Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A neat labelled diagram describes the parts of a typical angiospermic ovule.
उत्तर
The main part of the ovule is the nucellus which is enclosed by two integuments, leaving an opening called the micropyle. The ovule is attached to the ovary wall by a stalk, called funiculus. The basal part is Chalaza.
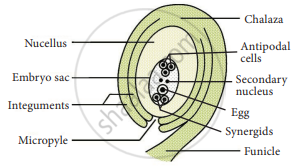
Structure of an Ovule
The embryo sac contains seven cells and the eighth nuclei located within the nucellus. Three cells at the micropylar end form the egg apparatus and the three cells at the chalazalnte9uments end are the antipodal cells. The remaining two nuclei are called polar nuclei found in the centre. In the egg apparatus, one is the egg cell (female gamete) and the remaining two cells are the synergids.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Name two hormones secreted by ovary of female reproductive system.
Why is zona pellucid retained around the egg till it reaches the uterus?
The largest cell in the human body of a female is ______.
Match the parts of the given figure with the correct option.
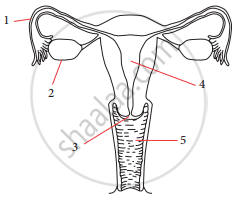
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
| a. | Fallopian tube | Oviduct | Uterus | Cervix | Vagina |
| b. | Oviduct | Cervix | Vagina | Ovary | Vas deferens |
| c. | Ovary | Oviduct | Uterus | Vagina | Cervix |
| d. | Fallopian tube | Ovary | Cervix | Uterus | Vagina |
Breasts are the modified ______ glands.
Which part of ovary in mammals acts as an endocrine gland after ovulation?
Structure connecting the fetus to placenta is ______.
To answer the question, study the graphs below for Subjects 1 and 2 showing different levels of certain hormones.

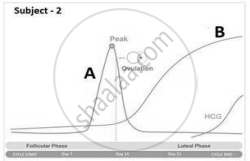
Which of the following statements is true about the subjects?
Read the following and answer from given below:
Oogenesis is the process of the formation of an ovum in the ovaries. It consists of three phases: multiplication, growth, and maturation. Oogenesis is controlled by hormones GnRH, LH, FSH. GnRH secreted by the hypothalamus stimulates the anterior lobe of the pituitary gland to secrete LH and FSH.
Identify the functions of LH.
- Release of a secondary oocyte from Graafian follicle.
- Stimulates corpus luteum to secrete progesterone.
- Stimulates estrogen formation.
- Promotes development of egg to form secondary oocyte.
Give reason:
Uterine lining becomes thick and spongy after fertilisation.
