Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A rod of length L has a total charge Q distributed uniformly along its length. It is bent in the shape of a semicircle. Find the magnitude of the electric field at the centre of curvature of the semicircle.
उत्तर
Consider an element of angular width dθ, as shown in the figure.
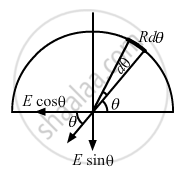
\[dq = \frac{Q}{L}Rd\theta\]
The net electric field has a vertical component only.
\[\text{So}, E_{net} = \int dE \sin\theta\]
\[ = \frac{1}{4\pi \epsilon_0}\frac{Q}{L} \int\limits_0^\pi \frac{Rd\theta}{R^2}\sin\theta\]
\[= \frac{- 1}{4\pi \epsilon_0}\frac{Q}{LR} \left[ \cos\theta \right]_0^\pi \]
\[ = \frac{2Q}{4\pi \epsilon_0 LR}\]
\[ = \frac{Q}{2 \epsilon_0 L^2} \left( \because \pi R = L \right)\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Write the expression for the displacement current in terms of the rate of change of electric flux.
Two particles A and B, each with a charge Q, are placed a distance d apart. Where should a particle of charge q be placed on the perpendicular bisector of AB, so that it experiences maximum force? What is the magnitude of this maximum force?
A positive charge Q is distributed uniformly over a circular ring of radius R. A particle of mass m, and a negative charge q, is placed on its axis at a distance x from the centre. Find the force on the particle. Assuming x << R, find the time period of oscillation of the particle if it is released from there .
Choose the correct option.
An electron is placed between two parallel plates connected to a battery. If the battery is switched on, the electron will
Answer the following question.
What is the magnitude of the charge on an electron?
Two parallel plates have a potential difference of 10 V between them. If the plates are 0.5 mm apart, what will be the strength of electric charge.
Two small conducting spheres of equal radius have charges +10 µC and -20 µC respectively and placed at a distance R from each other experience force F1· If they are brought in contact and separated to the same distance, they experience force F2. The ratio of F1 to F2 is ____________.
A conducting sphere of radius 0.104 m has an unknown charge. If the electric field at 0.20 m from the centre of the sphere is 1.5 x 103 NC-1 and points radially inward, what is the electric flux?
Assertion: The positive charge particle is placed in front of a spherical uncharged conductor. The number of lines of forces terminating on the sphere will be more than those emerging from it.
Reason: The surface charge density at a point on the sphere nearest to the point charge will be negative and maximum in magnitude compared to other points on the sphere.
When a glass rod is rubbed with silk, it ______.
A positive charge particle of 100 mg is thrown in opposite direction to a uniform electric field of strength 1 × 105 NC–1. If the charge on the particle is 40 μC and the initial velocity is 200 ms-1, how much distance it will travel before coming to the rest momentarily ______.
A certain charge Q is divided into two parts q and (Q - q). How should the charges Q and q be divided so that q and (Q - q) placed at a certain distance apart experience maximum electrostatic repulsion?
A straight infinitely long cylinder of radius R0 = 10 cm is uniformly charged with a surface charge density σ = + 10-12 C/m2. The cylinder serves as a source of electrons, with the velocity of the emitted electrons perpendicular to its surface. Electron velocity must be ______ × 105 m/s to ensure that electrons can move away, from the axis of the cylinder to a distance greater than r = 103 m.
A particle of mass m and charge q is placed at rest in a uniform electric field E and then released. The kinetic energy gained by the particle after moving a distance of y will be ______.
A charge of magnitude 3e and mass 2m is moving in an electric field E. The acceleration imparted to the charge is ______.
Two particles A and B having the same mass have charges +q and +4q, respectively. When they are allowed to fall from rest through the same electric potential difference the ratio of their speeds vA to vB will become ______.
