Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A parallel plate capacitor is connected to a battery as shown in figure. Consider two situations:
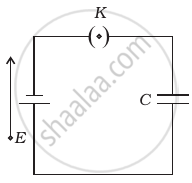
- Key K is kept closed and plates of capacitors are moved apart using insulating handle.
- Key K is opened and plates of capacitors are moved apart using insulating handle.
Choose the correct option(s).
- In A: Q remains same but C changes.
- In B: V remains same but C changes.
- In A: V remains same and hence Q changes.
- In B: Q remains same and hence V changes.
विकल्प
a and b
a and d
b and c
c and d
उत्तर
c and d
Explanation:
The battery maintains the potential difference across connected capacitor in every circumstance. However, charge stored by disconnected charged capacitor remains conserved.
Case A: When key K is kept closed and plates of capacitors are moved apart using insulating handle.
The battery maintains the potential difference across connected capacitor in every circumstance. The separation between two plates increases which in turn decreases its capacitance (C = ε0A/d)and potential difference across connected capacitor continues to be the same as capacitor is still connected with the battery. Hence, the charge stored decreases as Q = CV.
Case B: When key K is opened and plates of capacitors are moved apart using the insulating handle.
The charge stored by isolated charged capacitor remains conserved. The separation between two plates is increasing which in turn decreases its capacitance with the decrease of capacitance, potential difference V increases as V = Q/C.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Considering the case of a parallel plate capacitor being charged, show how one is required to generalize Ampere's circuital law to include the term due to displacement current.
The plates of a parallel plate capacitor have an area of 90 cm2 each and are separated by 2.5 mm. The capacitor is charged by connecting it to a 400 V supply.
(a) How much electrostatic energy is stored by the capacitor?
(b) View this energy as stored in the electrostatic field between the plates, and obtain the energy per unit volume u. Hence arrive at a relation between u and the magnitude of electric field E between the plates.
A slab of material of dielectric constant K has the same area as the plates of a parallel plate capacitor but has a thickness \[\frac{3d}{4}\]. Find the ratio of the capacitance with dielectric inside it to its capacitance without the dielectric.
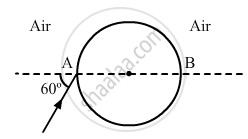
A ray of light falls on a transparent sphere with centre C as shown in the figure. The ray emerges from the sphere parallel to the line AB. Find the angle of refraction at A if the refractive index of the material of the sphere is \[\sqrt{3}\].
A parallel-plate capacitor is charged to a potential difference V by a dc source. The capacitor is then disconnected from the source. If the distance between the plates is doubled, state with reason how the following change:
(i) electric field between the plates
(ii) capacitance, and
(iii) energy stored in the capacitor
A parallel-plate capacitor of plate area 40 cm2 and separation between the plates 0.10 mm, is connected to a battery of emf 2.0 V through a 16 Ω resistor. Find the electric field in the capacitor 10 ns after the connections are made.
A parallel-plate capacitor has plate area 20 cm2, plate separation 1.0 mm and a dielectric slab of dielectric constant 5.0 filling up the space between the plates. This capacitor is joined to a battery of emf 6.0 V through a 100 kΩ resistor. Find the energy of the capacitor 8.9 μs after the connections are made.
A parallel plate air condenser has a capacity of 20µF. What will be a new capacity if:
1) the distance between the two plates is doubled?
2) a marble slab of dielectric constant 8 is introduced between the two plates?
Two charges – q each are separated by distance 2d. A third charge + q is kept at mid point O. Find potential energy of + q as a function of small distance x from O due to – q charges. Sketch P.E. v/s x and convince yourself that the charge at O is in an unstable equilibrium.
A parallel plate capacitor filled with a medium of dielectric constant 10, is connected across a battery and is charged. The dielectric slab is replaced by another slab of dielectric constant 15. Then the energy of capacitor will ______.
