Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A particular resistance wire has a resistance of 3 ohm per meter. Find :
The total resistance of three lengths of this wire each 1.5 m long, in parallel.
उत्तर
R = 3 ohm for 1 m
For 5 m : R = 3 x 5 = 15 ohm
But Area A is double i.e. 2A and Resistance is inversely proportional to area so Resistance will be half.
R = `15/2` = 7.5 ohm
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
In the circuit given below:
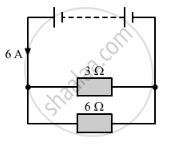
(a) What is the combined resistance?
(b) What is the p.d. across the combined resistor?
(c) What is the p.d. across the 3 Ω resistor?
(d) What is the current in the 3 Ω resistor?
(e) What is the current in the 6 Ω resistor?
A particular resistance wire has a resistance of 3 ohm per meter. Find the total resistance of three lengths of this wire each 1.5 m long, joined in parallel.
A battery of e.m.f 16 V and internal resistance 2 Ω is connected to two resistors 3Ω and 6Ω connected in parallel. Find:
- the current through the battery.
- p.d. between the terminals of the battery,
- the current in 3 Ω resistors,
- the current in 6 Ω resistor.
Show how would you connect three resistors, each of resistance 6 O so that
the combination has a resistance of(a) 9 Ω (b) 4 .Ω
What connection is used in domestic appliances and why?
Two resistors when connected in parallel give the resultant resistance of 2 ohms, but when connected in series the effective resistance becomes 9 ohms. Calculate the value of each resistance.
Three resistors of 1 Ω, 2 Ω and 3 Ω are connected in parallel. The combined resistance of the three resistors should be:
A piece of wire of resistance R is cut into three equal parts. These parts are then connected in parallel. If the equivalent resistance of this parallel combination is R1, what is the value of the ratio R1 : R?
You have three resistors of values 2 Ω, 3 Ω, and 5 Ω. How will you join them so that the total resistance is less than 1 Ω? Draw a diagram and find the total resistance.
A particular resistance wire has a resistance of 3·0 ohm per metre. Find the resistance of 5 m length of a wire of the same material, but with twice the area of cross section.
