Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A proton and an electron are placed in a uniform electric field.
विकल्प
The electric forces acting on them will be equal.
The magnitudes of the forces will be equal.
Their accelerations will be equal.
The magnitudes of their accelerations will be equal.
उत्तर
The magnitudes of the forces will be equal.
We know: \[\vec{F} = q \vec{E}\] For an electron and a proton, the value of q will be same, but the sign will be opposite.
Hence, they will experience a force that will be equal in magnitude but opposite in direction.
Now,
\[\vec{F} = q \vec{E} = m \vec{a} \]
\[ \Rightarrow \vec{a} = \frac{q \vec{E}}{m}\]
As the electron and proton have different values of mass m, they will have different magnitudes of acceleration. Also, they will differ in direction due to the opposite signs of q.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
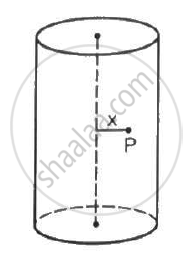
A long cylindrical volume contains a uniformly distributed charge of density ρ. Find the electric field at a point P inside the cylindrical volume at a distance x from its axis (see the figure).
The electric force experienced by a charge of 1.0 × 10−6 C is 1.5 × 10−3 N. Find the magnitude of the electric field at the position of the charge.
A rod of length L has a total charge Q distributed uniformly along its length. It is bent in the shape of a semicircle. Find the magnitude of the electric field at the centre of curvature of the semicircle.
A smple pendulum consists of a small sphere of mass m suspended by a thread of length l. The sphere carries a positive charge q. The pendulum is placed in a uniform electric field of strength E directed vertically downwards. Find the period of oscillation of the pendulum due to the electrostatic force acting on the sphere, neglecting the effect of the gravitational force.
A positively charged glass rod is brought close to a metallic rod isolated from ground. The charge on the side of the metallic rod away from the glass rod will be ______.
Answer the following question.
What is the magnitude of the charge on an electron?
Two parallel plates have a potential difference of 10 V between them. If the plates are 0.5 mm apart, what will be the strength of electric charge.
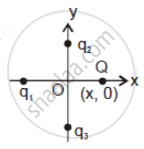
In figure two positive charges q2 and q3 fixed along the y-axis, exert a net electric force in the + x-direction on a charge q1 fixed along the x-axis. If a positive charge Q is added at (x, 0), the force on q1 ______.
(1) |
(2) |
When a glass rod is rubbed with silk, it ______.
Which of the following graphs shows the variation of electric field E due to a hollow spherical conductor of radius R as a function of distance from the centre of the sphere?
Which one of the following is the unit of electric charge?
A positive charge particle of 100 mg is thrown in opposite direction to a uniform electric field of strength 1 × 105 NC–1. If the charge on the particle is 40 μC and the initial velocity is 200 ms-1, how much distance it will travel before coming to the rest momentarily ______.
Two identical metallic spheres A and B when placed at certain distance in air repel each other with a force of F. Another identical uncharged sphere C is first placed in contact with A and then in contact with B and finally placed at midpoint between spheres A and B. The force experienced by sphere C will be:
A straight infinitely long cylinder of radius R0 = 10 cm is uniformly charged with a surface charge density σ = + 10-12 C/m2. The cylinder serves as a source of electrons, with the velocity of the emitted electrons perpendicular to its surface. Electron velocity must be ______ × 105 m/s to ensure that electrons can move away, from the axis of the cylinder to a distance greater than r = 103 m.
A particle of mass m and charge q is placed at rest in a uniform electric field E and then released. The kinetic energy gained by the particle after moving a distance of y will be ______.
The electrostatic potential inside a charged spherical ball is given by `Phi = ar^2 + b`, where r is the distance from the centre a, and b are constants. Then the charge density inside the ball is ______.
A charge of magnitude 3e and mass 2m is moving in an electric field E. The acceleration imparted to the charge is ______.
