Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
What is meant by radioactivity?
उत्तर
Elements with a high atomic number such as uranium, thorium, radium have a property of spontaneously emitting invisible, highly penetrating and high energy radiation. This property is called radioactivity. The nucleus of radioactive elements is unstable.
संबंधित प्रश्न
Answer the following questions based on a hot cathode ray tube
Name the charged particles
State three factors on which the rate of emission of electrons from a metal surface depends
A radioactive substance is oxidized. Will there be any change in the nature its radioactivity? Give a reason for your answer
Why is a cathode ray tube evacuated to a low pressure?
What is thermionic emission?
Name the unit in which the work function of a metal is expressed.
Radiations given out from a source when subjected to an electric field in a direction perpendicular to their path are shown below in the diagram. The arrows show the path of the radiation A, B and C. Answer the following questions in terms of A, B and C.
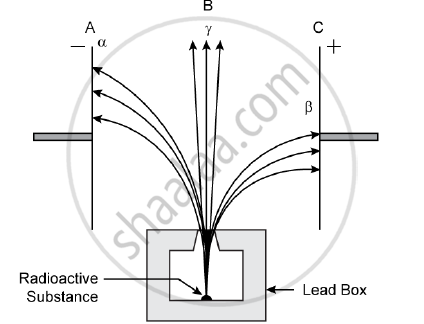
1) Name the radiation B which is unaffected by the electrostatic field.
2) Why does the radiation C deflect more than A?
3) Which among the three causes the least biological damage externally.
4) Name the radiation which is used in carbon dating.
Give a scientific explanation.
When the radiation coming out from a certain radioactive substance is passed through an electric field, marks are found at three places on the photographic plate placed in its path.
State the penetrating range of α, β and γ radiations.
Radioactive substances were found to give off three types of rays. Name them. How do they
(a) React to the magnetic field?
(b) React to the electric field?
(c) Act when different thickness of lead sheets is placed in their path?
A radioactive nucleus `""_"Z"^"A"` X first emits a beta particle and then an alpha particle to give the resulting nucleus `""_"Q"^"P"` Y What will be the values of P and Q in terms of A and Z?
A nucleus of an element X which has the symbol `""_84^202` X emits an alpha particle and then a beta particle. The final nucleus is `""_"b"^"a"` Y Find a and b.
A certain nucleus A (mass number 238 and atomic number 92) is radioactive and becomes a nucleus B (mass number 234 and atomic number 90) by the loss of one particle.
What particle was emitted?
State three safety precautions that you would take while handling the radioactive substances.
Define bound electrons.
Define atomic number of an element.
How is a cathode ray beam affected while passing through an electric field?
Why are materials of low work function preferred as thermionic cathode materials?
How is a cathode ray tube used to convert an electrical signal into a visual signal?
What do you understand by the term radioactivity?
Justify with reason, whether the following nuclear reactions are allowed or not.
\[\ce{^A_Z X -> ^A_{Z + 1}Y + ^0_{-1}β}\]
Which part of the atom undergoes a change in the process of radioactive decay?
What is the value of the speed of gamma radiations in air or vacuum?
State one use of radio-isotopes.
Unit of radioactivity is _______
The half-life of a radioactive nuclide is 100 hours. The fraction of original activity that will remain after 150 hours would be ______.
Two radioactive sources A and B of half lives of 1 hour and 2 hours, respectively, initially contain the same number of radioactive atoms. At the end of two hours, their rates of disintegration are in the ratio of ______.
