Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A point charge causes an electric flux of −1.0 × 103 Nm2/C to pass through a spherical Gaussian surface of 10.0 cm radius centred on the charge.
- If the radius of the Gaussian surface were doubled, how much flux would pass through the surface?
- What is the value of the point charge?
उत्तर
- The electric flux passing through a spherical Gaussian surface drawn around a point charge does not depend on its radius, so even if the radius is doubled, the electric flux passing through it will remain -1.0 × 108 newton-m2/coulomb.
- Φ = `q/ε_0`
or q = Φ ε0
or q = -1 × 103 × 8.85 × 10-12
or q = -8.85 × 10-9 C
= -8.85 nC
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A 36 cm long sonometer wire vibrates with frequency of 280 Hz in fundamental mode, when it is under tension of 24.5 N. Calculate linear density of the material of wire.
Explain why, for a charge configuration, the equipotential surface through a point is normal to the electric field at that point
"For any charge configuration, equipotential surface through a point is normal to the electric field." Justify.
A point charge of 2.0 μC is at the centre of a cubic Gaussian surface 9.0 cm on edge. What is the net electric flux through the surface?
Electric intensity outside a charged cylinder having the charge per unit length 'λ' at a distance from its axis is ________.
(a) E = `(2pi in_0 lambda)/(Kr^2)`
(b) E = `(in_0 lambda)/(2piKr^2)`
(c) E = `lambda/(2piin_0Kr)`
(d) E = `(4piin_0lambda)/(Kr^2)`
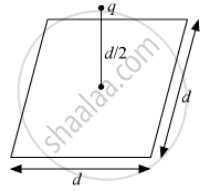
A point charge q is at a distance of d/2 directly above the centre of a square of side d, as shown the figure. Use Gauss' law to obtain the expression for the electric flux through the square.
State Gauss’Law.
Which statement is true for Gauss law -
Two wires A and B of the same material and of equal length with the radii in the ratio 1 : 2 are subjected to identical loads. If the length of A increases by 8 mm, then the increase in length of B is:
A spherical ball contracts in volume by 0.02% when subjected to a pressure of 100 atmosphere. Assuming one atmosphere = 105 Nm−2, the bulk modulus of the material of the ball is:
Through two parallel wires A and B, 10A and 2A of currents are passed respectively in opposite directions. If the wire A is infinitely long and the length of the wire B is 2m, then force on the conductor B, which is situated at 10 cm distance from A, will be:
If the ratio of radii of two wires of same material is 3 : 1 and ratio of their lengths is 5 : 1, then the ratio of the normal forces that will produce the same extension in the length of two wires is:
The electric field inside a spherical shell of uniform surface charge density is ______.
What is the nature of the Gaussian surface involved in the Gauss law of electrostatics?
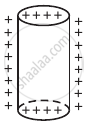
Sketch the electric field lines for a uniformly charged hollow cylinder shown in figure.
Consider a sphere of radius R with charge density distributed as
ρ(r) = kr for r ≤ R
= 0 for r > R
- Find the electric field at all points r.
- Suppose the total charge on the sphere is 2e where e is the electron charge. Where can two protons be embedded such that the force on each of them is zero. Assume that the introduction of the proton does not alter the negative charge distribution.
A solid metal sphere of radius R having charge q is enclosed inside the concentric spherical shell of inner radius a and outer radius b as shown in the figure. The approximate variation of the electric field `vecE` as a function of distance r from centre O is given by ______.

