Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A passenger arriving in a new town wishes to go from the station to a hotel located 10 km away on a straight road from the station. A dishonest cabman takes him along a circuitous path 23 km long and reaches the hotel in 28 min.
- What is the average speed of the taxi,
- the magnitude of average velocity? Are the two equal?
उत्तर
(a) Total distance travelled = 23 km
Total time taken = 28 min = `28/60 h`
∴Average speed of the taxi = `"Total distance travelled"/"Total time taken"`
= `23/(28/60) = 49.29 "km/h"`
(b) Distance between the hotel and the station = 10 km = Displacement of the car
∴ Average velocity = `10/(28/60) = 21.43 "km/h"`
Therefore, the two physical quantities (average speed and average velocity) are not equal.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A vector has both magnitude and direction. Does it mean that anything that has magnitude and direction is necessarily a vector? The rotation of a body can be specified by the direction of the axis of rotation, and the angle of rotation about the axis. Does that make any rotation a vector?
Given a + b + c + d = 0, state whether the following statement is correct or incorrect:
a, b, c, and d must each be a null vector.
A, B and C are three non-collinear, non co-planar vectors. What can you say about direction of A × (B × C)?
A river is flowing due east with a speed 3 m/s. A swimmer can swim in still water at a speed of 4 m/s (Figure).
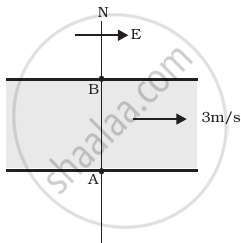
- If swimmer starts swimming due north, what will be his resultant velocity (magnitude and direction)?
- If he wants to start from point A on south bank and reach opposite point B on north bank, (a) which direction should he swim? (b) what will be his resultant speed?
- From two different cases as mentioned in (a) and (b) above, in which case will he reach opposite bank in shorter time?
