The fraction of original activity that will remain after 150 hours would be ______.
In U238 ore containing Uranium the ratio of U234 to Pb206 nuclei is 3. Assuming that all the lead present in the ore is final stable product of U238. Half life of U238 to be 4.5 × 109 years and the age of ore is ______ × 109 years. (in 109 years)
If 10% of a radioactive substance decays in every 5 years, then the percentage of the substance that will have decayed in 20 years will be ______.
Two radioactive materials A and B have decay constants 25λ and 16λ respectively. If initially they have the same number of nuclei, then the ratio of the number of nuclei of B to that of A will be "e" after a time `1/("a"lambda)` The value of a ______.
In the following atoms, which one is a radioisotope? Give one use of this isotope.
O16, C14, N14, He4
