Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The diagram below shows a lever in use.
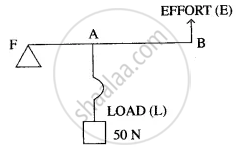
(i) To which class of lever does it belong?
(ii) If FA = 40 cm, AB = 60 cm, then find the mechanical advantage of the lever.
उत्तर
(i) Class 2 lever.
(ii) We know,
L × LA = E × EA.
M.A. =`"L"/"E"=("EA")/("LA")`
= `100/40`
= 2.5
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The diagram below shows a lever in use:
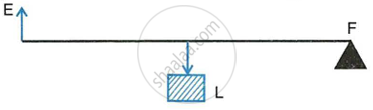
- To which class of levers does it belong?
- Without changing the dimensions of the lever, if the load is shifted towards the fulcrum what happens to the mechanical advantage of the lever?
Name a machine to obtain gain in speed ?
Write down a relation expressing the mechanical advantage of a lever.
Which class of lever found in the human body is being used by a boy when he holds a load on the palm of his hand.
The following belong to which class of lever?
A claw-hammer
The following belong to which class of lever?
A fire tongs
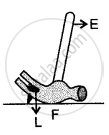
In the diagram shown alongside a claw hammer, mark the fulcrum (F) and indicate the directions of load (L) and effort (E) with arrows. What class of lever is it? Give one more example of this class of lever.
When we want to use a machine as a force multiplier, which class of lever should we preferably use? Give a simple diagram of such a lever.
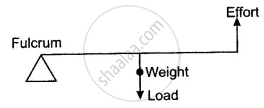
The diagram shows the use of a lever.
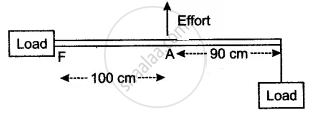
- State the principle of moments as applied to the above lever.
- Which class of lever is this? Give an example of this class of lever.
- If FA = 100 cm, AB = 90 cm, calculate the minimum effort required to lift the load.
The length of a nut-cracker is 12 cm. A nut, when kept at a distance of 4 cm from its fulcrum, requires an effort of 100 gf to crack it. What force will be required to crack the nut without using the nut-cracker?
